Big Data Tools
The Big Data Tools plugin is available for IntelliJ IDEA 2019.2 and later. It provides specific capabilities to monitor and process data with Zeppelin, AWS S3, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, Apache Hive, Apache Flink, Google Cloud Storage, MinIO, Linode, DigitalOcean Spaces, Microsoft Azure, and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
You can create new or edit existing local or remote Zeppelin notebooks, execute code paragraphs, preview the resulting tables and graphs, and export the results to various formats. 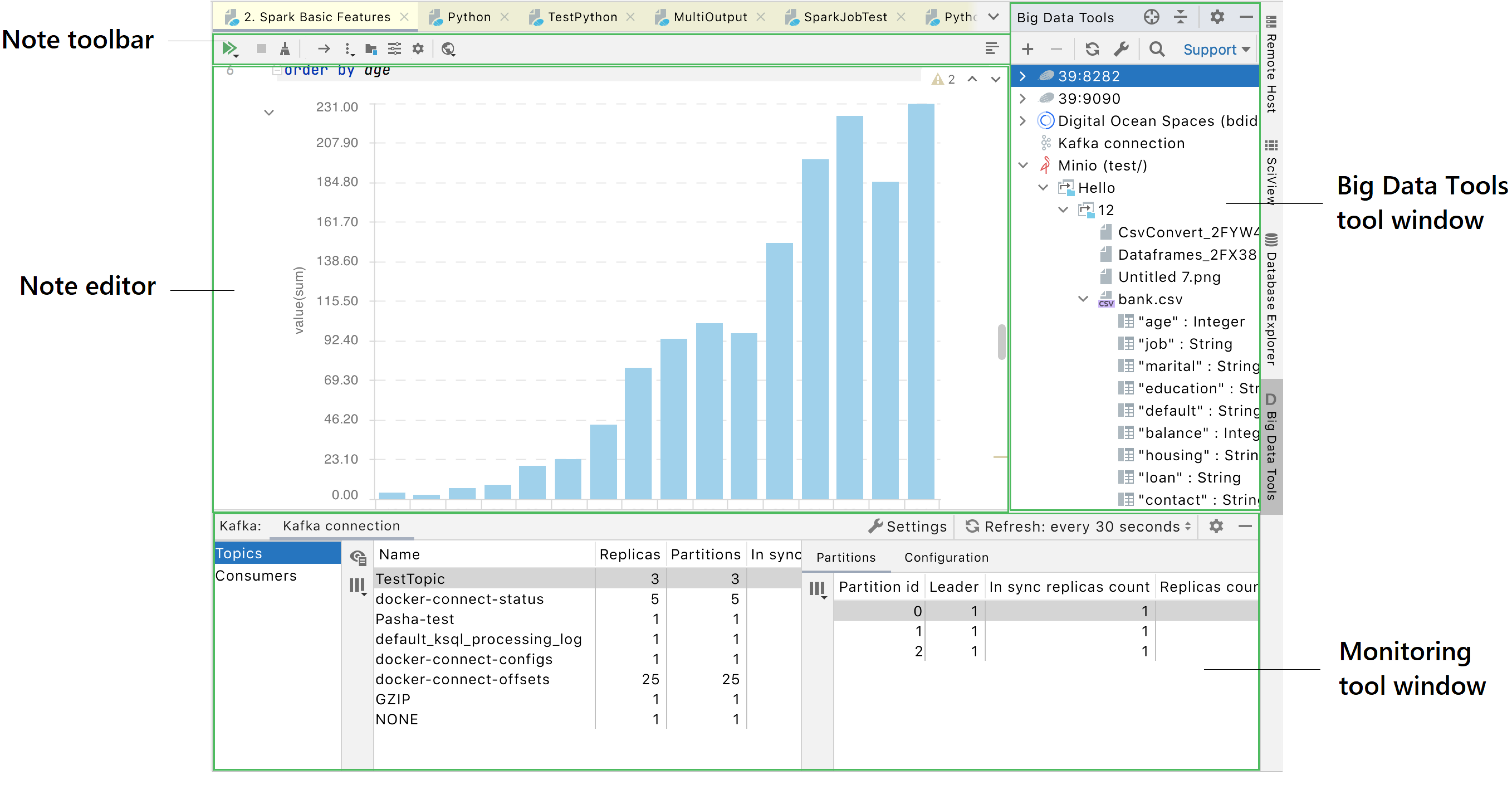
The plugin supports many IDE features to work with notebooks:
Coding assistance for Scala
Inspection and quick-fixes, including fixes for notebook dependencies.
Notebook features
Browsing, creating, and deleting notebooks
Adding and deleting paragraphs
Executing paragraphs
Running SQL statements
Previewing tables and charts
Getting started with Big Data Tools in IntelliJ IDEA
The basic workflow for big data processing in IntelliJ IDEA includes the following steps:
Configure your environment
Create a new project in IntelliJ IDEA.
Configure a connection to the target server.
Work with your notebooks and data files.
Work with notebooks
Execute the notebook.
Get familiar with the user interface
When you install the Big Data Tools plugin for IntelliJ IDEA, the following user interface elements appear:
Big Data Tools window
The Big Data Tools window appears in the rightmost group of the tool windows. The window displays the list of the configured servers, notebooks, and files structured by folders. Even when no connections are configured, you can see the available types of servers to connect to.
Basic operations on notebooks are available from the context menu.

You can navigate through the directories and preview columnar structures of .csv, .parquet, .avro, and .orc files.
Basic operations on data files are available from the context menu. You can also move files by dragging them to the target directory on the target server.

For the basic operations with the servers, use the window toolbar:
Add a new connection to a server. | |
Delete the selected connection. | |
For Zeppelin: find a note in your Zeppelin server. For storages: navigate to a file. | |
Refresh connections to all configured servers. | |
Open the connection settings for the selected server. | |
Only for storages. Open the storage in a separate tab of your editor |
If you have any questions regarding the Big Data Tools plugin, click the Support link and select one of the available options. You can join the support Slack channel, submit a ticket in the YouTrack system, or copy the support email to send your question. 
Notebook editor

In the notebook editor, you can add and execute Python, Scala and SQL code paragraphs. When editing your code paragraph, you can use all the coding assistance features available for a particular language. Code warnings and errors will be highlighted in the corresponding code constructs in the scrollbar. The results of paragraph execution are shown in the preview area below each paragraph.
Use the notebook editor toolbar for the basic operations with notebooks:
Executes all paragraphs in the notebook. | |
Stops execution of the notebook paragraphs. | |
Clears output previews for all paragraphs. | |
Select Export Note Code to HTML to save the note as an HTML file. Select Alter Code Visibility to hide code sections in paragraphs (by default, both code and result sections are shown). Select Show State Viewer Window to open State Viewer. | |
Opens the Interpreter Bindings dialog to configure interpreters for the selected notebook. | |
Click this button to open the notebook in the browser or copy a link to it. | |
Allows you to jump to a particular paragraph of a notebook. | |
Shows the minimap for quick navigation through the notebook. |
A toolbar of a local note contains a list of available Zeppelin servers, so that you can select one to execute the note.
The notebook editor toolbar also shows the status of the last paragraph execution: Finished, Aborted, or Failed and the synchronization status of State Viewer.
Monitoring tool windows
These windows appear when you have connected to a Spark or Hadoop server.


Building your BigData project
With the dedicated project type and the corresponding wizard, you can create a project in IntelliJ IDEA that has all the required Spark dependencies. You can start developing Spark applications without any additional configurations.
Create a dedicated project
Select from the main menu
Select Big Data from the options on the left, then ensure that the Spark type of project is specified. Click Next.

On the next page of the wizard, specify your project's name, location, build system (SBT, Gradle or Maven), JDK, and artifact coordinates.

Fields in the More settings section are populated automatically based on the project's name value. You can alter them, if needed.
Click Finish to complete the task.
For more details on developing Spark applications, see the Spark Programming Guide.