Model Context Protocol (MCP)
You can connect Junie to Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. This will provide Junie with executable functionality for working with data sources and tools, such as file systems, productivity tools, or databases.
- Supported transport types
Currently, Junie supports only MCP servers that use the Standard Input/Output (stdio) transport type.
- Where to get an MCP server
There is a variety of local and remote MCP servers available, depending on your use case and setup. As a starting point, you can explore the reference servers provided in the official MCP repository, which includes examples, usage instructions, and configuration details.
- What is needed to connect to an MCP server
To connect Junie to an MCP server, you need a JSON configuration that defines the command and arguments for starting the server. The exact configuration depends on the specific MCP server. In most cases, the server's developers will provide a recommended configuration you can get and use.
How it works
When running a prompt, Junie analyzes what commands registered with the configured MCP servers as available tools are relevant, and executes them through the respective MCP server.
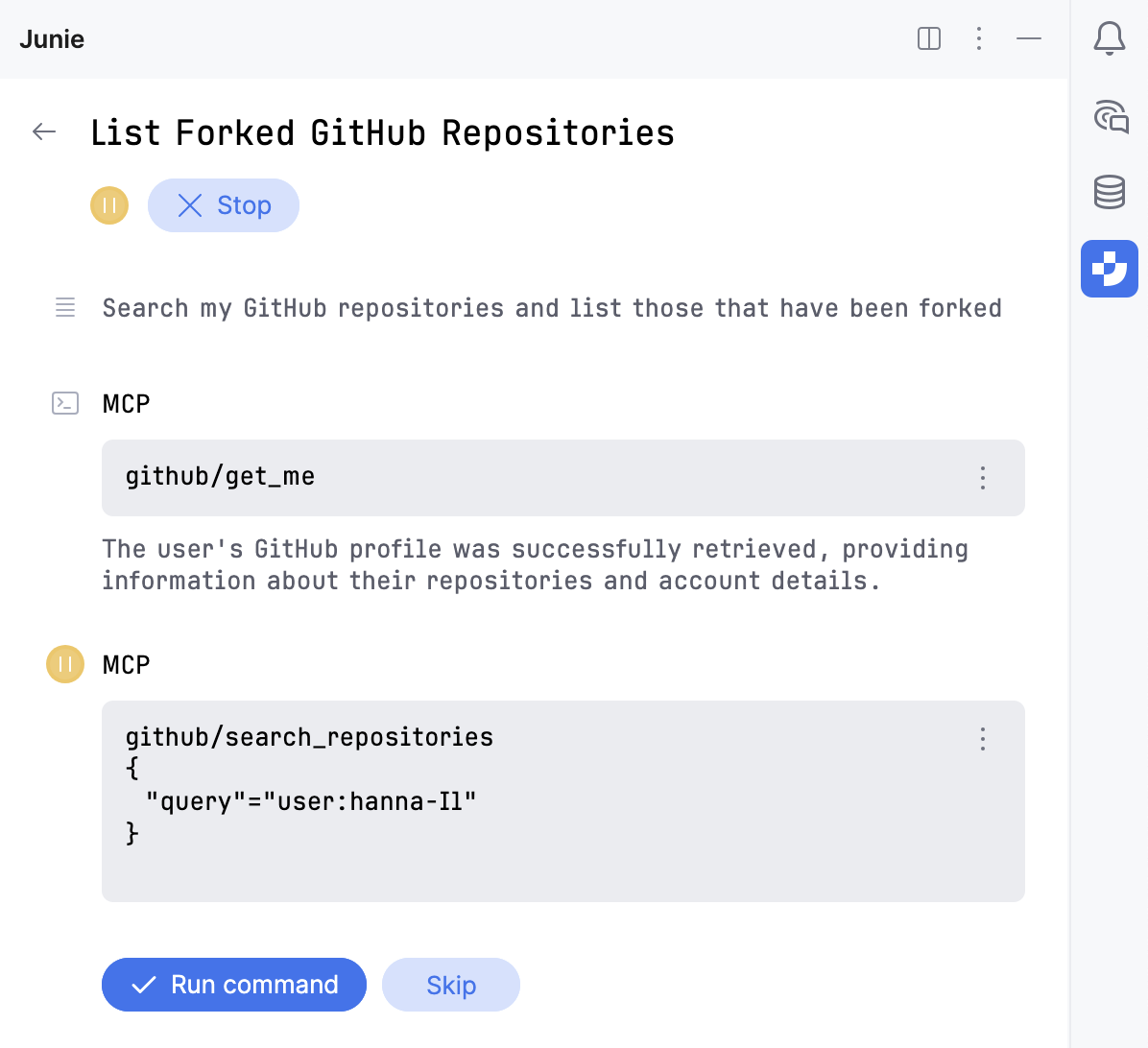
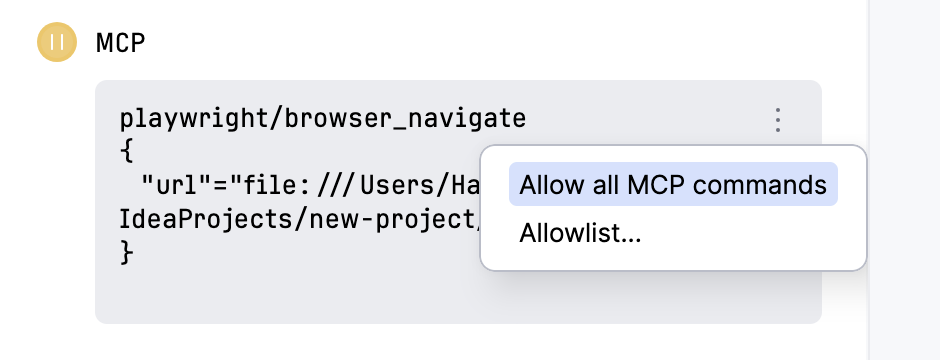
User approval
By default, Junie asks for user approval before executing the relevant tool. You can authorize Junie to run MCP commands without approval on the Action Allowlist settings page or from Junie's tool window by clicking next to the command as Junie executes it.
Add an MCP server
To connect Junie to an MCP server, use the mcp.json file in Junie's settings.
In the IDE settings (Ctrl+Alt+S), go to .
Click
on the toolbar. In the
mcp.jsonfile that opens, add one or multiple server configurations in the"mcpServers"key.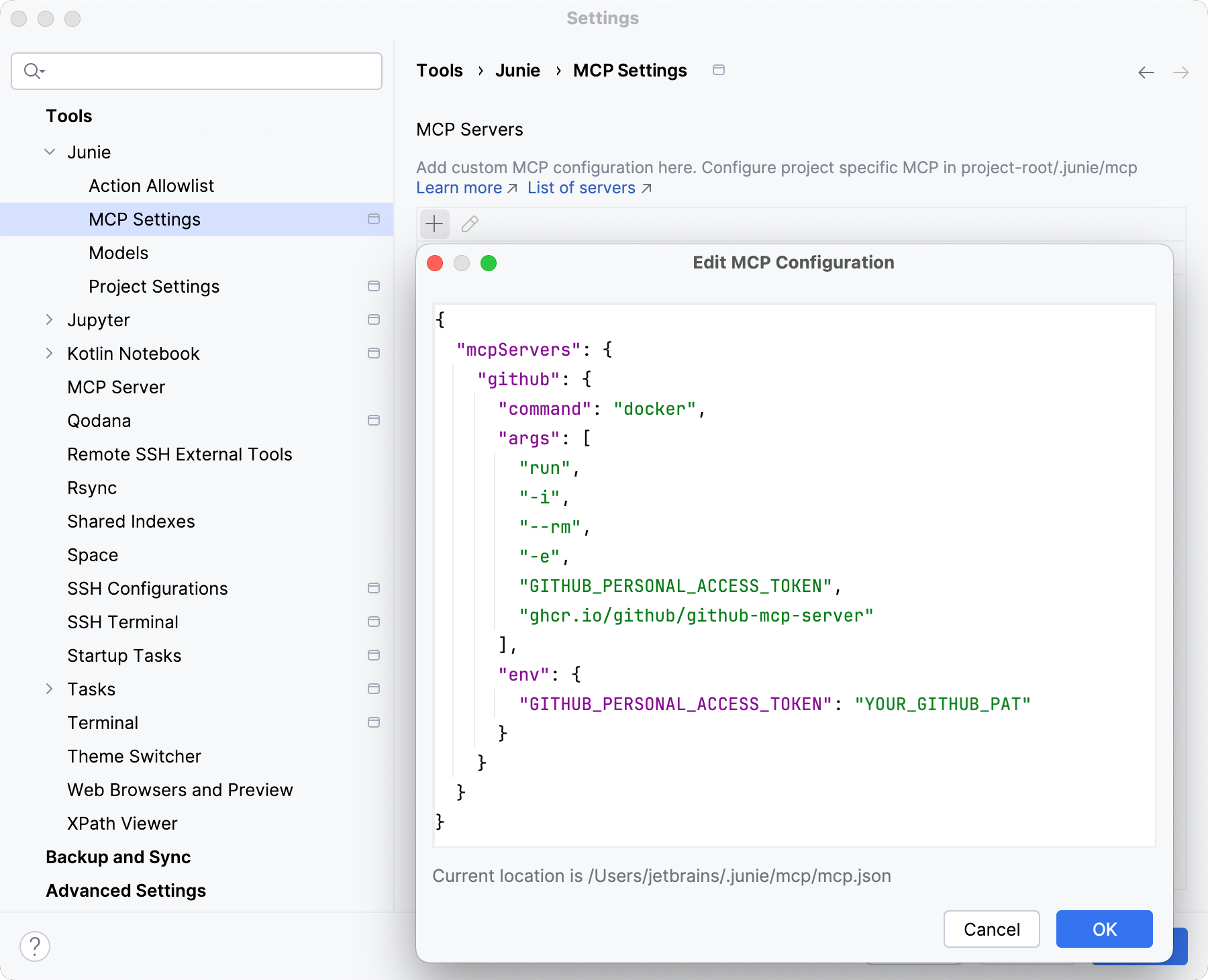
For the JSON schema, refer to the documentation of the MCP server you are adding. For example, a configuration that sets up a GitHub MCP server looks as follows:
{ "mcpServers": { "github": { "command": "docker", "args": [ "run", "-i", "--rm", "-e", "GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN", "ghcr.io/github/github-mcp-server" ], "env": { "GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN": "YOUR_GITHUB_PAT" } } } }
Global configuration
The MCP servers added via the MCP Settings page are saved to the ~/.junie/mcp/mcp.json file in the home directory. Such servers are available globally for all projects that are opened in the IDE.
Project-level configuration
To configure an MCP server at the project level, add an mcp.json file manually to the .junie/mcp/ folder in the project root.
Authentication
At the moment, Junie does not support security tokens in MCP configs. As a workaround, you can load environment variables from Docker's .env file. For example, in the GitHub MCP server config example, you can move the "GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN" secret to the ~/.env.mcp file:
If the MCP server is not run via Docker, you can preload environment variables from a file using an additional script, for example npx dotenv -- npx ....
Manage configured MCP servers
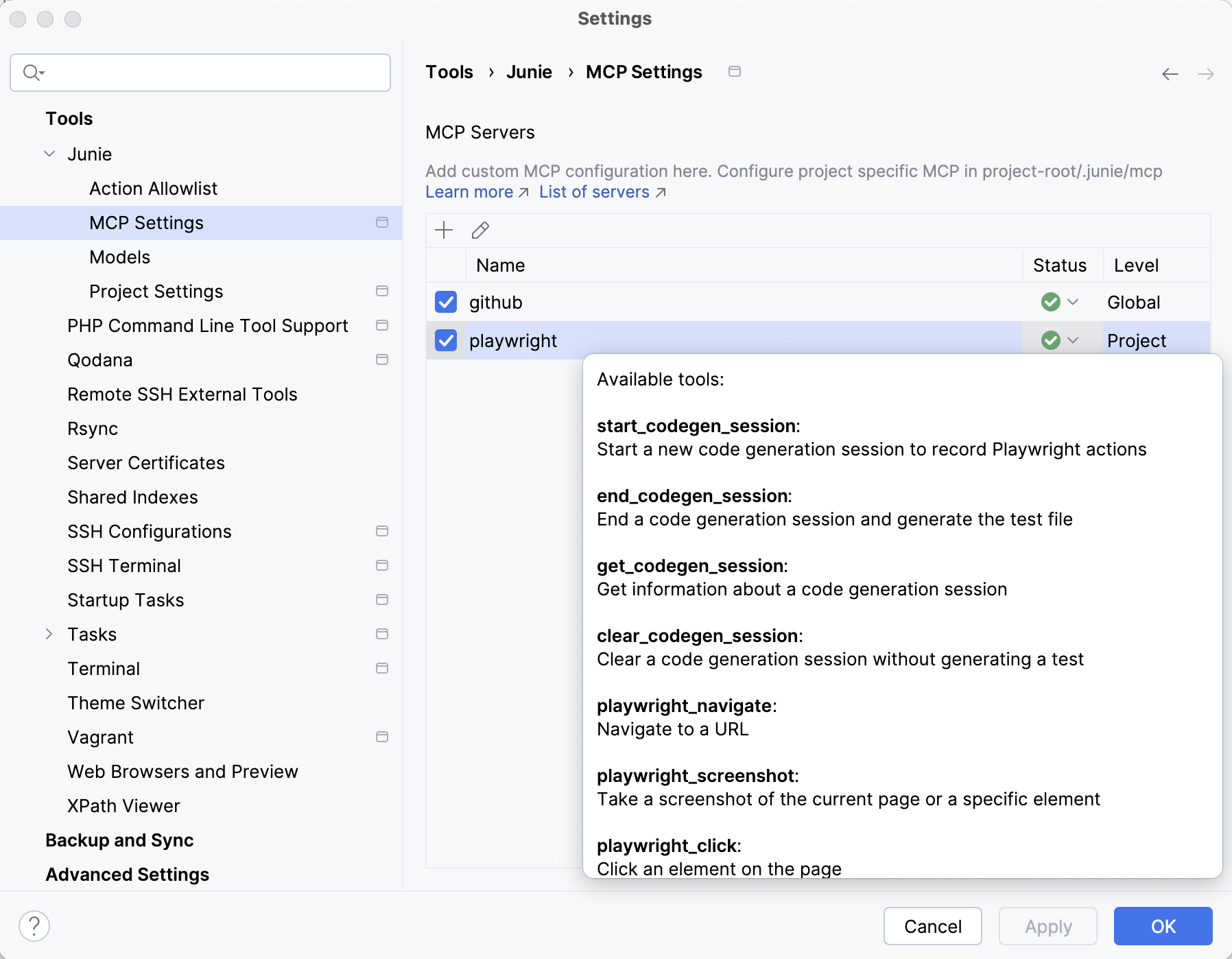
The MCP servers configured at both global and project levels are displayed on the MCP Servers list in (Ctrl+Alt+S) .
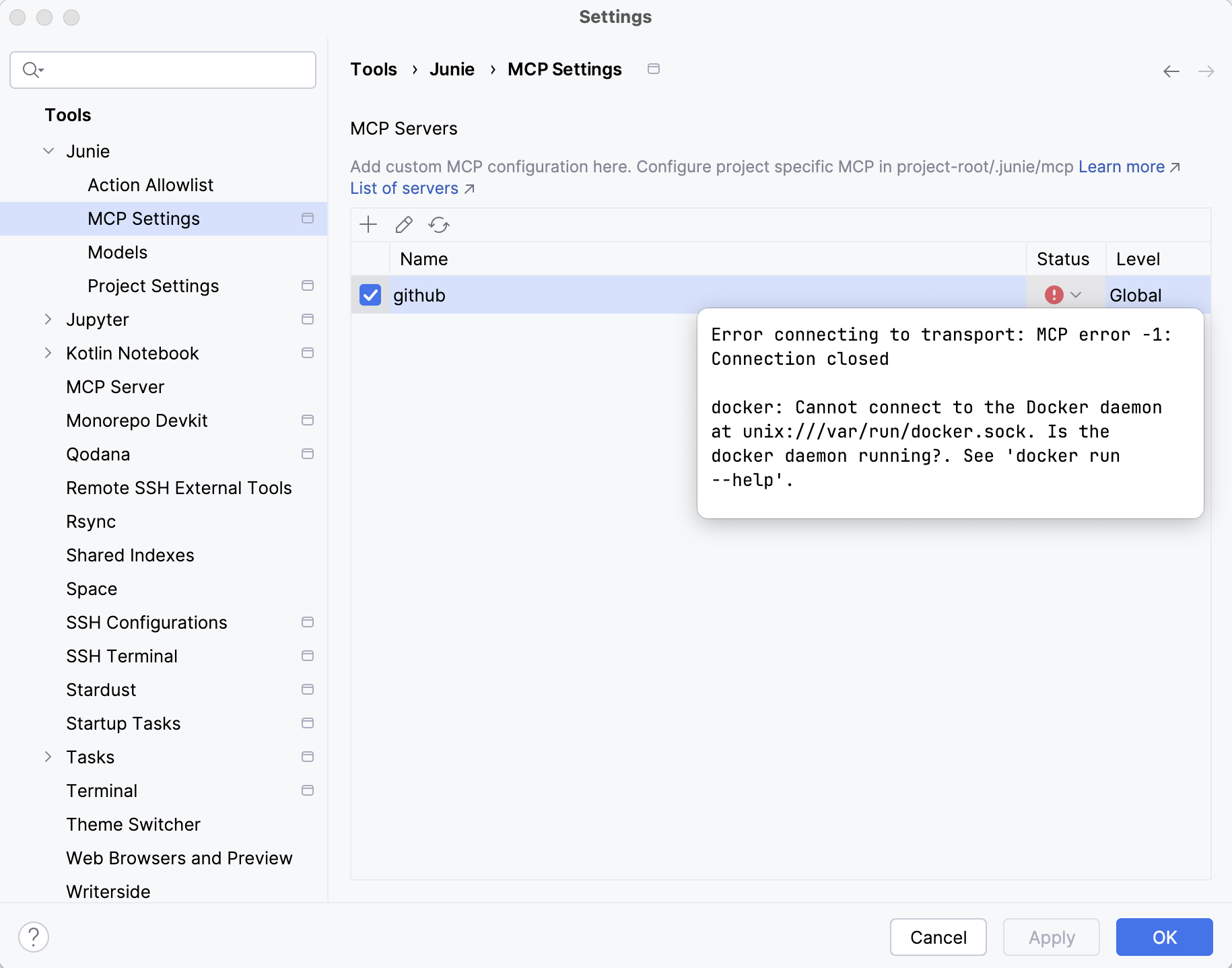
Server connection status
To see the connection status for a configured server, check the Status column. In case of a connection failure, hover over the status icon to see the error message.
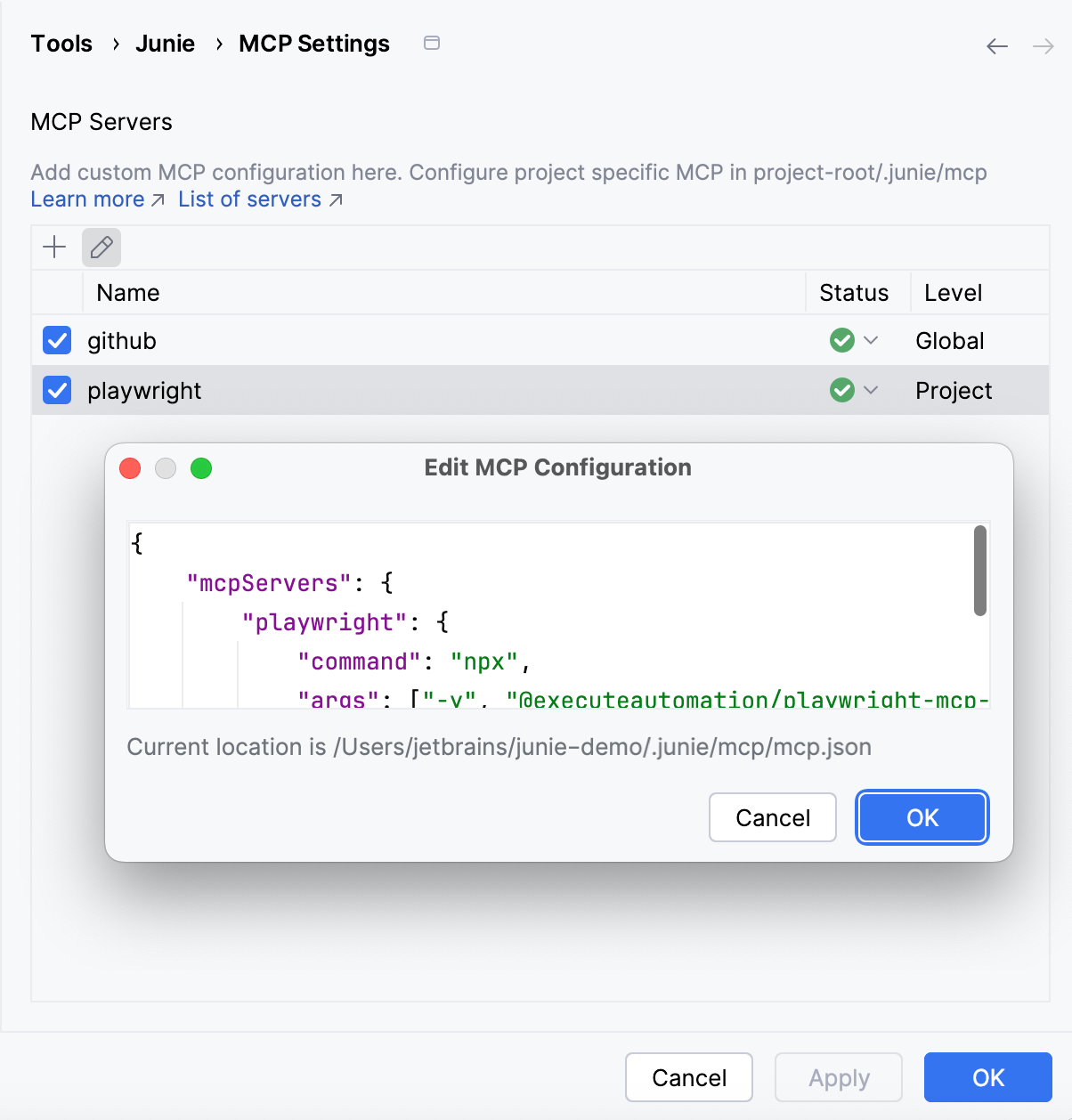
Edit server configuration
To edit a configuration, select it on the list and click on the toolbar.
View available tools
Actions that Junie can perform through configured MCP servers are listed as available tools.
To view what tools are available for a specific MCP server, navigate to (Ctrl+Alt+S) , locate the server on the list, and expand the Status drop-down list.