Integration with the SwiftUI framework
Compose Multiplatform is interoperable with the SwiftUI framework. You can embed Compose Multiplatform within a SwiftUI application as well as embed native SwiftUI components within Compose Multiplatform UI. This page provides examples both for using Compose Multiplatform inside SwiftUI and for embedding SwiftUI inside a Compose Multiplatform app.
Use Compose Multiplatform inside a SwiftUI application
To use Compose Multiplatform inside a SwiftUI application, create a Kotlin function MainViewController() that returns UIViewController from UIKit and contains Compose Multiplatform code:
ComposeUIViewController() is a Compose Multiplatform library function that accepts a composable function as the content argument. The function passed in this way can call other composable functions, for example, Text().
Next, you need a structure that represents Compose Multiplatform in SwiftUI. Create the following structure that converts a UIViewController instance to a SwiftUI view:
Now you can use the ComposeView structure in other SwiftUI code.
Main_iosKt.MainViewController is a generated name. You can learn more about accessing Kotlin code from Swift on the Interoperability with Swift/Objective-C page.
In the end, your application should look like this:
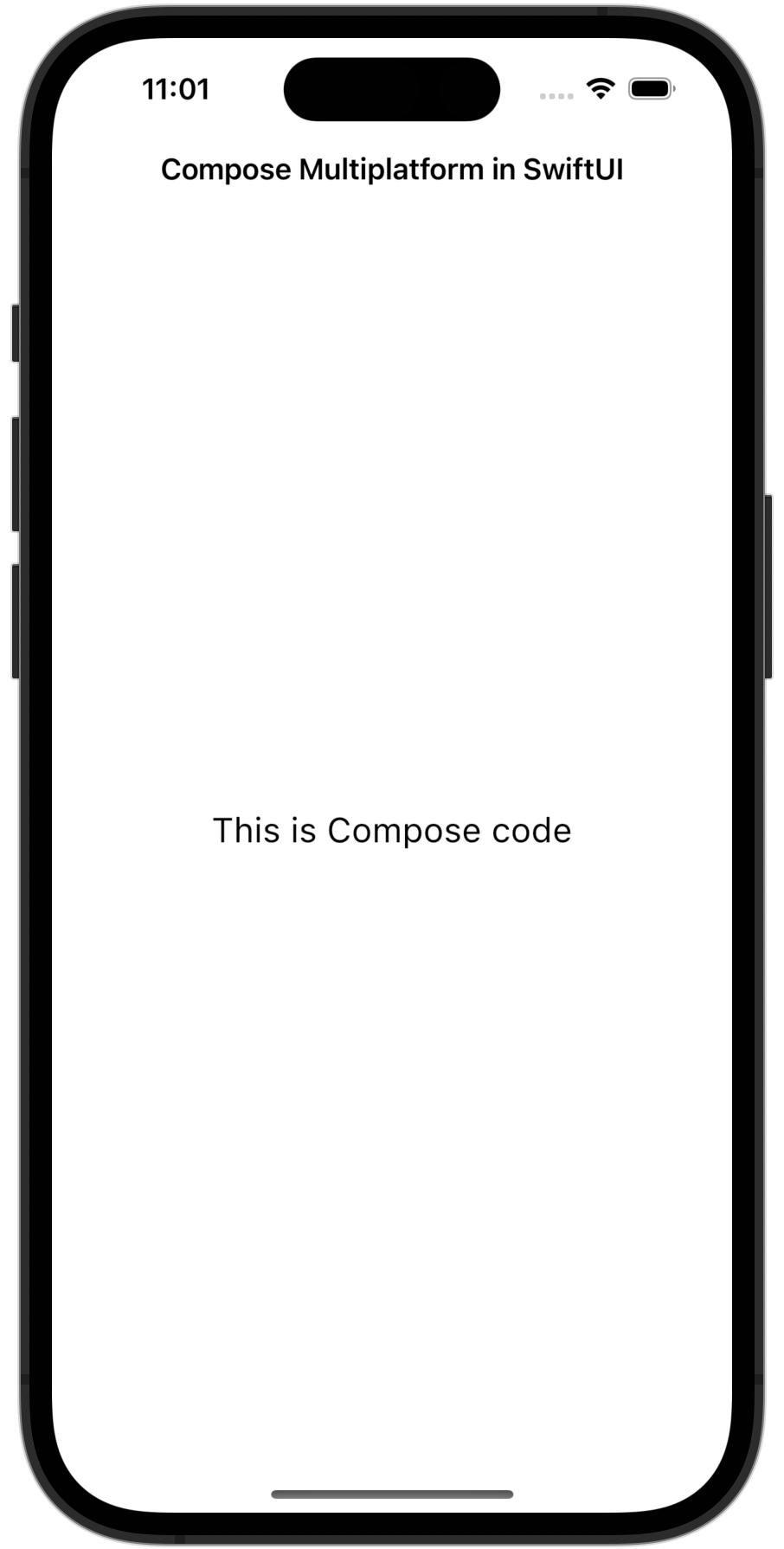
You can use this ComposeView in any SwiftUI view hierarchy and control its size from within SwiftUI code.
If you want to embed Compose Multiplatform into your existing applications, use the ComposeView structure wherever SwiftUI is used. For an example, see our sample project.
Use SwiftUI inside Compose Multiplatform
To use SwiftUI inside Compose Multiplatform, add your Swift code to an intermediate UIViewController. Currently, you can't write SwiftUI structures directly in Kotlin. Instead, you have to write them in Swift and pass them to a Kotlin function.
To start, add an argument to your entry point function to create a ComposeUIViewController component:
In your Swift code, pass the createUIViewController to your entry point function code. You can use a UIHostingController instance to wrap SwiftUI views:
In the end, your application should look like this:

Explore the code for this example in the sample project.
What's next
You can also explore the way Compose Multiplatform can be integrated with the UIKit framework.