Testing frameworks
PyCharm enables usage of the following testing frameworks:
Framework | Code completion | Run/debug configuration | Ability to create a test | Navigation between tests and tests subjects | Ability to run tests | Code inspections |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partially | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Partially | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partially | |
No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Partially | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | |
N/A | Yes | No | N/A | Yes | Yes | |
Available only in PyCharm Pro | ||||||
Yes | Yes | Yes (for step definitions) | Yes (between steps and features) | Yes | Partially | |
Before you start working with the testing framework of your choice, make sure that the desired framework is installed on your machine. For more information about installation details, refer to the framework documentation.
PyCharm auto-detects a test runner that is installed on your Python interpreter and uses it to run tests. Still, you always have an option to explicitly specify the required test runner in the project settings.
Set a testing framework
To set a test runner, press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and select Tools | Python Integrated Tools, and then select the target test runner from the Default test runner list.
Choose the desired test runner:
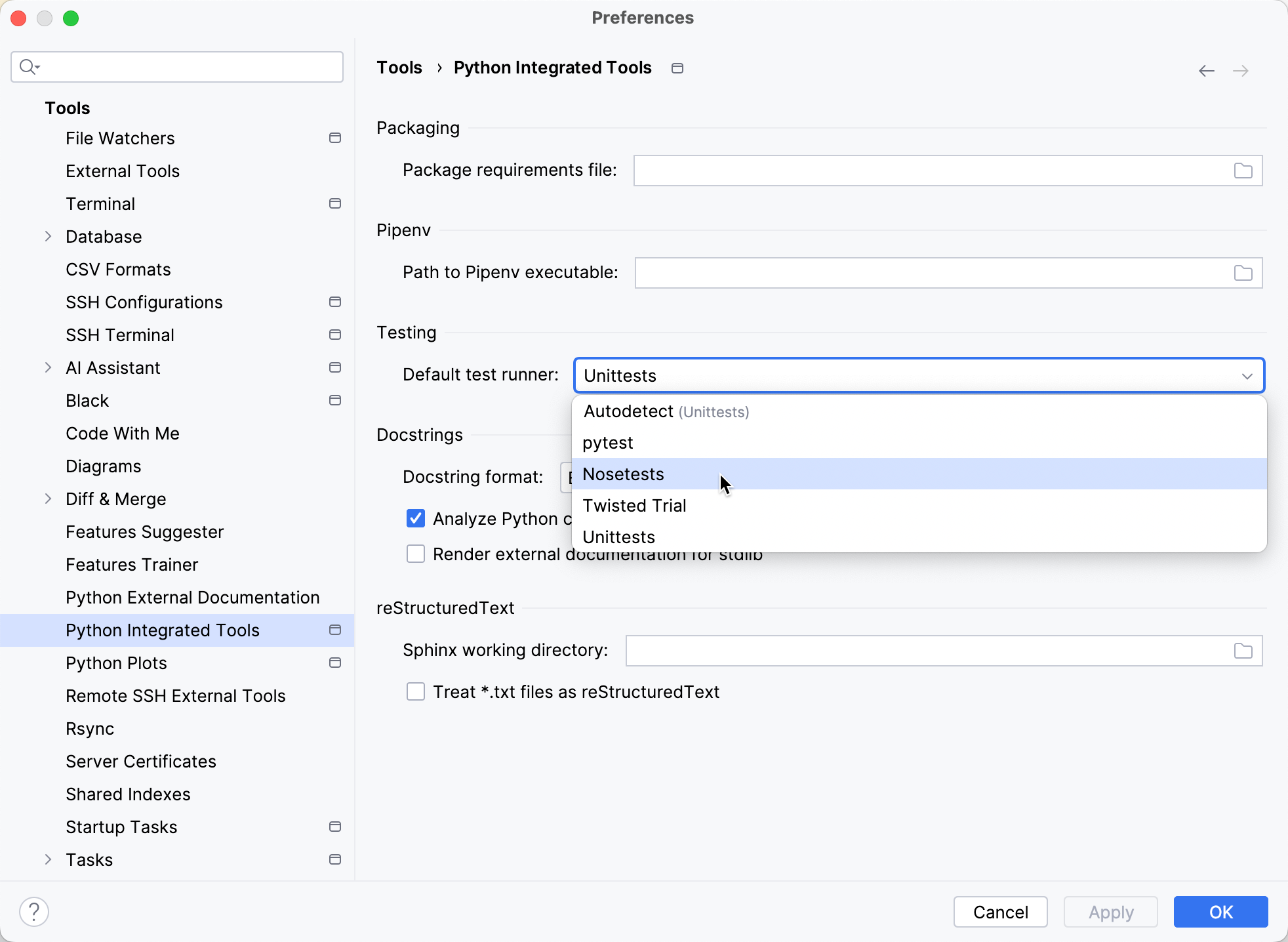
If the selected test runner is missing in the specified interpreter, the appropriate notification appears.
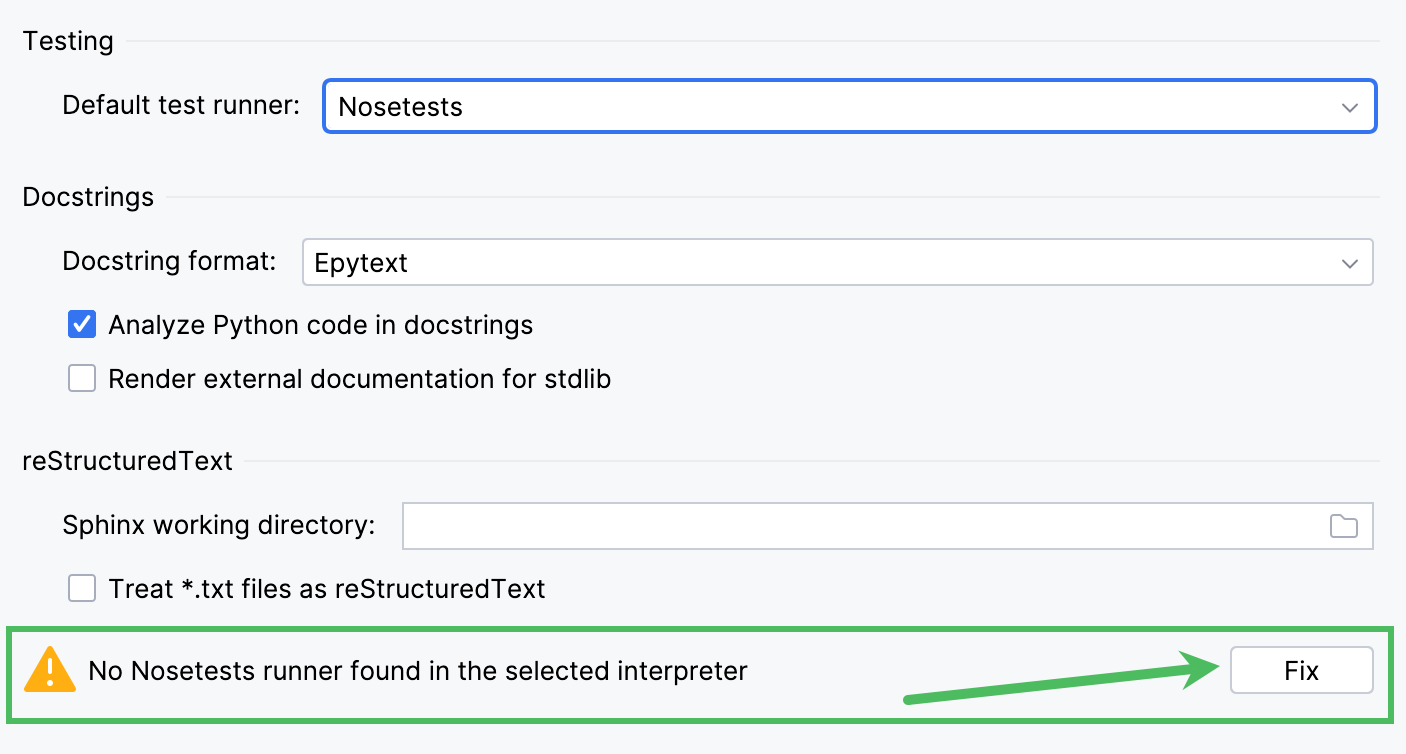
Click the Fix button to download and install the corresponding framework.
By default, the suggested default test runner is unittest. However, you can redefine the default framework and change it to nosetest, pytest or TwistedTrial.
Change the default testing framework
In the main menu, go to for Windows and Linux, or for macOS.
Select .
In the Testing area, select the test runner that will be default for all newly created projects.
With the test runner selected, PyCharm suggests the appropriate default run/debug configuration:

If a user already has the testing run/debug configuration for a specific file and for a specific testing framework, then PyCharm will launch this run/debug configuration, regardless of your chosen default test runner. For more information in how to change or delete such a configuration, refer to Run/debug configurations.