Navigate To
Navigate To is a single shortcut for most of your navigation needs. It opens a list with all contextually available navigation destinations. You can invoke this command from the Solution Explorer, File Structure window, and other tool windows.
View contextually available navigation actions
Place the caret at symbol in the editor or select the symbol in a tool window window, or just place the caret anywhere in the editor.
Press Control+Shift+G or choose from the main menu. Alternatively, you can press Control+Shift+A, start typing the command name in the popup, and then choose it there.
In the Navigate To list that appears, you will see all relevant navigation options.
Select an option from the list and click it or press Enter.
If the selected option has a single destination, ReSharper will bring you there immediately, if there are several destination, another list will open providing you with the further choice. You can study one of the corresponding topics to learn more about the selected navigation option.
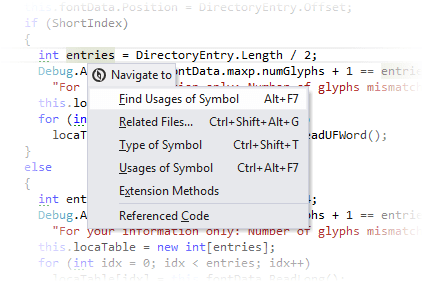
Where applicable, the Navigate To list includes general navigation features, specifically:
In addition, Navigate To extends the developer's toolset with a bunch of contextual navigation features that are not directly available from the menu:
- Assembly Explorer
- Conflicting Declarations
- Control Flow Target
- Decompiled Sources
- Exposing APIs
- Consuming APIs
- Extension Methods
- Function Exits
- Generic Substitutions
- Implementing Members
- Member Overloads
- Metadata View
- Object Browser
- Overriding Members
- Parameter Declaration
- Sources from Symbol Files
- Test Explorer and Tests Sessions
- To-do Explorer
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies:
The instructions and examples given here address the use of the feature in C#. For more information about other languages, refer to corresponding topics in the Languages and frameworks section.