Move Type to Outer Scope refactoring
This refactoring helps you move a nested type one level up. All corresponding references are automatically updated, even if the nested type uses members of the parent type.
Move a type to outer scope
Select a nested type in one of the following ways:
In the editor, place the caret at the name of a nested type.
Select a nested type in the Solution Explorer.
Select a nested type in the File Structure window window.
Select a nested type in the Class View.
Select a nested type in the Object Browser.
Select a nested type in the type dependency diagram.
Do one of the following:
Press F6 and then choose Move to Outer Scope
Press Control+Shift+R and then choose Move to Outer Scope.
Right-click and choose Refactor | Move to Outer Scope from the context menu.
Choose from the main menu.
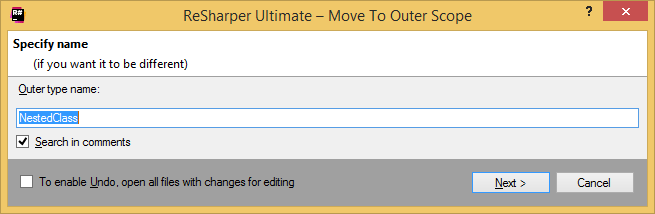
The Move to Outer Scope dialog will open.
Optionally, you can specify a different name for the type.
Select the Search in comments checkbox to update references to the type in comments.
To apply the refactoring, click Next.
If no conflicts are found, ReSharper performs the refactoring immediately. Otherwise, it prompts you to resolve conflicts.
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies:
The instructions and examples given here address the use of the feature in C#. For more information about other languages, refer to corresponding topics in the ReSharper by language section.