Inspections
Inspections detect and highlight various problems in the file currently open in the editor, such as invalid markup, missing elements, duplicate IDs, and non-existent references. Inspections are a feature of the IntelliJ platform, so you can read about them in IntelliJ IDEA Help: Inspections.
Most inspections are enabled by default, and Writerside continuously scans the files in your project and shows the number of problems detected in the current file in the top-right corner of the editor:
![]()
You can click this widget or press Alt+6 to open the Problems tool window that lists all problems in the current file.

Inspections have different severity levels ranging from errors that are critical and will most likely break something, through warnings that should be addressed to avoid potential problems, to typos and considerations for improvement. For more information about severity levels, see IntelliJ IDEA Help: Change inspection severity.
When you see an inspection highlighting something in a file, hover over it to see the popup with the inspection name. Put the cursor at the highlighted element and press Alt+Enter to see the available context actions, including automatic quick-fixes.
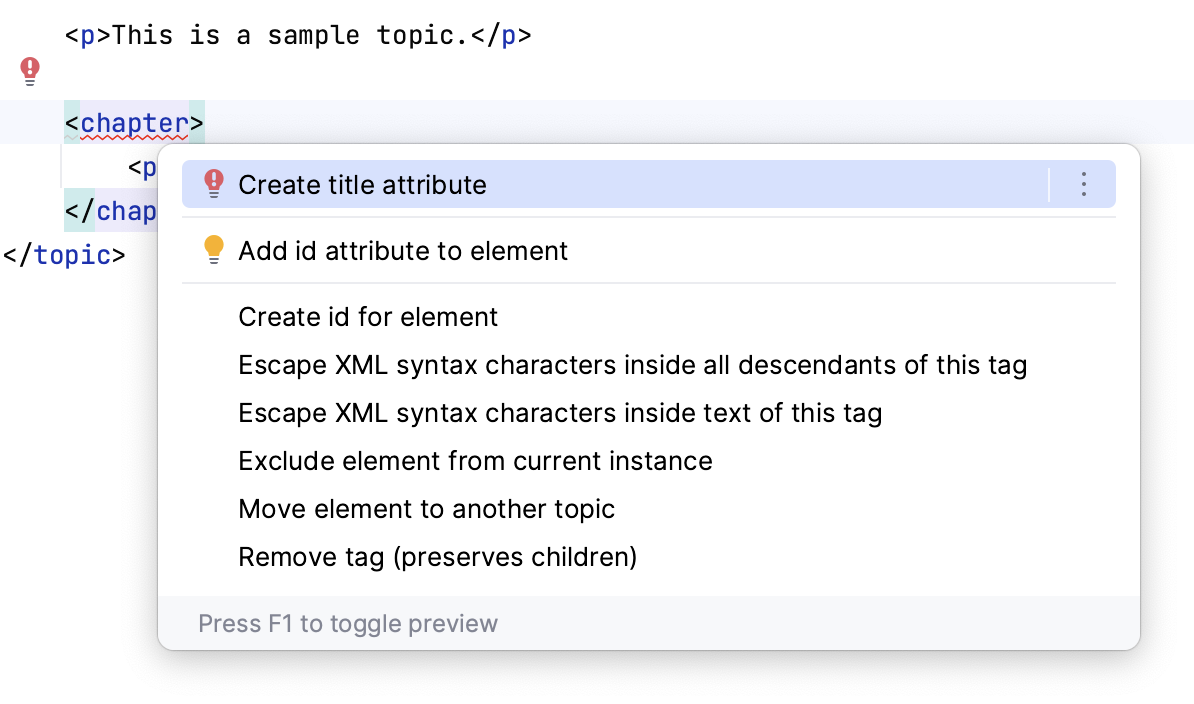
Run inspections on all project files
If you want to find and fix all issues in your project, you don't need to open every topic file manually. Instead, run Writerside inspections on the whole project and get a full report.
From the main menu, select .
In the Specify Inspection Scope dialog, select Whole Project.
If necessary, change the inspection profile, that is, the set of inspections to use. There are many inspections in the default profile that are not relevant for you, so you can disable all inspections except the ones specific to Writerside.
Click Analyze and wait for the analysis to finish. Depending on the size of your project, it may take a while. You will see the results in the Problems tool window.
Writerside includes the following inspections that are specific to topic files, tree files, and various configuration files in a Writerside project.
Configuration
- Duplicate category sort order
Detects non-unique sort order values of
<seealso>categories inc.list.The
c.listfile defines categories for the<seealso>block at the end of topics. Use theorderattribute to set the order in which Writerside renders the categories. Make sure that order values are unique within thec.listfile to avoid conflicts.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
Content validity
- Anchor is overridden
Detects overridden anchors in XML
<a href>links.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Card tag with more than one media
Checks if 'card' tag has more than one media.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Combinable elements
Detects elements that can be combined.
Such elements as
<var>,<title>,<web-file-name>,<show-structure>,<help-id>,<card-summary>,<link-summary>, and<web-summary>are generally one per topic or chapter. If you define them multiple times with overlapping scopes, they can usually be combined for clarity.For example:
<title instance="foo">Custom title</title> <title instance="bar">Custom title</title>Can be combined as:
<title instance="foo,bar">Custom title</title>Enabled by default with severity
Weak warning.
- Element filter shadowed by ancestors
Detects content filters that are shadowed by filters of parent elements.
Example:
<p instance="foo">Click <control instance="bar">OK</control>.</p>In this example,
baris shadowed byfoo, meaning that it will never be included in any instance. Make sure that all parent elements include filters that you expect for the child elements. So in this case, you should addbarto the parent paragraph.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Empty code block
Detects empty code blocks and empty source code files.
It detects literally empty
<code-block>elements only if there is no source file specified in thesrcattribute. Otherwise, it checks the contents of the source file.Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- File glossary.xml not found
Suggests creating
glossary.xmlwhentooltipused, butglossary.xmlnot listed.Enabled by default with severity
Weak warning.
- Format element checker
Checks the
<format>element style and color validity. A valid<format>element must specifycolor,style, or both attributes, and they must contain valid values.stylecan be a valid combination of the following:bold,italic,strikethrough,underline,superscript,subscript.colorcan be a hexadecimal RGB code or a valid color name, such as#ff0000orRed.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- GIF can be replaced with video
Checks if there is an MP4 video to replace an animation with.
Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Include uses 'filter' instead of 'use-filter'
Detects includes with the
filterattribute instead ofuse-filter.Usually,
filteris used on elements inside snippets, and when you include the snippet, you specifyuse-filter.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Incorrect build group path
Detects an invalid path for build group.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Incorrect label ID
Detects incorrect references to
<primary-label>and<secondary-label>identifiers.You can either select one of the existing labels, create a new one with the specified ID, or remove the label element.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Invalid filter value
Reports problematic filter declarations that may result in unexpected behavior:
Explicit
emptyvalues infilterattributesRedundant or misplaced negation
!operators
Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Large image without a thumbnail
Detects large images without a thumbnail and suggests making them expandable.
Thumbnails are small previews that you can use in place of large images. When the user clicks on the thumbnail, it expands to the full image.
You can either set
thumbnail="true"to make the original image expandable (optionally, also set the `width` to make the image thumbnail smaller), or usepreview-srcto specify a custom preview image as a thumbnail.You can set the maximum image width allowed by the inspection in Settings | Editor | Inspections.
Disabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Link to topic not in current instance
Detects links pointing to an existing topic that is not in the current help instance tree.
It ignores such links if the current topic itself is not in the current help instance tree.
You have several options to deal with this issue:
Mark the link with
nullable="true", which will render it as plain text if the target is not availableExclude the containing element (such as the paragraph with the problematic link) from the current help instance
Include the target topic into the current help instance
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Missing 'openapi-path' attribute
Detects missing
openapi-pathattribute either in the<api-endpoint>element directly or in the parent<api-doc>element.Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Missing alt attribute inspection
Detects
<img>elements without thealtattribute.Always use the
altattribute to provide a textual alternative to non-text content (in our case, to screenshots and icons) on web pages.The purpose of using the
altattribute is to:Make the page accessible to people who use screen readers.
Display information about non-textual page elements when they cannot be displayed.
Provide search engines with semantic information about the page contents.
Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Missing entity reference
Detects attribute values that reference non-existent entities.
For example, there must be a topic file named
introduction.topicwith an existing anchormy_anchorto reference it like this:<a href="introduction.topic" anchor="my_anchor"/>This also applies to
from,element-id,instance,use-filter, and other similar attributes.Disabled by default with severity
Error.
- Missing title
Checks for missing
titleattribute inchapter,def, andtabelements.Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Non-empty code block uses source file
Detects non-empty code blocks that also define a valid source file via the
srcattribute.By default, Writerside inserts the contents of the referenced source file into the code block. If you really want to use the contents of the source file, remove text inside the
<code-block>element and collapse it. Otherwise, keep the text in the code block and remove thesrcreference to the source file.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Redundant link text
Detects links to topics where the topic title matches the link text.
When you add a link to another topic, Writerside uses the topic title as the link text, unless you put some text inside the
<a>tag. If this text matches the topic title, Writerside suggests removing the text and collapsing the<a>tag.Enabled by default with severity
Weak warning.
- Title tag is ignored
Detects
<title>tags that do not affect the topic title.In Writerside XML topics, only the first
<title>tag in the file defines the topic title. All subsequent<title>tags are ignored and can be removed.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Top-level header is implicitly converted to a chapter
Detects top-level headers in Writerside Markdown topics that will be converted to chapter headers in the generated documentation.
In Writerside Markdown topics, the first top-level (level 1) header is interpreted as the topic title. All subsequent top-level headers are implicitly converted to chapter titles (level 2 Markdown headers).
Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Topic title is missing
Detects Markdown topics with a missing topic title. Every Markdown topic must have a first-level
#header, which serves as the topic title. Alternatively, you can also use a YAML front matter block:--- title: Topic title ---There are two suggested quick fixes: adding a
# Topic titleto the very beginning of the topic or converting the first header of any other level to H1.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Unexpected media file type
Detects media references that do not match their expected media types, for example, image references in
<video>tags and videos in image elements.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Unreachable external image
Detects unreachable URLs to external images.
You can add an external image to your documentation by providing its URL in the
srcattribute. This inspection sends a request to the specified URL and reports a problem if the response status code is 400 or more.Disabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Unreachable external link
Detects unreachable external links.
You can add an external link to your documentation by providing a URL in the
hrefattribute. This inspection sends a request to the specified URL and reports a problem if the response status code is 400 or more.Disabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Unreachable external video
Detects unreachable URLs to external videos.
You can add an external video to your documentation by providing its URL in the
srcattribute. This inspection sends a request to the specified URL and reports a problem if the response status code is 400 or more.Disabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Unresolved reference
Detects unresolved references to images, topics, resources, and other referencable objects.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Unsupported language in code block
Detects unsupported languages in code blocks.
Such code blocks will be rendered as plain text, without syntax highlighting.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Video has no preview image
Detects videos without a preview image.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Wide code block
Detects code blocks with long lines.
The frontend adds a horizontal scroll bar to code block elements with lines that don't fit inside the block. The maximum width of the code block element can fit lines up to 70 characters without a scroll bar. This inspection highlights code blocks with long lines: rearrange such code to avoid truncated examples for your readers.
You can change the maximum line length for this inspection.
Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
Detects XML-like tags inside
<code-block>.If you need to show XML-like markup in a code block, either wrap the contents of the code block with
CDATAor use HTML character entities instead of angle brackets.Enabled by default with severity
Error.
Element id problems
- Element id occurs more than once
Detects duplicate element IDs.
You can use IDs to set up links to topic elements or to reuse them in other topics, so element IDs must be unique within a file.
Replace matching IDs and make sure that new IDs are easy to distinguish.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Element id occurs more than once in Markdown file
Detects duplicate element identifiers in Markdown Writerside topics.
You can use IDs to set up links to topic elements or to reuse them in other topics, so element IDs must be unique within a file.
Replace matching IDs and make sure that new IDs are easy to distinguish.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Element without an 'id' attribute
Highlights elements that don't have the
idattribute.All elements in the generated help instance get random unique hash IDs, unless an element has the
idattribute. By default,idis mandatory for structural elements, such as chapters and procedures, for elements with titles and anchor links, such as tabs and definition list items, and for snippets that are expected to be referenced by their ID. Use this inspection's settings to define a comma-separated list of elements that should have anid.Enabled by default with severity
Weak warning.
- Root file tag must have an 'id' attribute
Detects missing or incorrect topic IDs in XML files. Every XML topic must have the
idattribute in the root<topic>tag with the value equal to the topic file name without the extension.The quick fix either adds or corrects the ID to match the topic file name.
For example, if the topic file name is
some_intro.topic, then the root<topic>tag must haveid="some_intro".Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Unresolved anchor reference
Reports unresolved references in Markdown links.
Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
Style checks
- Missing space
Detects the absence of whitespace characters around tags.
Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
Table of contents
- Duplicate redirect
Detects duplicate redirects.
You can use the
accepts-web-file-namesattribute on a<toc-element>to specify HTML pages from which you want to redirect to this TOC entry. For example, when you remove a topic, you probably want to redirect its web filename to another topic. If you use the same web filename for multiple redirects, it will lead to a conflict. This inspection detects duplicate redirects and suggests removing the duplicates.Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Duplicate topic in TOC
Detects topics that are added to the TOC more than once.
Every entry in the table of contents references a specific topic. If you add a topic to the same help instance tree more than once, it will lead to conflicts. This inspection detects TOC elements that reference the same topic and suggests removing the TOC element.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Missing start-page attribute
Detects non-library instance-profile tag without 'start-page' attribute and offers to add it.
Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Library topic in tree file
Detects TOC elements in tree files that reference library topics.
A library topic is a topic with
is-library="true". Although you can re-use content from any topic file, it is better to keep reusable snippets in dedicated library topics, which are not meant to be published with any help instance.Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Redirect from existing topic
Detects redirects from web filenames of existing topics.
You can use the
accepts-web-file-namesattribute on a<toc-element>to specify HTML pages from which you want to redirect to this TOC entry. For example, when you remove a topic, you probably want to redirect its web filename to another topic. If you use a web filename of an existing topic, it will lead to a conflict. This inspection detects such conflicts and suggests removing the redirect.Enabled by default with severity
Error.
- Redundant TOC title
Detects TOC titles that match the topic title.
By default, Writerside renders the topic title in the TOC. If the topic title is too long for the TOC, you can assign a shorter TOC title for it by specifying the
toc-titleattribute in<toc-element>. The TOC title is used only for the corresponding TOC entry and does not change the topic title.If the TOC title matches the topic title, this inspection highlights the redundant
toc-titleattribute and suggests removing it.Enabled by default with severity
Warning.
- Unreachable URL in TOC
Detects external URLs in the table of contents that can't be reached.
You can add a link to any URL to the table of contents with the
hrefattribute. This inspection sends a request to the specified URL and reports a problem if the response status code is 400 or more. For values that start withmailto:, it ensures that the email has valid syntax.Disabled by default with severity
Warning.
Unused symbols
- Topic not in current instance
Warns you when the topic currently open in the editor is not in the current help instance.
You can either add this topic to the current help instance or select a help instance with this topic.
Enabled by default with severity
Weak warning.
- Unused snippet
Detects snippets that are not included anywhere.
For regular topics, Writerside suggests unwrapping the
<snippet>element (preserving the content).For library topics, Writerside suggests removing the
<snippet>element (preserving only descendant snippets that are used somewhere).Enabled by default with severity
Weak warning.
- Unused topic
Warns you when the topic file is not used anywhere.
If the topic file is not included in any table of contents and does not have anything from it included in other topics, consider removing it from the project.
Enabled by default with severity
Weak warning.