What's New in ReSharper 2025.2
The ReSharper 2025.2 release brings significant performance improvements, exciting new language features, and enhanced developer productivity across the board. With Out-of-Process (OOP) mode now available for preview and expanded support for C# 14 and C++, this release helps you write modern, reliable code faster than ever.
Performance
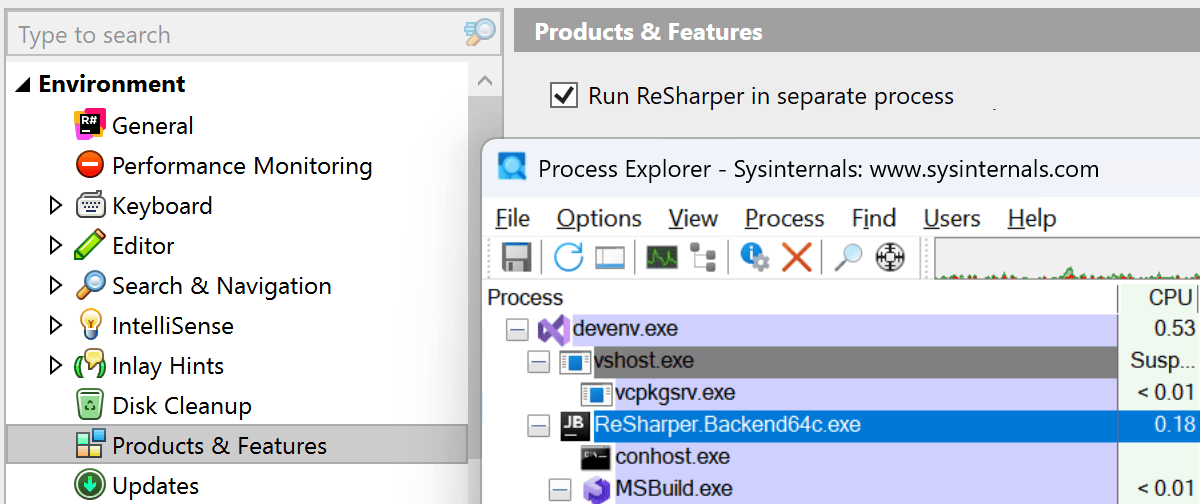
Out-of-Process mode Public Preview
We’re thrilled to announce that ReSharper 2025.2 is the first stable release to include support for running ReSharper out of process (OOP) with Microsoft Visual Studio. This long-anticipated architectural change lays the foundation for better stability and performance in the future, as it decouples the ReSharper process from the Visual Studio one.
To switch to Out-of-Process mode, go to ReSharper's Options | Environment | Products & Features and select the Run ReSharper in separate process option. Click the Save and restart button to apply the changes and reinitialize ReSharper without having to restart the IDE.
Instant navigation at startup
With ReSharper 2025.2, you can use Ctrl+T to start navigating to files immediately after opening a solution – no need to wait for full indexing.
Razor/Blazor processing tuning
We’ve reduced memory overhead and eliminated redundant processing for include files like _ViewImports and _ViewStart. Find Usages is now faster for Razor component types, and several false warning issues are eliminated.
Better Rename refactoring
The Rename refactoring is now significantly faster and more transparent. We’ve parallelized the validation phase, improved progress reporting, and reduced memory consumption.
Smoother inplace refactorings
We’ve reduced the performance impact of inplace refactorings, minimizing interference with typing and improving the overall editing experience.
Faster solution loading and initial indexing
ReSharper now takes better advantage of modern SSDs by removing legacy logic that enforced sequential disk operations during indexing. This logic was originally optimized for HDDs, but SSDs are free from physical limitations of the HDDs and enable parallel I/O operations with high throughput. This change, along with optimized background processing, results in a slightly faster indexing and startup on modern hardware. Solution loading has also been improved for projects that include references to Source Generators.
Want the full story behind these performance gains? Head over to our blog for a deep dive.
ReSharper for Visual Studio Code Public Preview
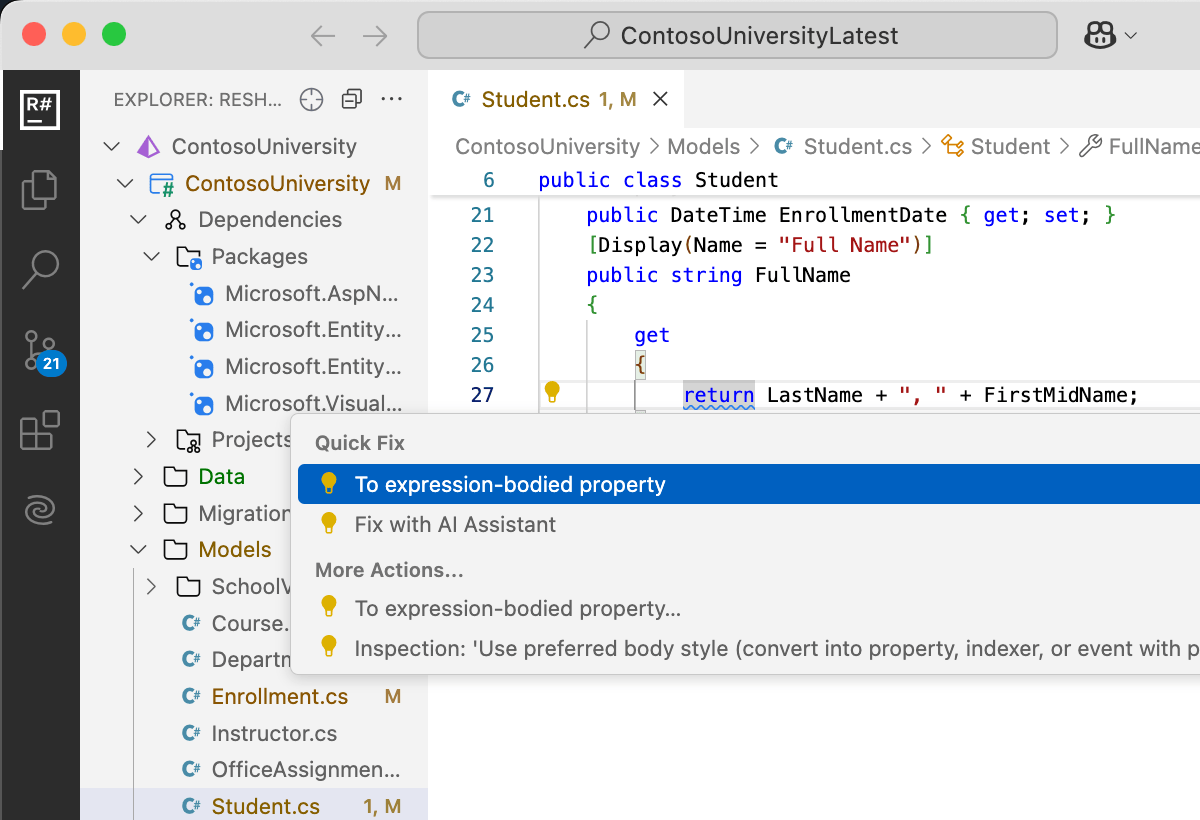
ReSharper is now also available as an extension for Visual Studio Code. If you use Visual Studio Code as part of your workflow, you can now benefit from familiar ReSharper features directly inside the editor. Code inspections, quick-fixes, navigation, and the Rename refactoring are all supported and powered by the same underlying engine.
ReSharper for VS Code is free to use during the public preview.
C# support
New language features
ReSharper 2025.2 brings initial support for the latest additions in C# 14:

Extensions Initial support
ReSharper previews support for new C# 14 extension members by providing code completion, code analysis, Find Usages, the Rename refactoring, and more.

Partial events and constructors
C# 14 continues to extend possibilities of source generation with partial events and constructors. ReSharper is updated to cover these new use cases.
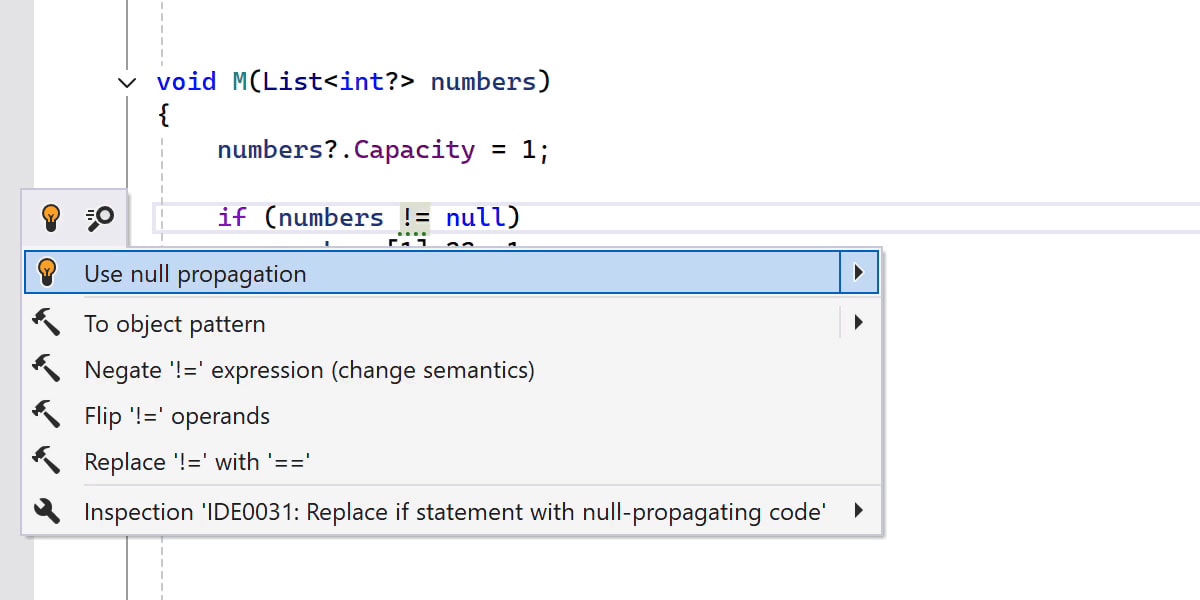
Null-conditional assignments
ReSharper 2025.2 lets you use the new a?.b = c and a?[i] = c patterns to simplify your code while safely handling potential null values.

User-defined compound assignment operators
ReSharper now correctly understands and processes user-defined compound assignment operators introduced in C# 14.
Ignored preprocessor directives
ReSharper now recognizes the new #! and #: preprocessor directives.
Better logging with LoggerMessage
ReSharper 2025.2 introduces several improvements to help you write more efficient and maintainable logging code with ILogger.
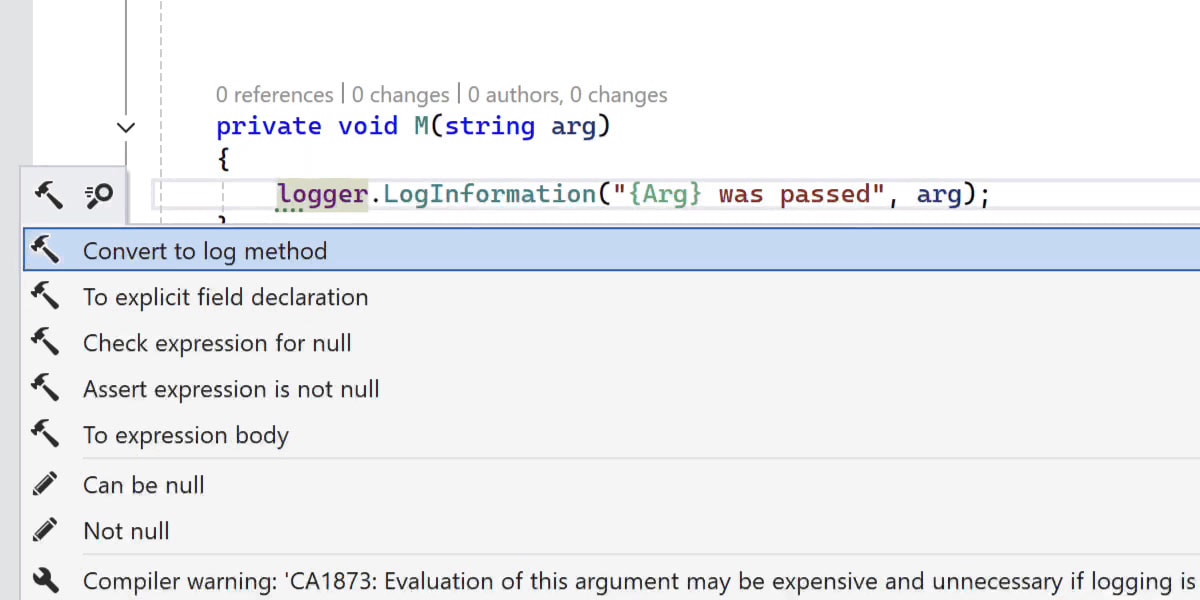
New refactoring option to convert logger calls to LoggerMessage-generated methods
ReSharper can now automatically convert your ILogger method calls into LoggerMessage-based methods. This reduces runtime overhead and improves performance, especially in high-throughput applications.
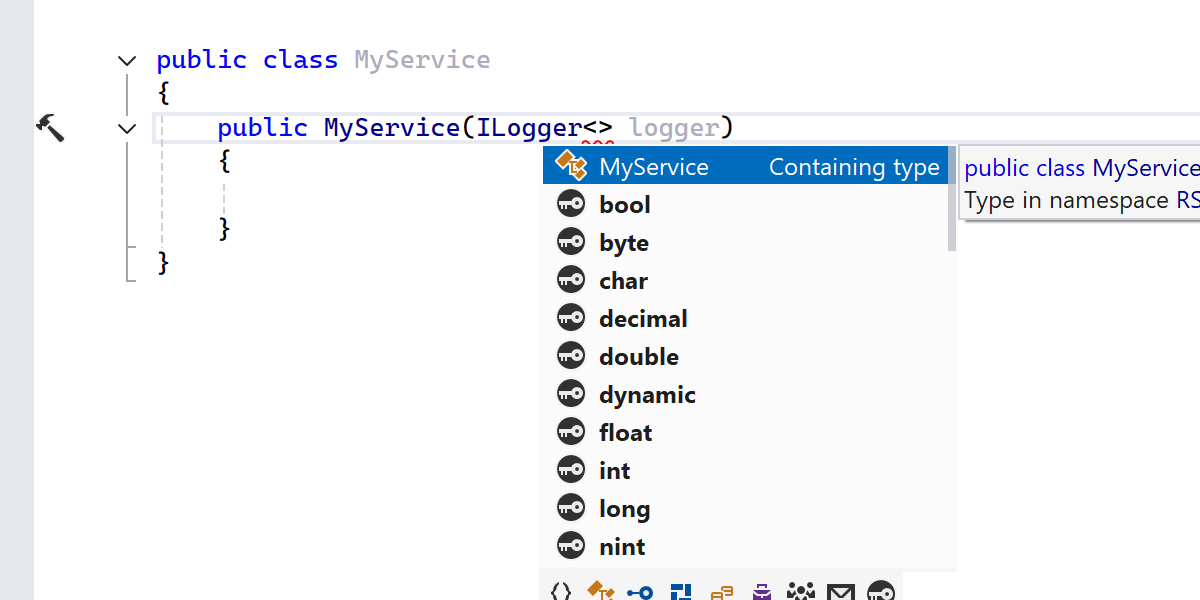
Smarter code completion for ILogger<T>
When writing ILogger<>, ReSharper now suggests the current type as a completion inside the angle brackets, saving you time during setup.

Improved parameter name handling in [LoggerMessage] attributes
ReSharper provides handy completion of parameter names in [LoggerMessage] attributes and correctly updates code when corresponding parameters are renamed.
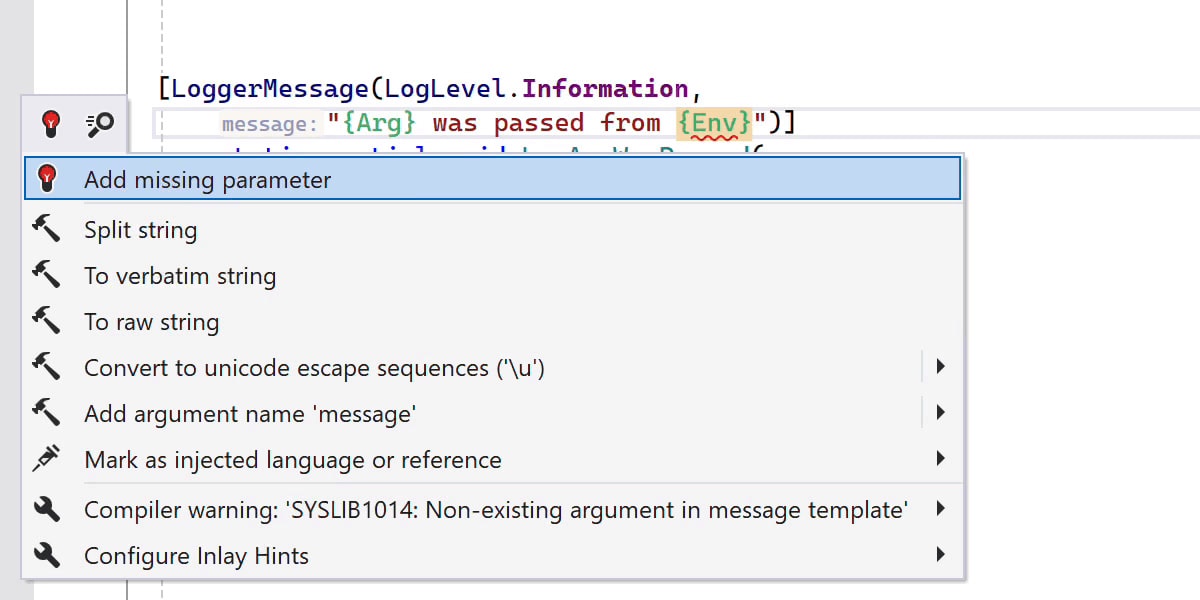
New inspections for LoggerMessage usage
ReSharper now detects missing parameters and duplicated log items in [LoggerMessage] attributes and provides quick-fixes to resolve these problems.
Miscellaneous
Range indexer suggestions
ReSharper recognizes more cases when range indexers can be used, for example, suggesting s[a..b] instead of s.Substring(a, b - a) where applicable.
Improved detection of redundant bounds in range expressions
ReSharper now identifies redundant bounds in range expressions more effectively, making your slicing operations clearer and more reliable.
Improved Roslyn integration
ReSharper now integrates more tightly with Roslyn’s inspection settings, with support for enabling or disabling inspections via #pragma and Roslyn’s severity configuration.
Productivity

Inplace refactorings with inlay hints
Inplace refactorings now appear via inlay hints, making them easier to discover and consistent with JetBrains IDEs. You can configure their appearance under ReSharper | Settings | Environment | Editor | Appearance.

New context action: Convert to local function
You can now quickly convert a method to a local function with a dedicated context action, improving code structure and readability.
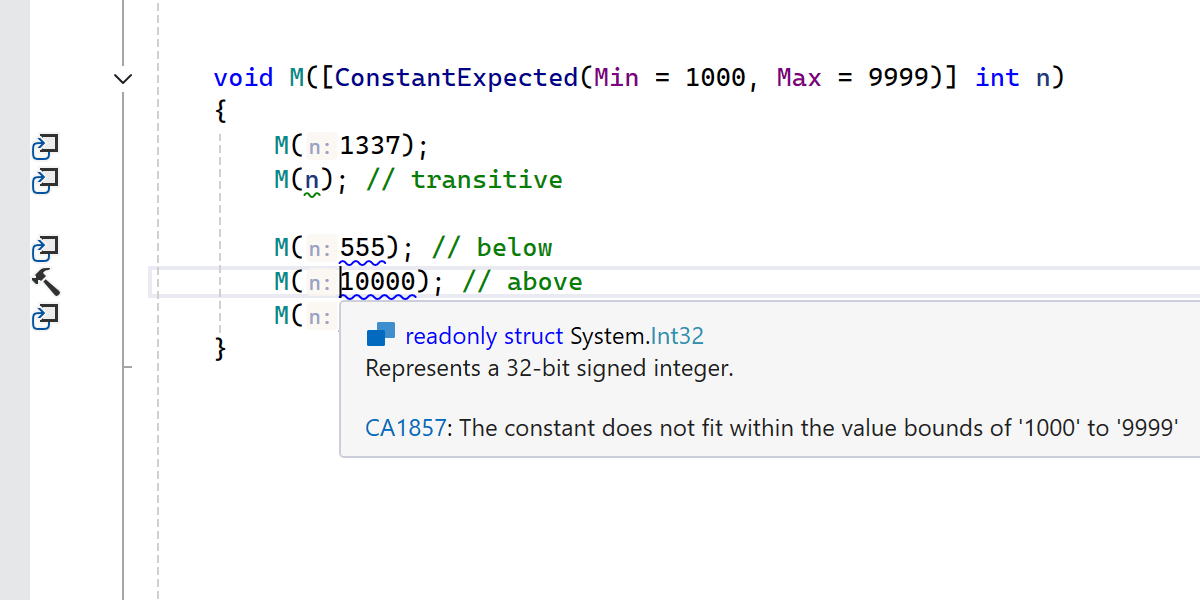
Support for the ConstantExpected attribute
ReSharper warns when non-constant values are passed to parameters marked with the [ConstantExpected] attribute, helping you avoid subtle bugs.
New inspection for duplicated switch arms
ReSharper detects duplicated switch arms and provides a quick-fix to merge them, making your code more concise.
C++ support
ReSharper 2025.2 introduces further enhancements for modern C++ development:
- Support for an initial set of language features from the recently finalized C++26 standard.
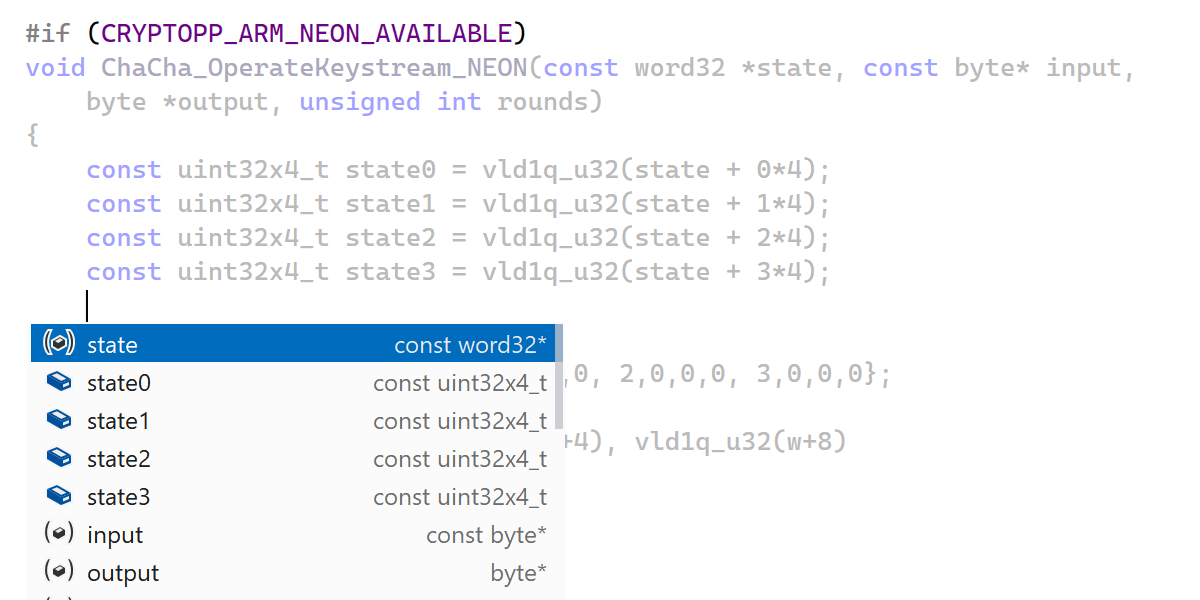
- Coding assistance features are now fully available when you edit code inside
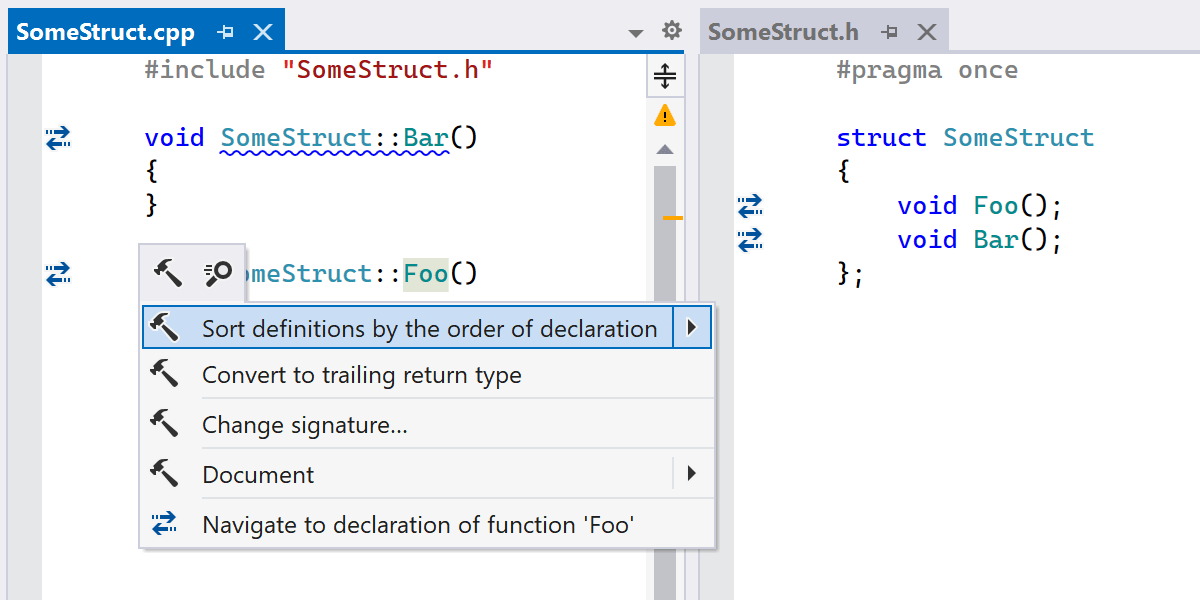
#if-ed out blocks, without having to switch your active build configuration. - A new syntax style setting and a context action help you keep definitions in a source file sorted by their declaration order.
- Identifier highlighting for global constants, support for variable references in OpenMP
#pragmadirectives, and other new coding assistance features.
Learn more about the C++ updates from the What's New in ReSharper C++ 2025.2 page.
Continuous integration
TeamCity extension sunsetting
As part of the 2025.2 release, we will be discontinuing the TeamCity extension for Visual Studio.
This change is part of our ongoing efforts to streamline tooling and focus on the most impactful developer experiences. While we understand that this may affect some workflows, we believe this decision will ultimately lead to better performance and a more sustainable ecosystem across our tools.
Code quality
CQRS validation Experimental
ReSharper 2025.2 introduces experimental inspections to help enforce the Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) pattern. These inspections detect naming mismatches, context intersections, and conflicts between annotations and names. Quick-fixes are available that remove redundant attributes or rename entities to follow conventions.
CQRS validation is disabled by default and can be enabled in Options | Code Inspection | CQRS Validation. The required annotations are available in JetBrains.Annotations.