What’s New in ReSharper C++
ReSharper C++ 2024.1 improves C++20 modules support and implements outgoing calls in Call Tracking. Coding assistance enhancements include improvements to the Change Signature refactoring, updated documentation comments support, and more. For Unreal Engine developers, ReSharper C++ 2024.1 offers support for the Slate UI framework and asset path completion in C++ code.
C++20 modules support
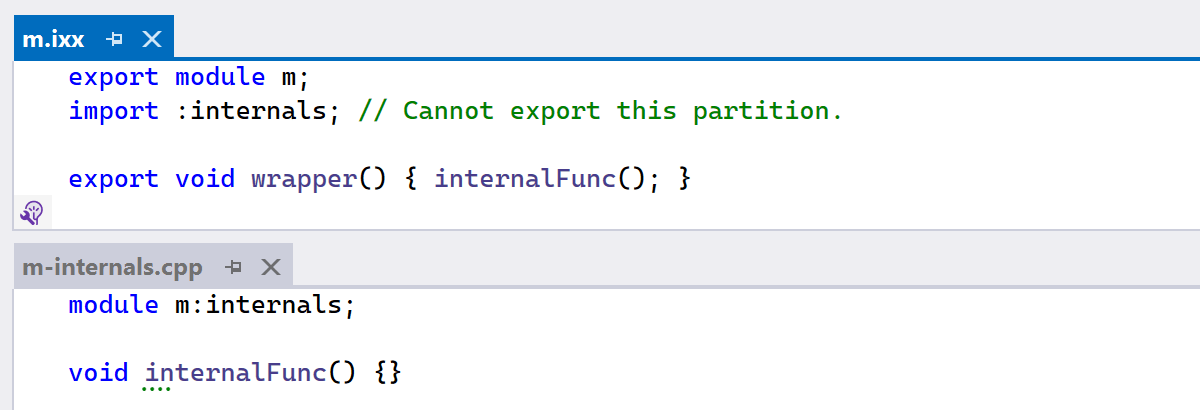
Thanks to the updated process of module discovery, ReSharper C++
now supports internal partition units, which are module partition units that do not
contribute to the external interface of a module. In other words, they are module
partitions without an associated export module declaration.

We’ve reworked the internal representation of exported C++20 modules to facilitate transitive references to entities imported from other modules. Previously, these entities were reexported from the module that imported them. We expect this change to significantly reduce the footprint of exported modules and enhance performance in projects utilizing C++20 modules.
Unreal Engine
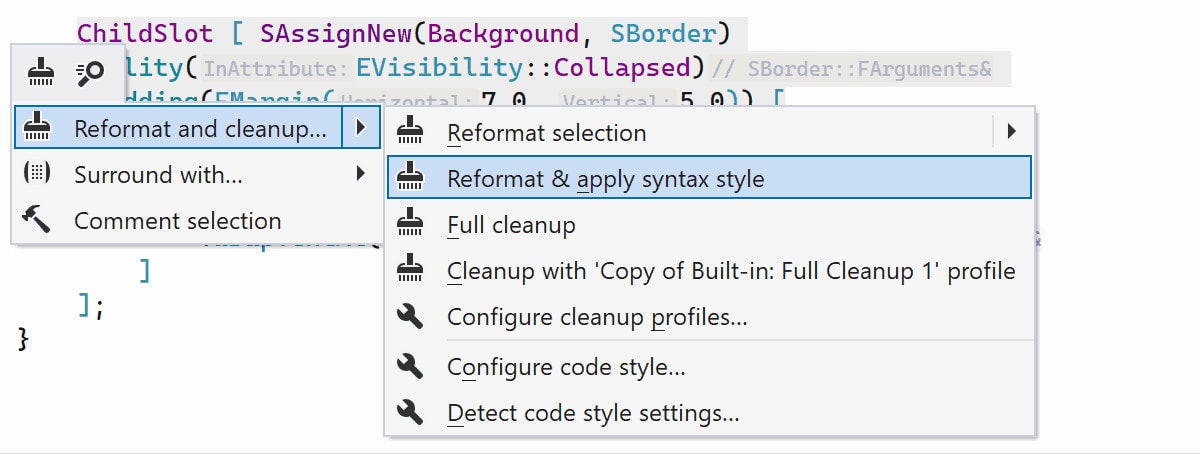
ReSharper C++ 2024.1 introduces support for Unreal Engine’s Slate UI framework. You can rely on ReSharper’s code formatter and typing assistance to format your Slate code according to Unreal Engine’s conventions. Features, like Go to declaration, Find Usages, and Rename, have also been updated to understand Slate’s declarative syntax.
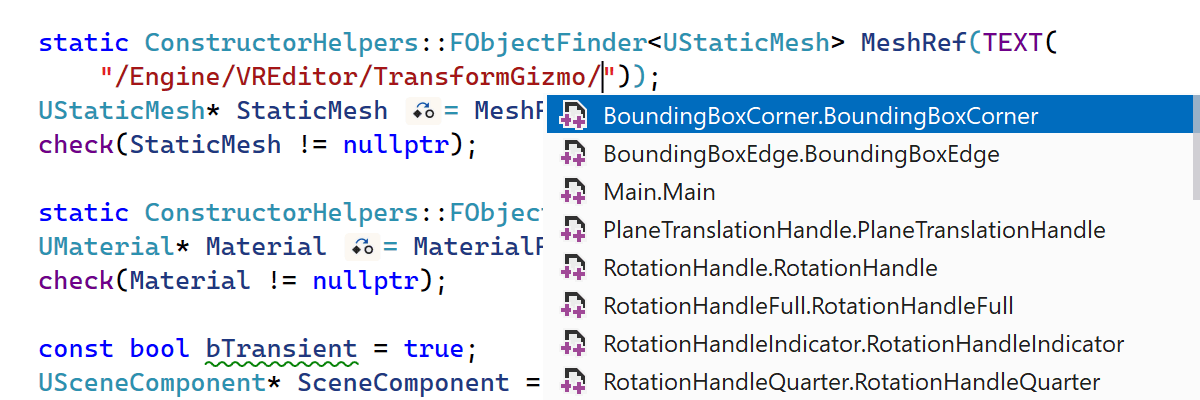
ReSharper C++’s integration with Blueprint functionality continues, with support for adding core redirects when renaming a UENUM instance, as well as completion of asset paths for resource names in C++ code.
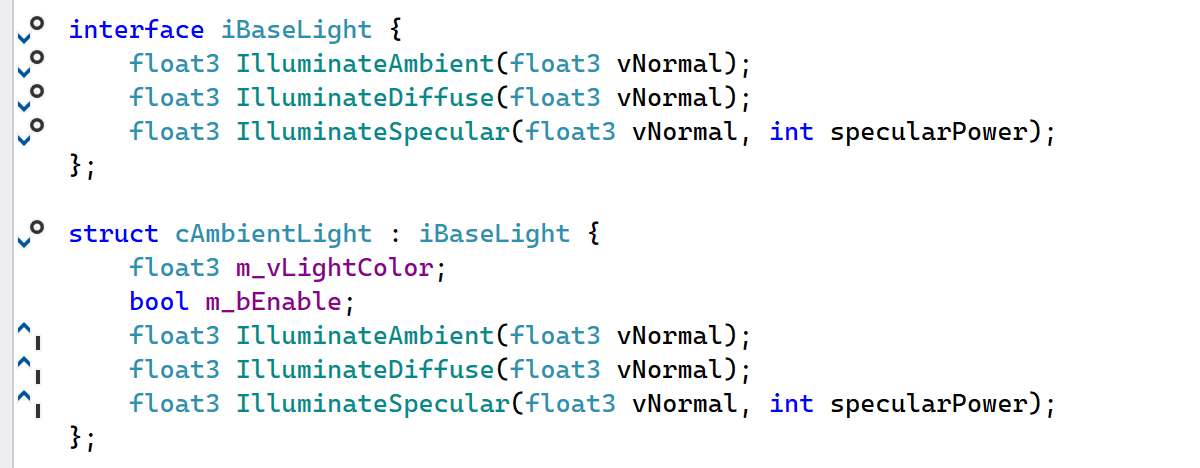
HLSL interfaces used for dynamic shader linkage are now supported in shader code.
If you’re interested in a stand-alone cross-platform IDE for Unreal Engine development, consider Rider. The Unreal Engine support in Rider and ReSharper C++ is aligned, and you can expect the same improvements in the Rider 2024.1 update.
Outgoing calls in Call Tracking
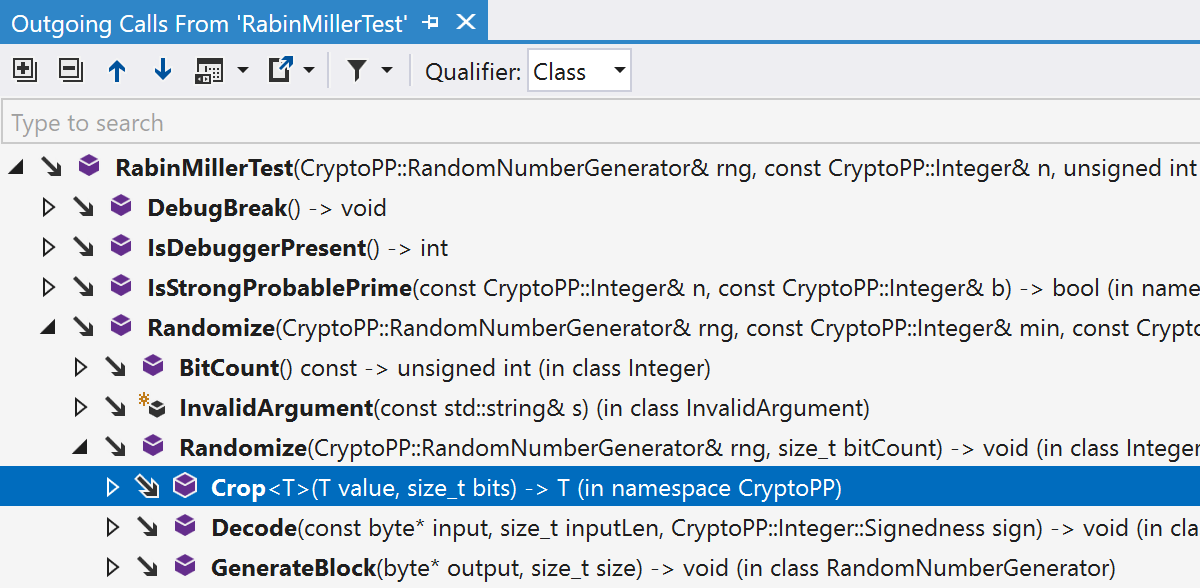
ReSharper’s Call Tracking now supports navigation through outgoing C++ call chains, in addition to the existing support for tracking incoming calls. To explore outgoing calls, place the caret at any function and select Inspect | Outgoing calls from the context menu. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+A to invoke it from the Inspect This menu.
Change Signature improvements
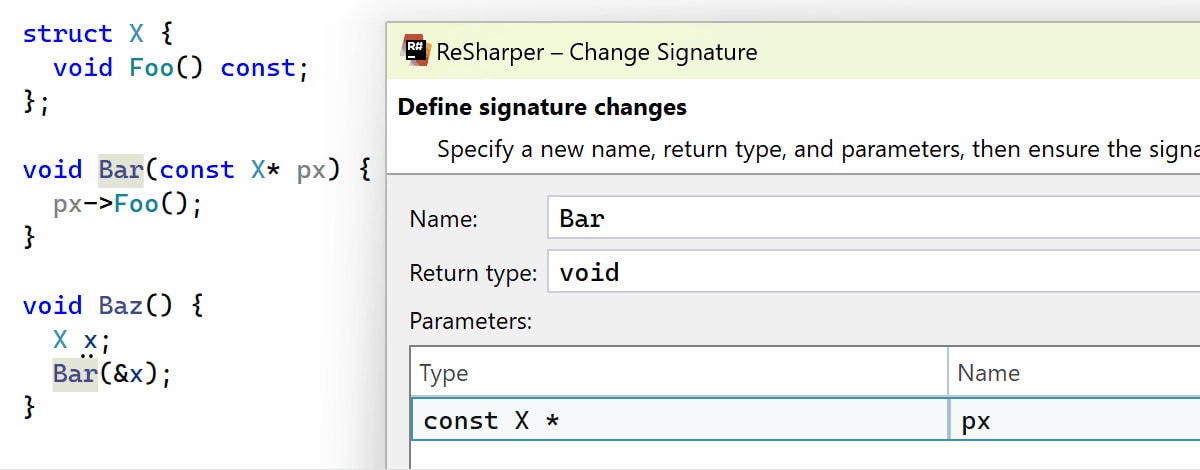
With Change Signature, you can now easily change the type of a function parameter between a pointer, a reference, or a value type. ReSharper will automatically update parameter usages within the function body and adjust function arguments at the function call sites, adding dereferencing or address-of operators where required.
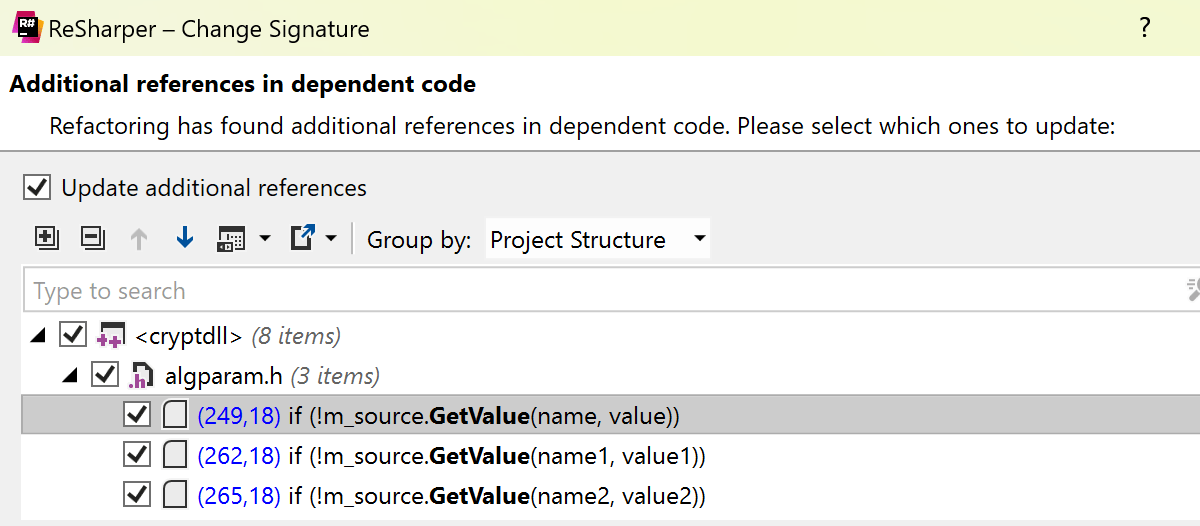
When Change Signature is invoked on a function that has potential usages in dependent code, the refactoring now lets you verify the changes and confirm which usages need to be updated.
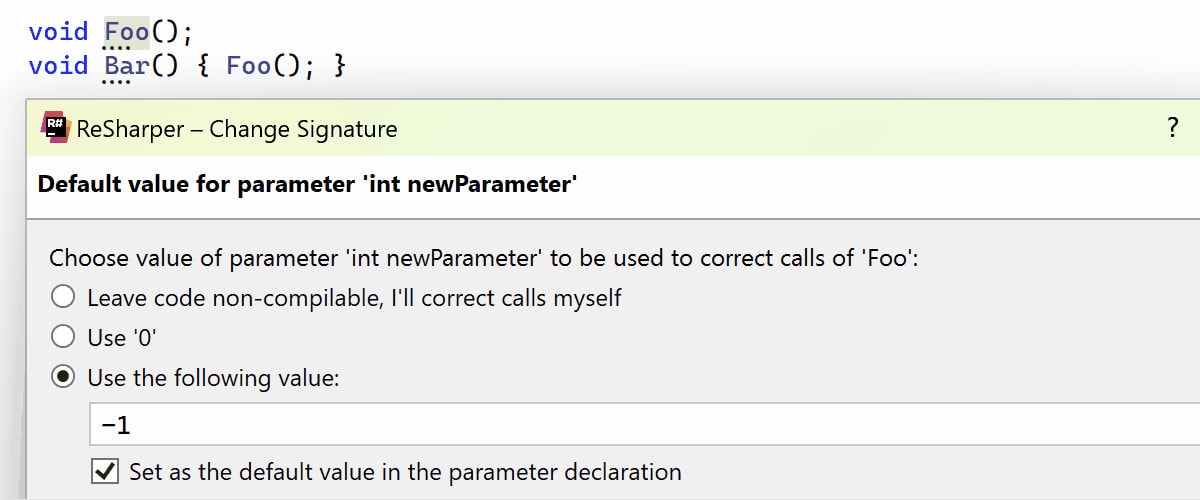
You can also now specify default arguments for new function parameters added using Change Signature.
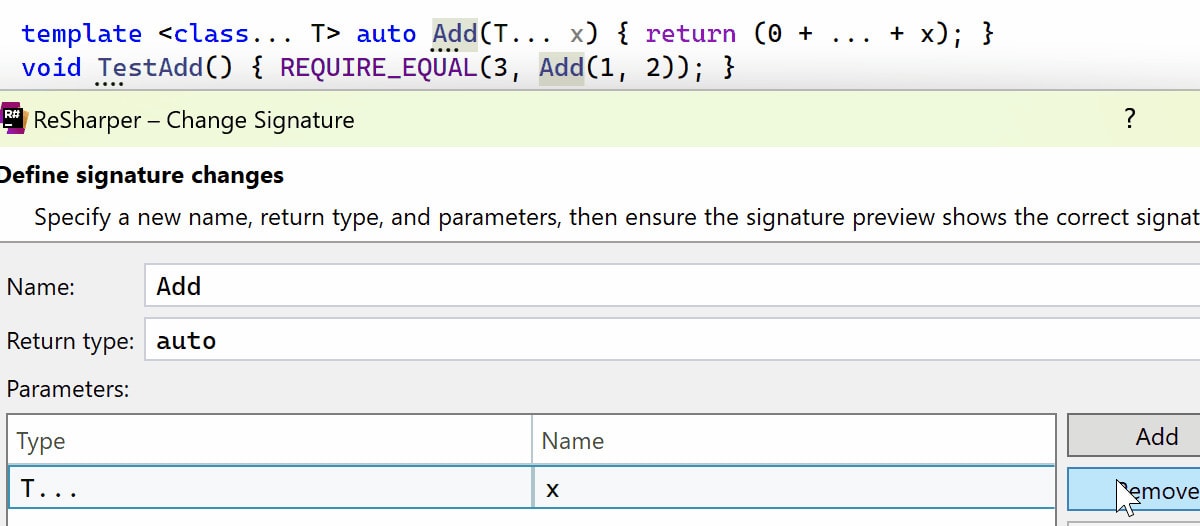
Other notable updates to Change Signature include:
- Improved handling of variadic function templates.
- Correct updating of function arguments for call sites inside macro calls.
-
Change Signature now preserves array types and the
inttype specifier inunsigned inttypes.
Documentation comments
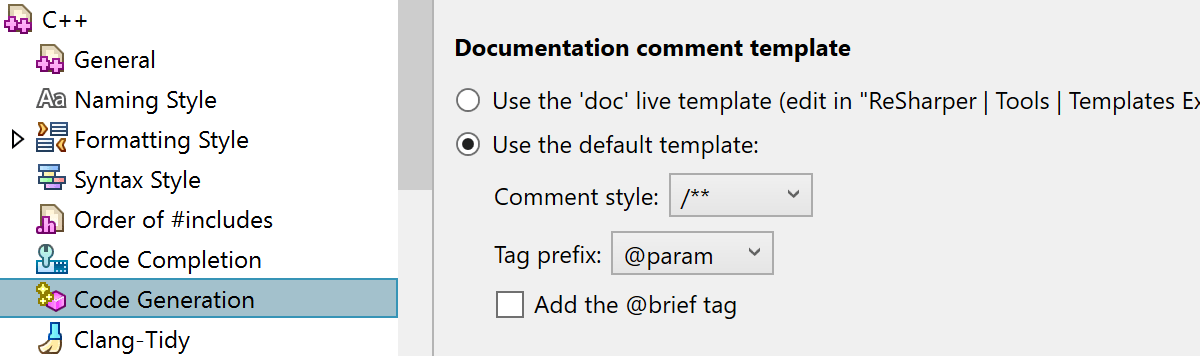
You can now customize the style of generated documentation comments without the need to edit a live template. To configure the style of documentation comments, go to ReSharper’s Settings | Code editing | C++ | Code generation.
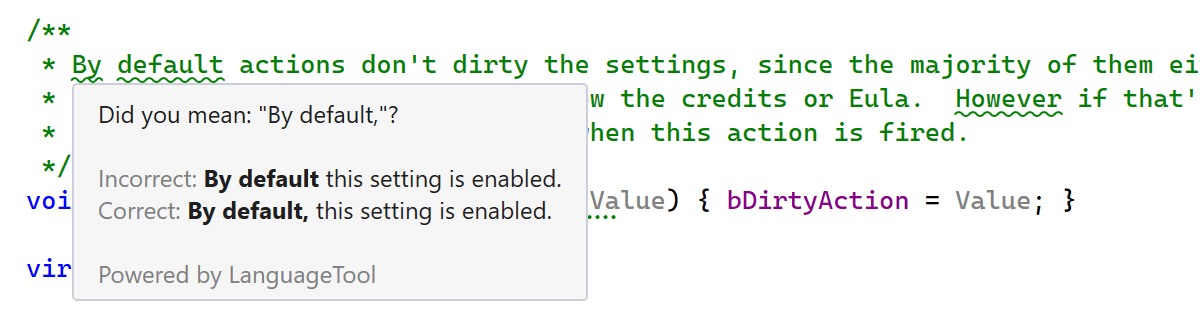
JetBrains Grazie is ReSharper’s new built-in grammar and spelling checker, introduced in ReSharper 2023.3. In the 2024.1 release, Grazie-powered grammar inspections are also available inside C++ documentation comments.
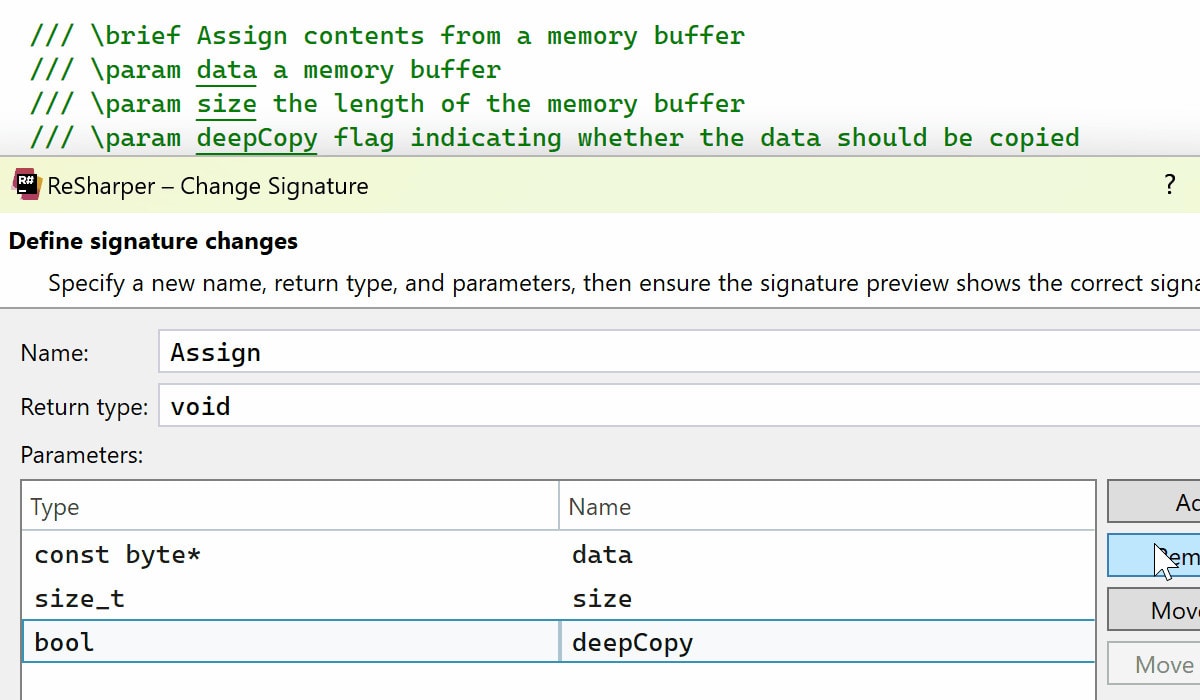
The Change Signature refactoring now keeps @param commands in sync
with the list of function parameters. This refactoring deletes @param
commands for removed parameters, adds commands for new parameters, and rearranges
existing commands to match the updated order of included parameters.
Code analysis

Based on the latest results from the extensive test suite for C++ refactoring tools maintained by Richard Thomson, ReSharper C++ continues to outperform other tools by passing the most test cases. As a part of our constant work on improving the quality of ReSharper’s suggestions, we’ve addressed several issues identified by Richard’s test suite in ReSharper C++ 2024.1. For example, the Create constructor from usage quick-fix now adds a default constructor when needed.
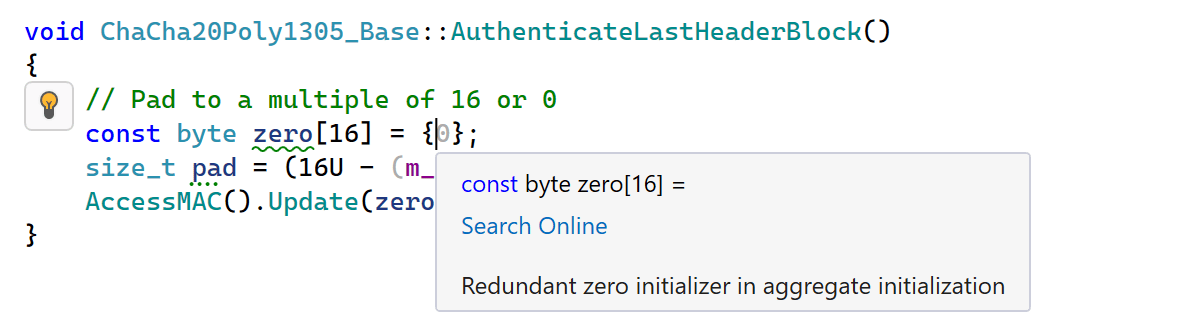
ReSharper C++ 2024.1 now suggests removing redundant
idiomatic zero initializers in aggregate initialization. Several new inspections
find various issues with static data members, such as redundant inline
specifiers on static constexpr data members.
Code cleanup adds new items to remove redundant accessibility specifiers and to make
classes without inheritors final. Apply ‘auto’ style now handles
global variables and class members in addition to local variables.

If you want to suppress an inspection in a specific scope, previously, you could use
ReSharper-specific // ReSharper disable comments.
ReSharper C++ 2024.1 additionally recognizes the
NOLINT, NOLINTNEXTLINE, and NOLINTBEGIN ... NOLINTEND
comments that clang-tidy uses.
Code formatting
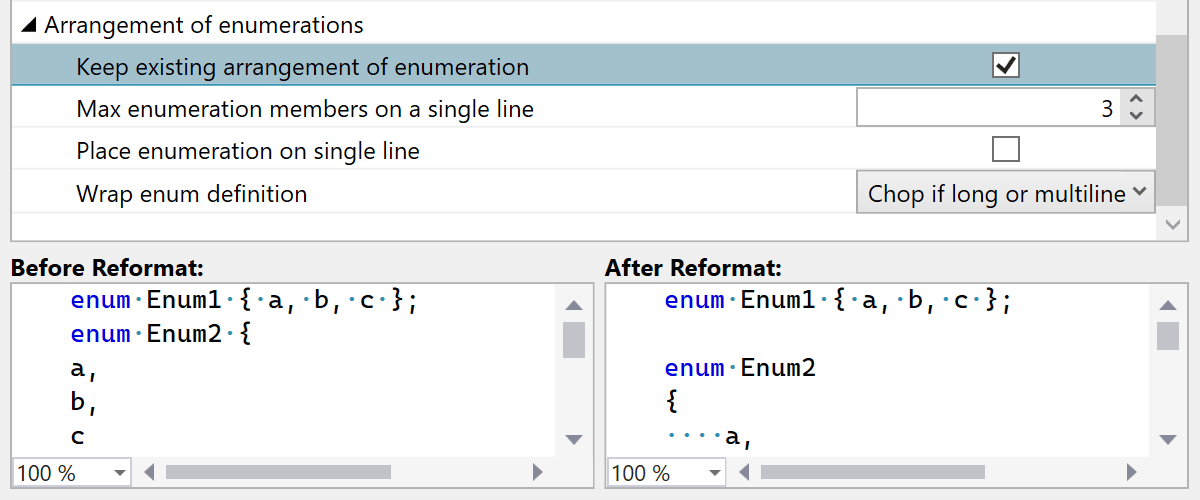
ReSharper C++ 2024.1 introduces several new formatting options:
- Break line after goto labels and Indent goto labels enhance the formatting of labeled statements.
- Settings that control wrapping inside enumerations under Arrangement of enumerations.
- Empty braces formatting now includes the Do not change option.
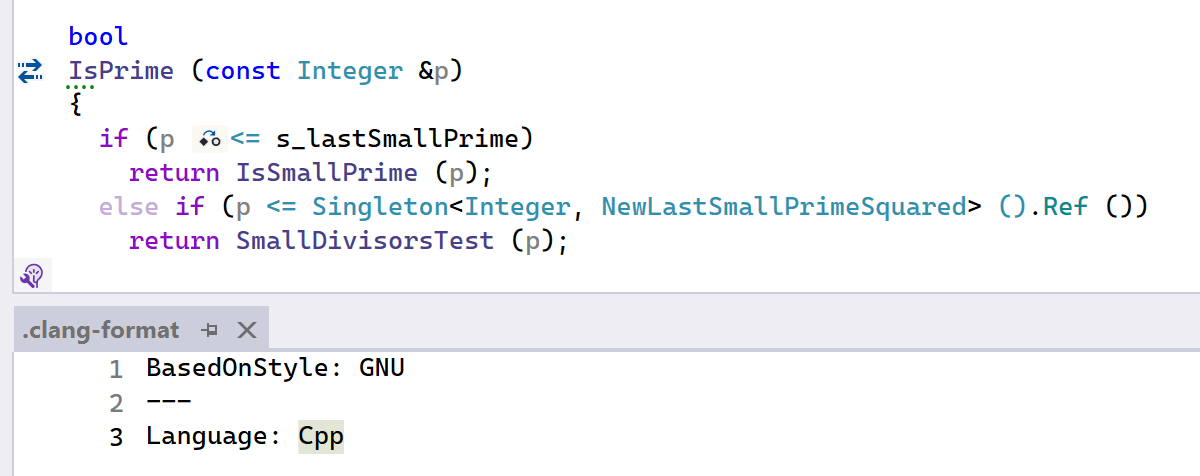
When using a .clang-format config, ReSharper’s formatter now respects the
DisableFormat and IndentAccessModifiers settings. The GNU
built-in clang-format style is now also supported.
Take a look at the What's New in ReSharper page to learn about all of the other changes introduced in this release.
ReSharper C++ 2023.3
AI Assistant is out of preview General Availability
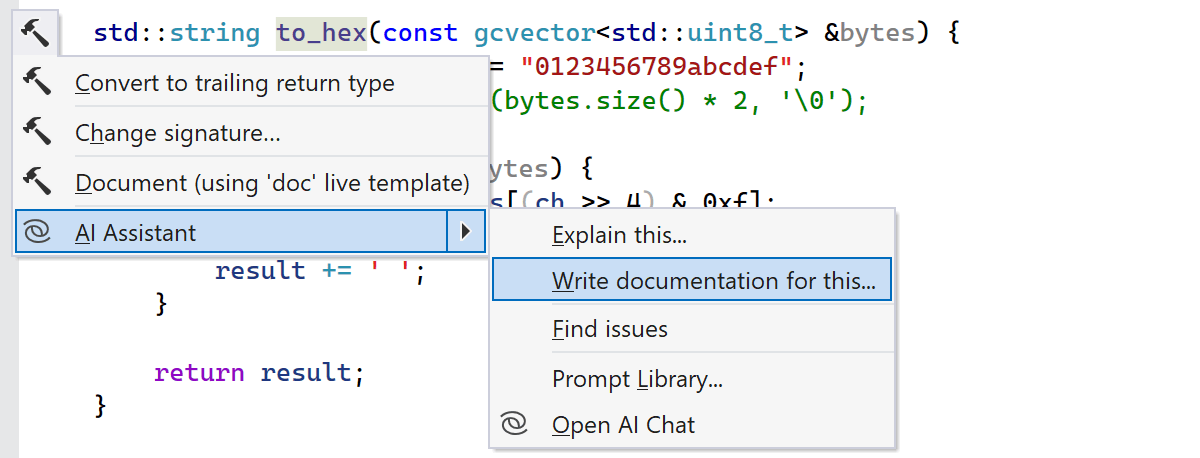
JetBrains AI Assistant is now generally available with a number of new and improved features to increase your productivity. Our latest set of improvements includes better project awareness for AI Actions and a prompt library.
Use AI Assistant in ReSharper C++ as a supplemental feature with a JetBrains AI Service subscription.
HLSL and Unreal Engine updates

HLSL 2021 introduced C++-like template functions and data types. The latest ReSharper C++ update brings full support for HLSL templates.
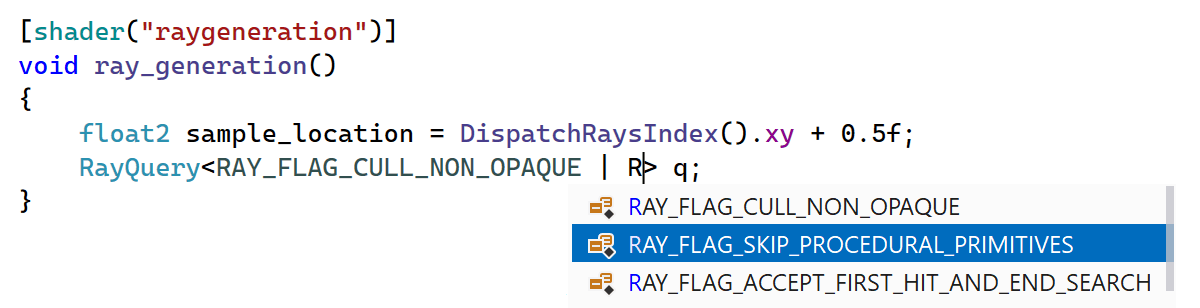
ReSharper C++ 2023.3 introduces support for the
HLSL built-in RayQuery type and enhances code completion to suggest
the corresponding flags.
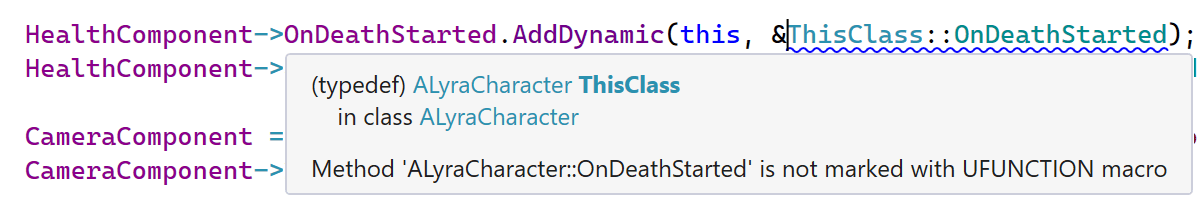
A new inspection helps you avoid falling into one of the common traps of the AddDynamic
helper macro. You’ll now get a warning when a dynamic delegate function is not marked
with the UFUNCTION macro.
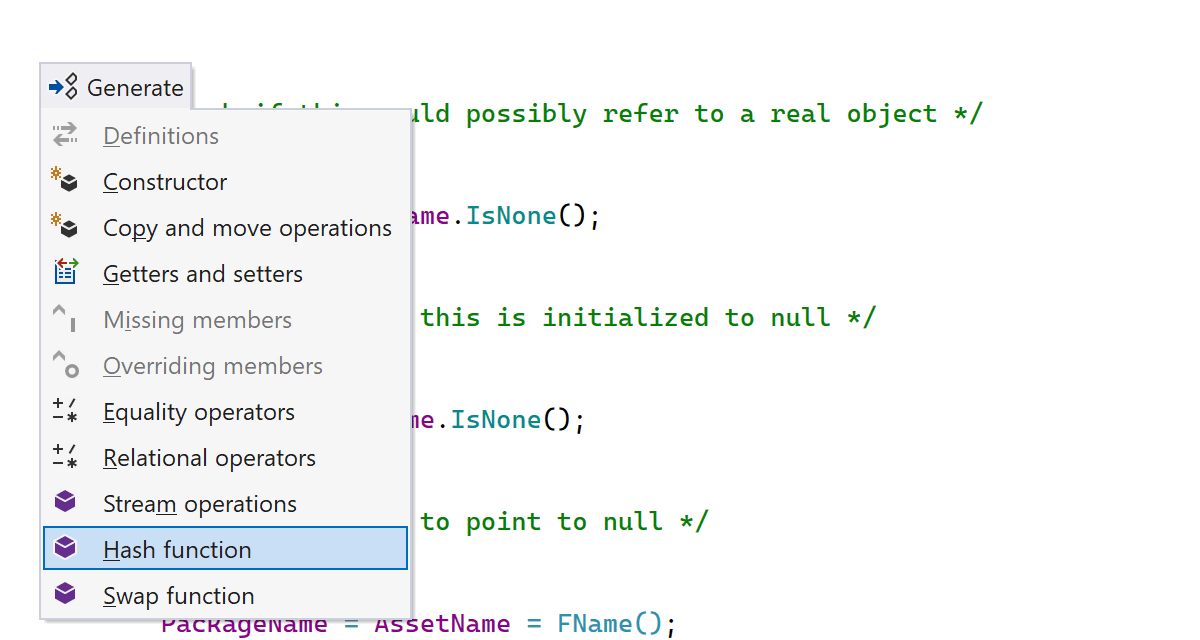
If you still find yourself writing boilerplate code occasionally, don’t forget that
the Alt+Insert shortcut is available to automatically generate common type
members. In ReSharper C++ 2023.3, we’ve tuned the generation
of hash functions to follow the Unreal Engine conventions.
If you’re interested in a stand-alone cross-platform IDE for Unreal Engine development, consider Rider. The Unreal Engine support in Rider and ReSharper C++ is aligned, and you can expect the same improvements in the Rider 2023.3 update.
C and C++ support
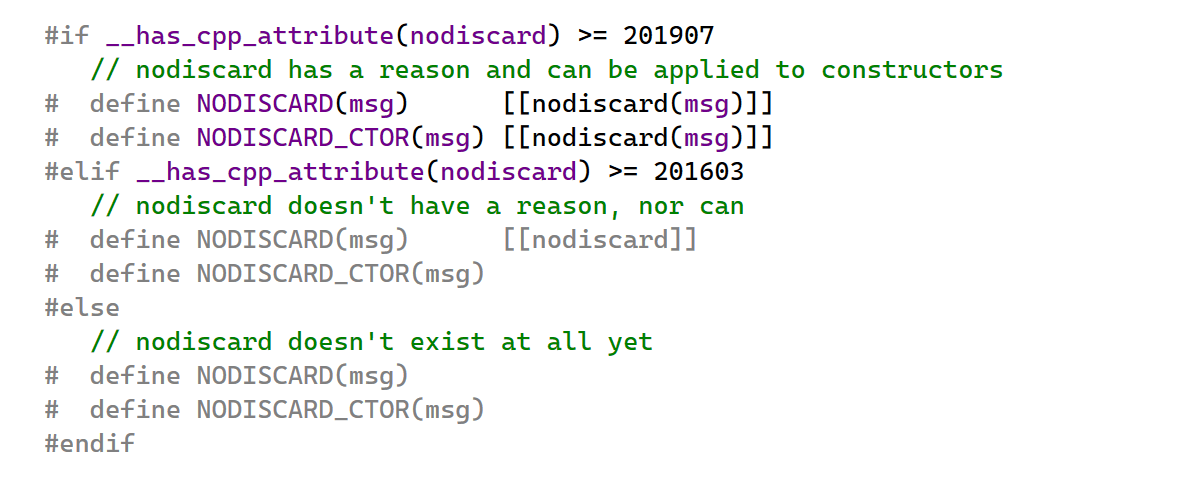
If you ever need to check whether some specific attribute is available in the current
standard or compiler version, C++20’s feature testing is here to save the day. By
using __has_cpp_attribute(operand) in preprocessor conditions, you can
test whether the compiler recognizes the attribute referenced by its operand.
ReSharper C++ now correctly handles
__has_cpp_attribute to better support attribute annotations in C++
standard libraries.
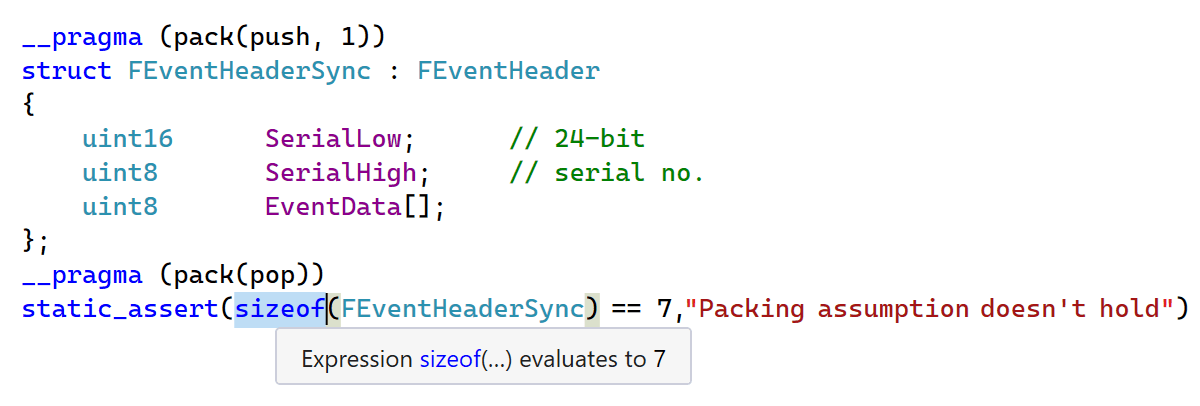
We’ve introduced support for the pack pragma used with the __pragma keyword.
The __pragma (pack) syntax is sometimes used inside macro definitions since
it’s not possible to use #pragma directives inside a macro definition. In cases like this,
ReSharper C++ now correctly computes sizes of packed structures
so that you can rely on code analysis results.

ReSharper C++ adds support for several C features:
-
The C99
restricttype qualifier that can be used in pointer declarations. -
Type deduction,
constexpr, andnullptrfrom C23.
We’ve also introduced support for several new clang intrinsics, such as
__is_const(), __is_member_pointer(), and others, to make
ReSharper C++ work better with cross-platform code.
For cross-platform C and C++ development, you can try an early preview of the standalone CLion Nova IDE. It is powered by ReSharper C++, and absolutely free to use at this stage – simply register, start coding, and send us your feedback!
Grammar and spelling checking
JetBrains Grazie has become ReSharper’s new built-in grammar and spelling checker. Grazie supports over 20 languages and catches natural language errors within programming languages supported by ReSharper (C#, C++, VB.NET), markup languages (HTML, XML, XAML), and comments. To add other natural languages to Grazie, go to Options | Grammar and Spelling | General in ReSharper.
Please note that grammar checking is currently not available in doxygen comments.
Working with inactive code
With platform-specific or configuration-specific code, you may often find yourself editing currently inactive code blocks inside conditional preprocessor branches. Previously, code completion in inactive code only offered macros. In ReSharper C++ 2023.3, we’ve improved code completion in these scenarios to include symbols from the global scope.

Find Usages now finds possible usages in inactive code and macro bodies. Previously, if you wanted to find these usages, you had to use Find Usages Advanced and investigate textual occurrences. Now Find Usages results include potential usages in macro bodies and inactive code by default. These usages are grouped into separate sections to distinguish them from usages in active code.
Code analysis

You can use ReSharper-specific C++ attributes to make ReSharper analyze your solution
with greater accuracy and insight. In ReSharper C++ 2023.3,
we’ve added the [[jetbrains::...]] prefix in addition to
[[rscpp::...]] for the existing [[jetbrains::format]],
[[jetbrains::guard]], and [[jetbrains::has_side_effects]] attributes.
The new [[jetbrains::pass_by_value]] attribute lets you suppress the
Pass value by const reference inspection for function parameters.
Find out more.
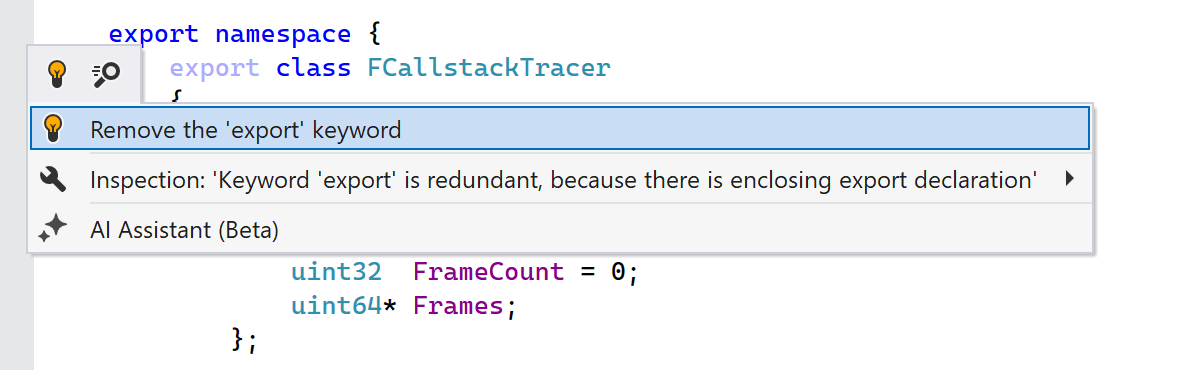
We’ve introduced a set of inspections for incorrect usage of the export keyword in C++20
modules. ReSharper C++ now suggests removing export when
another export declaration already encloses the declaration or when the declaration is
not part of a module interface unit and cannot be exported. You’ll also get a suggestion
to move export if you try templating the export declaration instead of exporting the
template declaration.

We’ve upgraded the bundled clang-tidy binary to Clang 17, bringing updates from the latest LLVM release.

Some clang-tidy checks output more details in addition to the warning text. ReSharper C++ now shows these additional notes in the tooltip.

A new inspection warns about the usages of multicharacter literals. They are conditionally supported with implementation-defined values and should be used carefully in portable code.
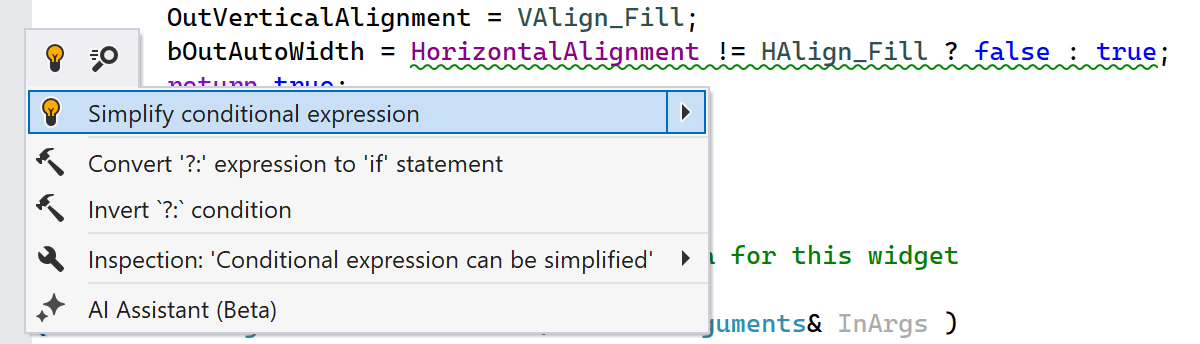
ReSharper C++ now suggests a quick-fix to remove redundant conditional operators and simplify ternary conditional expressions.
Coding assistance
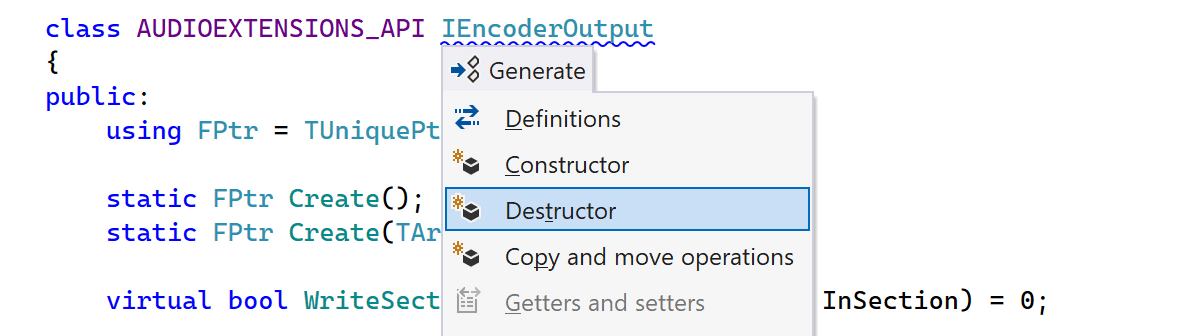
The Alt+Insert Generate menu helps you quickly create boilerplate code. In ReSharper C++ 2023.3, we’ve added a new action to the list, allowing you to generate a destructor.
When invoked in a polymorphic class, the action will use syntax style settings to insert
the required virtual and/or override specifiers. You can
configure the body style of the generated destructor on the
Code Editing | C++ | Code Generation options page.
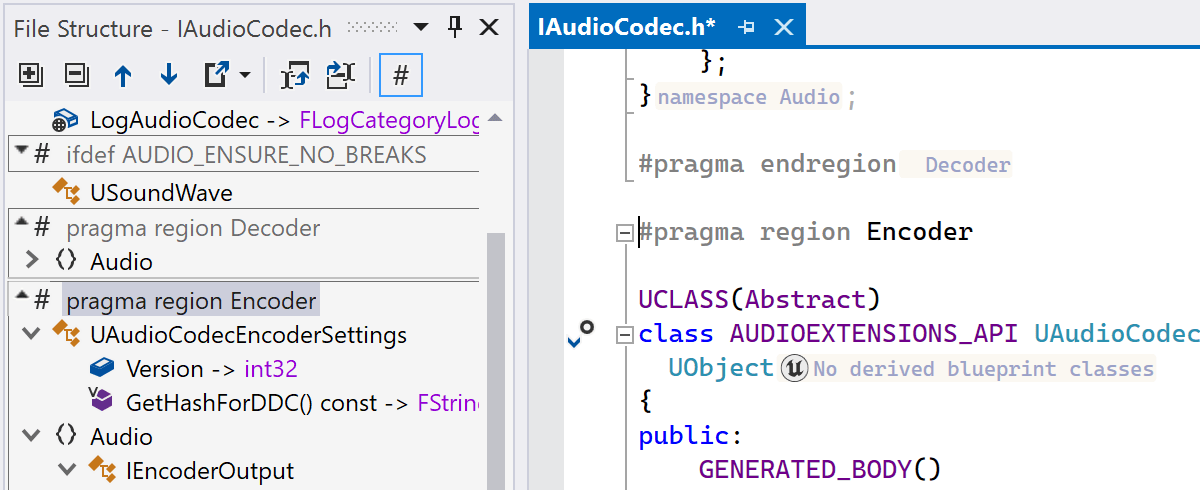
The #pragma region and #pragma endregion directives let you
specify a foldable block of code. Similar to other matching directives, you can now
jump between the two using the Go to Declaration action on a #pragma
directive or a new inlay hint with the region name.
Furthermore, the File Structure window now allows you to conveniently fold regions and navigate to the corresponding code blocks.

In C code, void should be used in the parameter list of a function to indicate that the
function doesn’t take any arguments. ReSharper C++ now
preserves this special void when you invoke the Extract method or
Change signature refactorings, generate a definition for the function, or
create a new function from its usage.

Reference inlay hints now have a separate [>>] text so that you can spot
forwarding references at a glance.
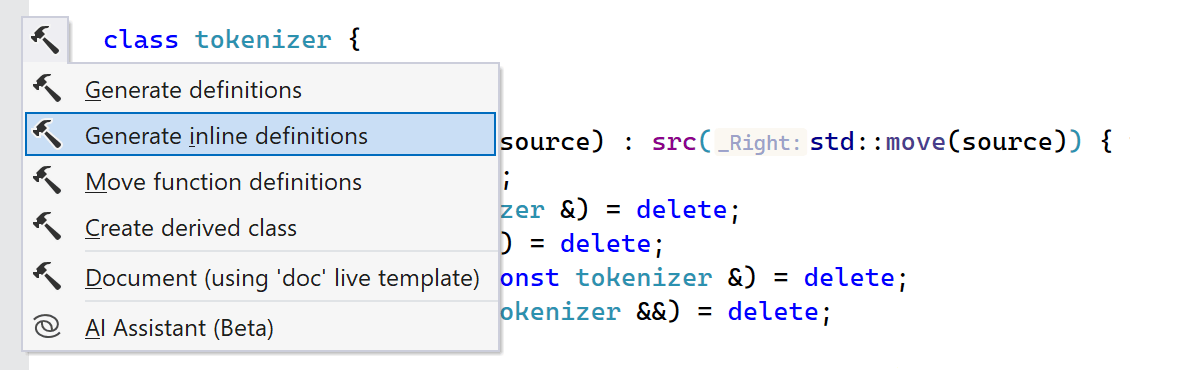
The new Generate inline definitions action lets you quickly generate bodies for several functions simultaneously. Similar to the existing Generate definitions, the new action is available when a class name or several function declarations are selected in the editor.

When you invoke the Introduce variable or Introduce field refactorings on a nested expression, ReSharper C++ now lets you choose the target expression explicitly instead of automatically using the outermost one.
To improve the code navigation experience, symbols that came from macro substitutions are now hidden from Go to and the File Structure window. This is helpful with macros that introduce many auxiliary symbols during their expansion, like declarations of test cases in popular unit-testing frameworks.
Code formatting

ReSharper C++ 2023.3 introduces several new formatting options:
- Break line before
->in trailing return types. - Break line after
->in trailing return types. - Spaces within empty blocks.
- Allow comments after
{.
We’ve also upgraded the bundled clang-format binary to Clang 17 and implemented support
for the InsertNewlineAtEOF clang-format setting both when importing formatter
settings from a .clang-format config and when using clang-format instead of the built-in
formatter.
Take a look at the What's New in ReSharper page to learn about all of the other changes introduced in this release.
ReSharper C++ 2023.2
AI Assistant Limited access
AI Assistant is not bundled with ReSharper and must be installed separately. For the time being, there’s a waiting list for access to the AI Assistant feature.
Learn more about AI Assistant and how to install it via the Toolbox App or dotUltimate installer in our webhelp.
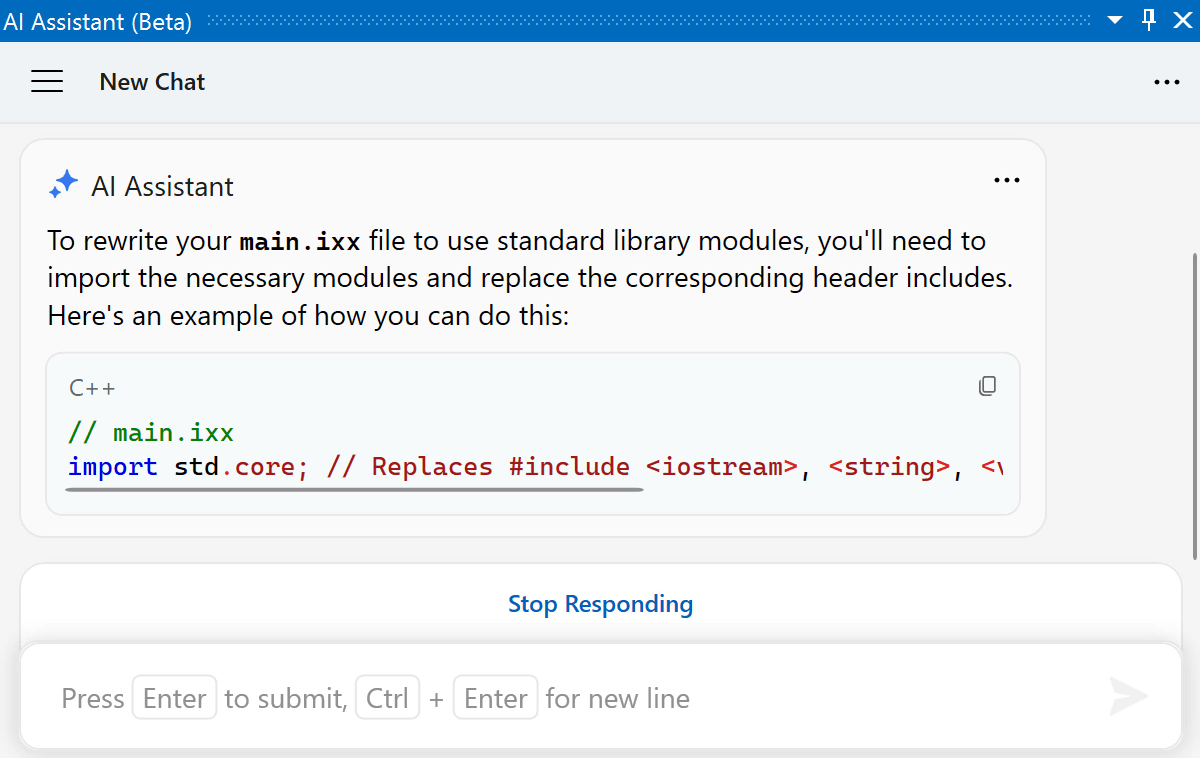
ReSharper C++ 2023.2 brings in the ReSharper AI Assistant – an AI-driven chat specifically designed to answer programming questions and help you with troubleshooting, refactoring, documenting, and other development workflows.
ReSharper’s AI Assistant takes into consideration the language and technologies used in your project. This context awareness tailors its responses right out of the gate, saving you time and effort.
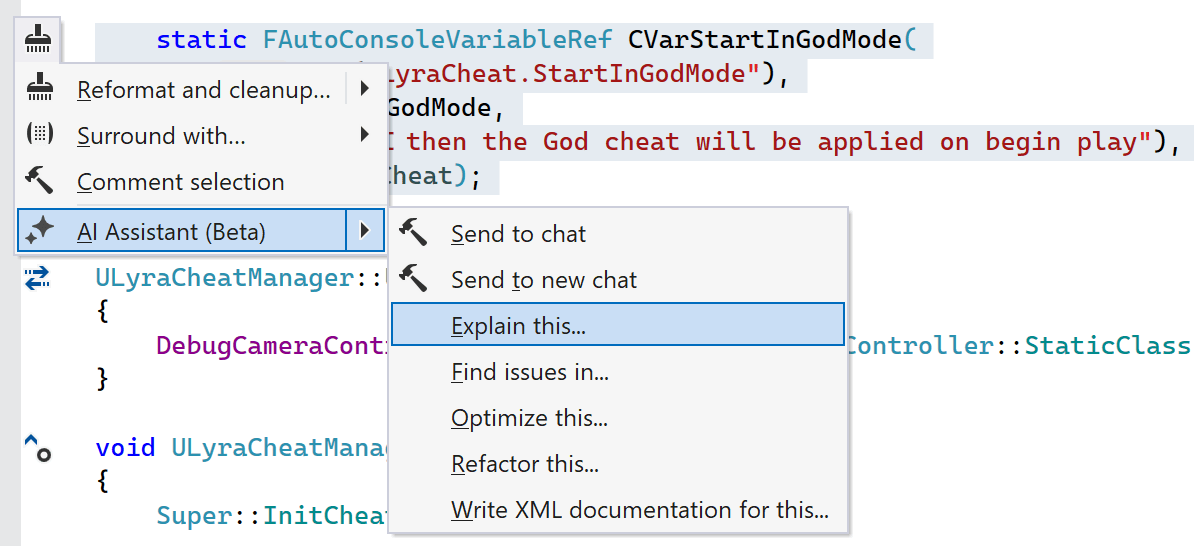
Feel free to include parts of the source code in your queries. ReSharper will detect the code you sent or pasted into the chat and properly format it, while the AI model will explain the logic behind the code and help you refactor, find issues, or document it.
C++23 support
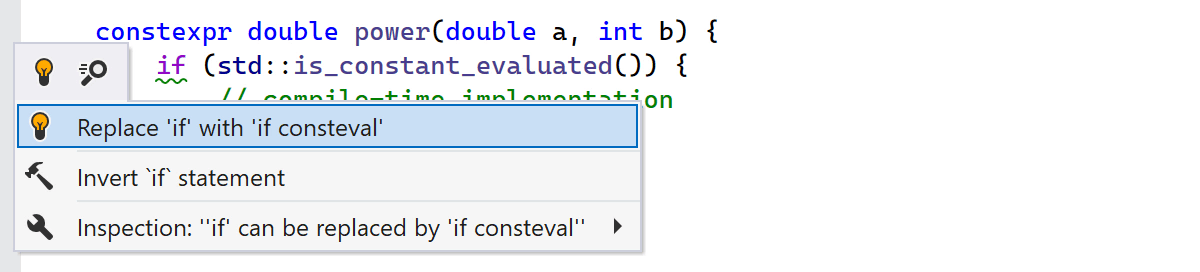
The if consteval statement is a new constant evaluation feature in C++23
that further develops the idea of C++20 consteval and
std::is_constant_evaluated(). If the evaluation of the
if consteval statement occurs during a constant evaluation, then the
following compound statement is executed. Otherwise, the else branch
is executed.
ReSharper C++ introduces support for if consteval
and brings a set of related inspections:
consteval ifis always constant.std::is_constant_evaluatedalways evaluates to a constant.ifcan be replaced byif consteval.
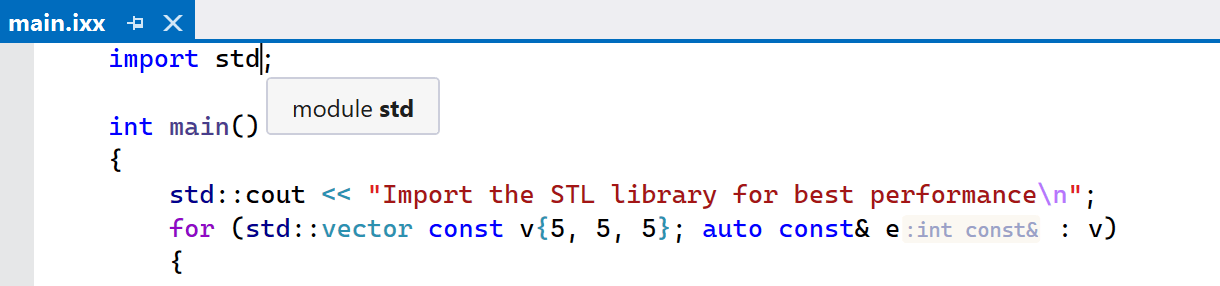
ReSharper C++ now supports the named modules std
and std.compat introduced in the C++23 standard library. If you use Visual
Studio 17.6 or later, you can now use import std or
import std.compat to import the entire standard library instead of using a
precompiled header or including specific standard library headers.

Before C++23, all operators had to be non-static member functions. Call operators,
however, are often used with member-less function objects, and allowing operators to
be static in this case can lead to more efficient code. C++23 allows both
operator() and operator[] to be static.
C++20 support

We’ve been working hard on polishing the C++20 modules support, fixing various corner issues in real-world projects that use modules. When processing modules internally, ReSharper C++ now implements the discarding of declarations that are not decl-reachable, significantly improving performance on modules that include a lot of headers into the global module fragment.
In addition, we’ve implemented several changes to better support modules in CMake
projects. ReSharper C++ now recognizes .cppm
files as module interfaces and includes experimental support for modules located outside
of the project folder.

C++20’s new [[no_unique_address]] attribute indicates that a unique address
is not required for a non-static data member of a class, allowing the compiler to lay out
members of the class in a more efficient way. ReSharper C++
now takes [[no_unique_address]] into account when calculating the size of
an object.

ReSharper C++ 2023.2 also implements the recently accepted
C++20 defect report that allows the initialization of a char or
unsigned char array with a UTF-8 string literal.
Safe Delete refactoring
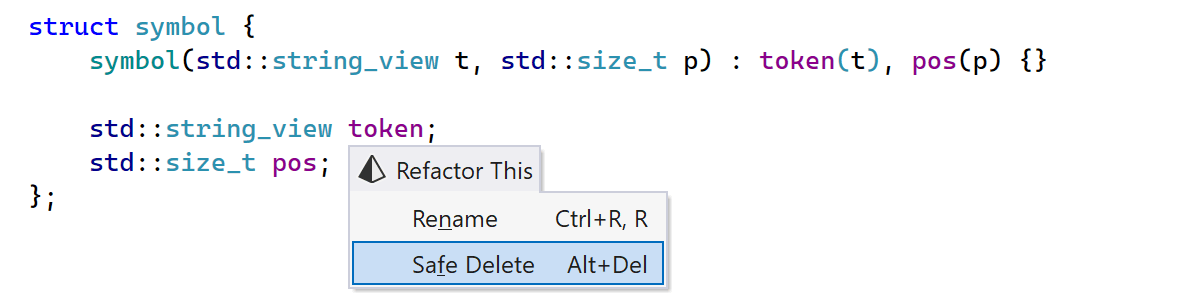
ReSharper C++ introduces the Safe Delete refactoring to let you safely remove symbols from your source code. This refactoring is available for classes, functions, variables, enumerators, namespaces, and even concepts.
To invoke the refactoring, place the caret on the symbol you want to delete and press Alt+Del, or select Safe Delete from the Refactor This menu.
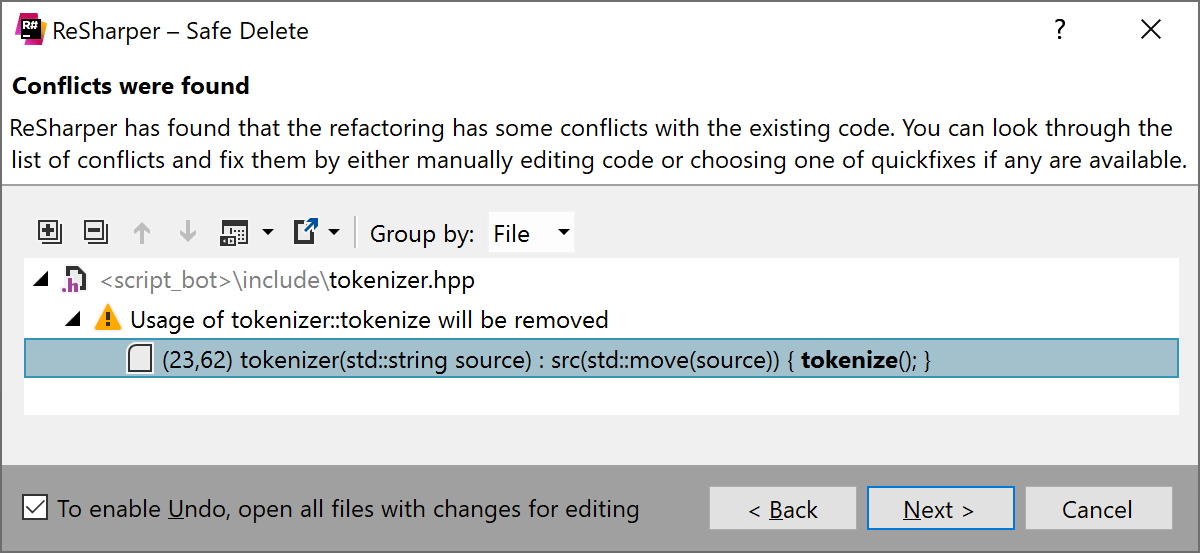
Before deleting a symbol, ReSharper C++ searches for its usages and lets you preview the changes to the source code, so you can be sure that all the removals are intended. If you try to delete a complex entity like a class or a namespace, ReSharper C++ will recursively check the usages for all its members.
Unreal Engine
This release brings performance improvements for indexing Blueprints. The first time you open a project, ReSharper C++ indexes all of your Blueprint assets to power features like Find Usages and show the values of serialized data directly in the text editor.
Previously, ReSharper C++ would index these assets at the same priority as your C++ code, meaning that it took longer before the project was ready for work. ReSharper C++ 2023.2 will index assets in the background after indexing your C++ code without interfering with your work.
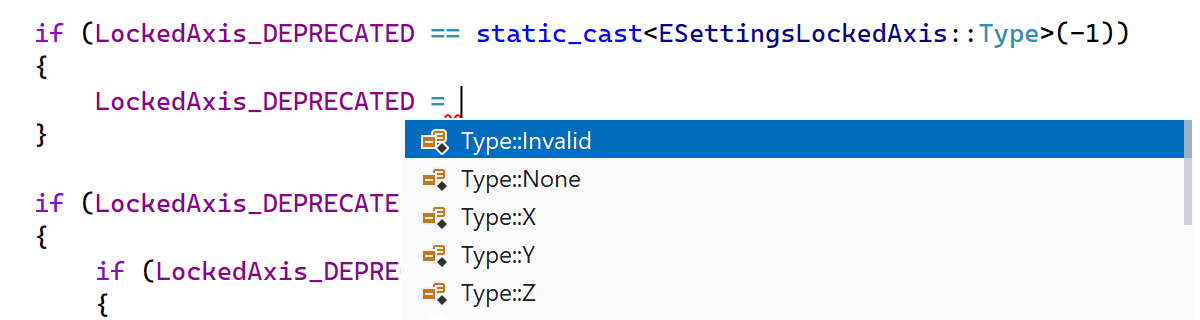
We’ve improved smart completion for wrapper types with standard assignment semantics.
For example, when assigning to a variable of the TEnumAsByte type,
completion will suggest enumerators from the underlying enumeration type.
For Unreal Engine 5.1 projects, we’ve introduced support for the
UE_INLINE_GENERATED_CPP_BY_NAME macro, which lets you inline generated
files into your module to improve compilation time.
Coding assistance

With improved completion for dependent code, you will now get completion items when the
type is restricted by a concept or a trait. ReSharper C++
now considers the standard std::is_same/std::is_base_of type traits, their
_v value-aliases, the corresponding std::same_as/std::derived_from
concepts, and the Unreal Engine TIsSame trait.
For more helpful code completion suggestions, ReSharper C++
now also extracts type and value requirements from requires-clauses,
if constexpr, and SFINAE.
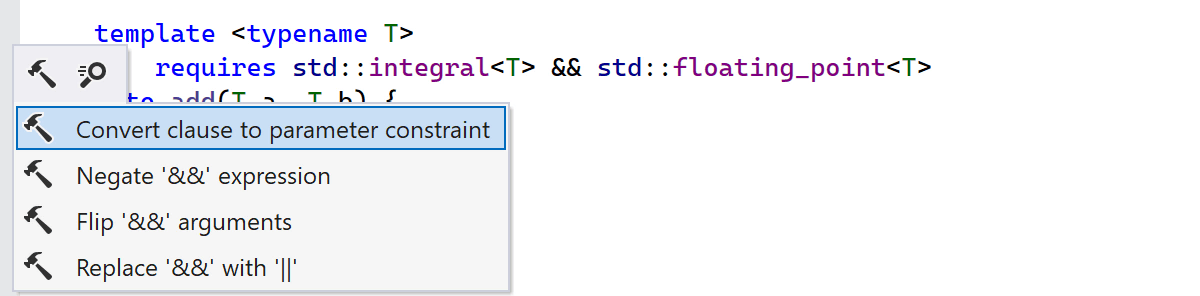
There are two new complementary context actions to help you move a template parameter
constraint to the requires-clause and convert a requires-clause
to a template parameter constraint.

If you have a recursive call, ReSharper C++ will mark it in the gutter, making it more visible.
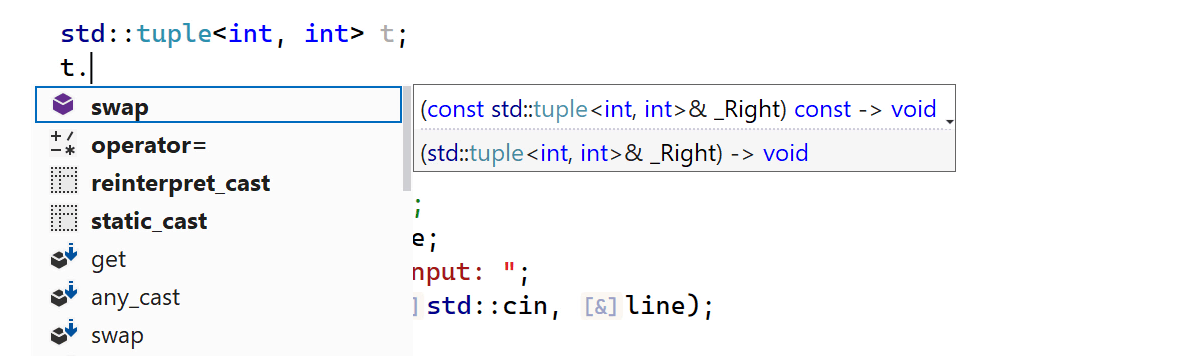
The code completion list now filters out reserved identifiers and suggests them only after
_. This means you no longer have to scroll through the suggestions from
standard libraries unless you need them.
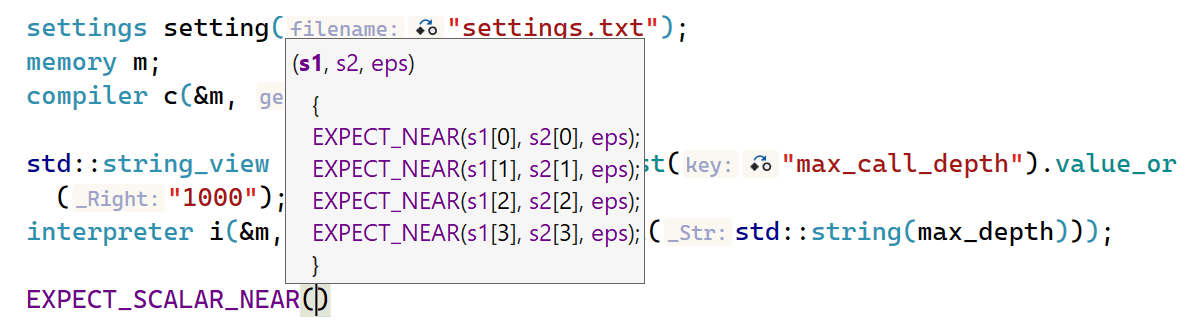
ReSharper C++ 2023.1 introduced proper highlighting and formatting for macro substitution in the Quick Documentation popup and tooltips on hover. In the 2023.2 release, these improvements will also work for macro definitions and Parameter Info in code completion.
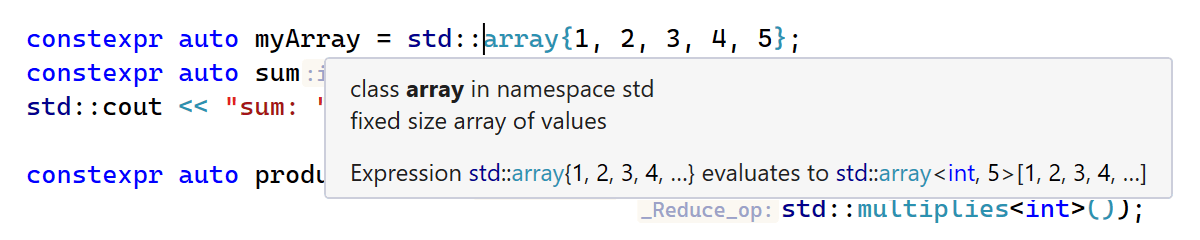
We’ve improved the evaluation engine to support aggregate initialization of
constexpr arrays.

We've improved compatibility with GCC and Clang compilers and libc++/libstdc++ standard
libraries. This includes support for more builtins like __integer_pack,
__is_convertible/__is_nothrow_convertible, and updates for the previously
supported ones.

When you specify the parameter direction with the [in], [in,out],
or [out] attribute of the Doxygen param command, the tooltips now fetch them
from your comment.
Code analysis
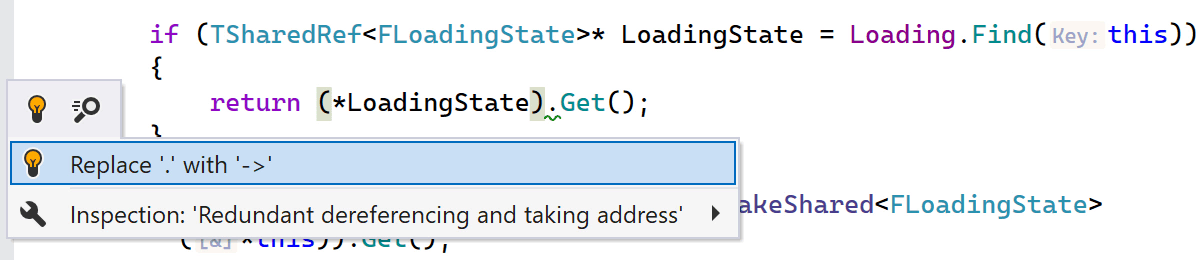
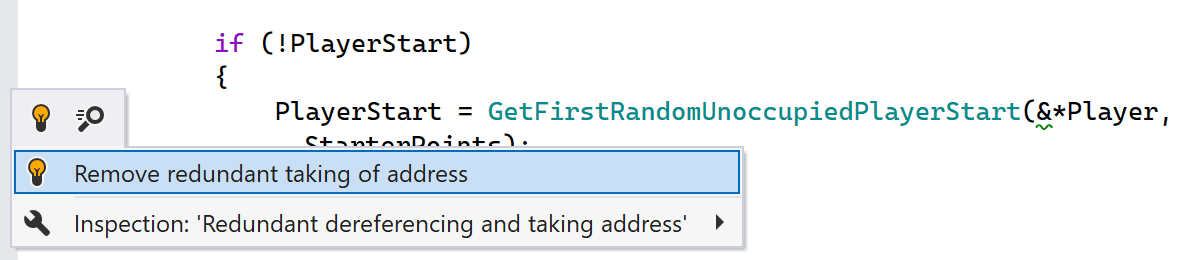
ReSharper C++ 2023.2 adds a new inspection that detects redundant dereferencing and address-of operators. It offers you several quick-fixes to simplify member access and remove redundant operators.

Another new inspection highlights redundant template arguments that match the corresponding default template argument and can be omitted.
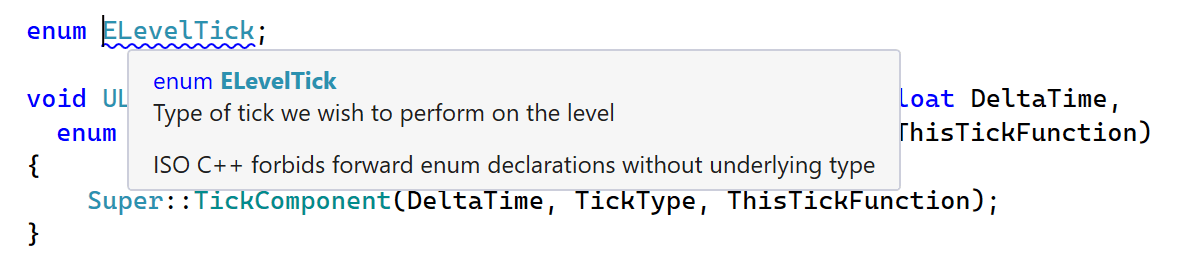
A new compatibility inspection warns you about forward declarations of C-style enums without an underlying type, which are forbidden by the C++ standard but accepted by MSVC, possibly causing non-portable code.

ReSharper C++ now highlights the #error and
#warning diagnostic preprocessor directives according to their severity level.

We’ve also updated the bundled clang-tidy binary to Clang 16, providing new checks and fixes.
MSVC can use either the traditional or the new standard-conforming preprocessor
depending on the value of the /Zc:preprocessor compiler argument.
ReSharper C++ now reads the value of this argument from
the project properties and adjusts the behavior of the built-in preprocessor accordingly.
Navigation

ReSharper C++ 2023.2 brings several improvements to Go to declaration for more consistent and straightforward code navigation without extra steps:
- When invoked on a class name in a constructor call, Go to declaration now navigates to the constructor instead of the containing class.
-
Go to declaration now navigates to the first
typedefor type alias declaration instead of showing the menu with all declarations. - Go to declaration on a module name jumps between interface and implementation units for the same module.
-
Go to declaration on a folder in an
#includepath opens the folder.
Additionally, Type of symbol is now available on non-declarator symbols. The way it works there is similar to Go to declaration.
Formatting and typing assist

When generating documentation comments, ReSharper C++
will now adjust the documentation template according to the comment style from the
editor. For /**, typing assistance will generate the comment in the
/** */ style, and for ///, the comment will be in the
/// style.
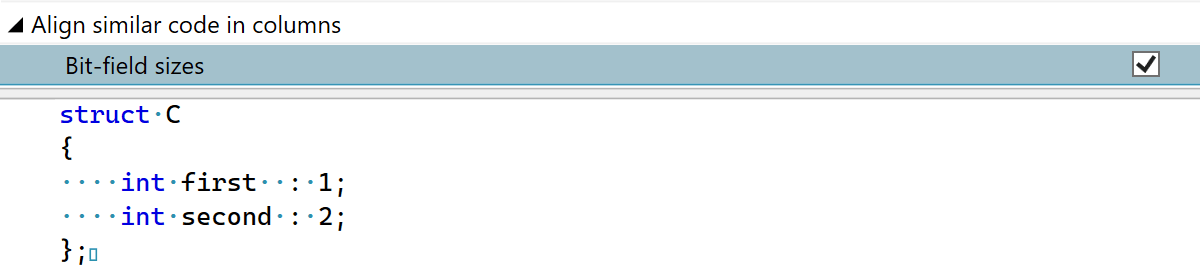
This release brings several improvements to the formatting of bit-field members. The options to align initializers and declaration names in columns now support bit-fields. There are also two new formatting settings for spaces before and after the colon in bit-field declarations and for alignment of bit-field sizes in columns.

A new typing assist option lets you turn off the generation of documentation comments to avoid conflicts with Visual Studio's built-in generator (ReSharper | Options | Environment | Editor | Behavior | C++, C, HLSL | Generate documentation comments).
We've also updated the bundled clang-format binary and fixed the clang-format engine to prevent it from removing the newline at the end of a file.
Take a look at What's New in ReSharper to learn about the other changes introduced in this release. For example, ReSharper introduces the predictive debugger, which foresees all possible states triggered by executing a program without having to actually execute it.