Code Generation in C++
ReSharper provides a variety of ways to generate boilerplate code. For example, you can use undeclared code symbols and automatically generate these symbols based on usages, generate type members, and more.
Member generation options for the current type are available with Alt+Insert (). These and many other code generation actions are also available as context actions with Alt+Enter.
Generate code from usage
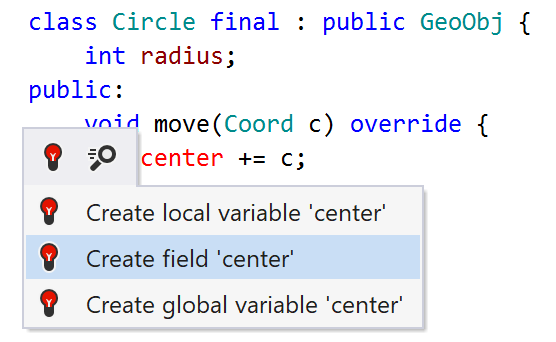
ReSharper lets you use code symbols (methods, variables, fields, and so on) before you declare them. When ReSharper detects an undeclared symbol, it suggests one or more quick-fixesAlt+Enter for generating a declaration based on the usage, and then smartly adjust the declaration according to the usage context:
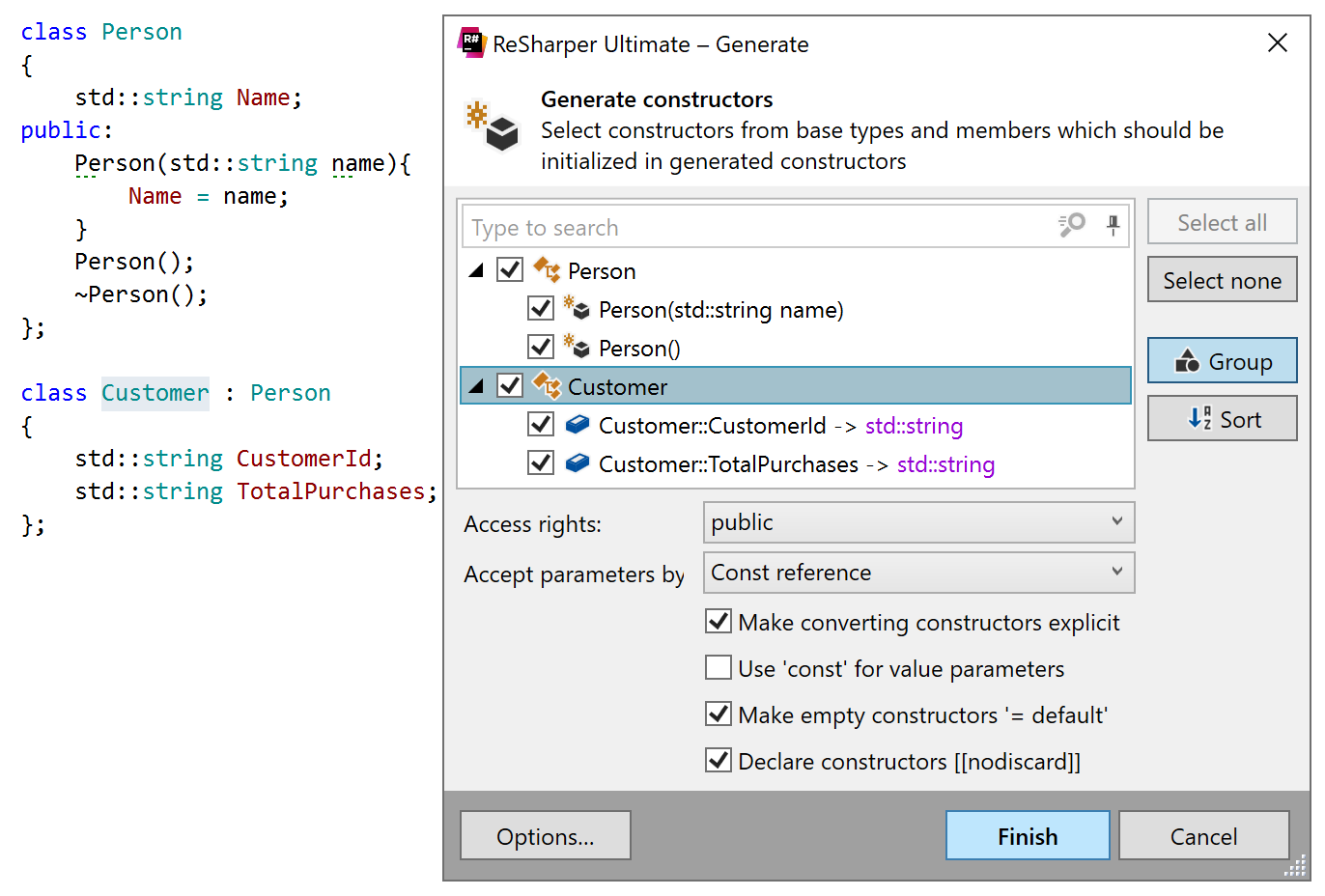
Generate constructors
The constructor generation wizard creates a non-default constructor that takes parameters for selected fields .
All generated constructors follow the same pattern where:
Each field included in the constructor is initialized with a parameter.
The name of the parameter is derived from the name of the corresponding field .
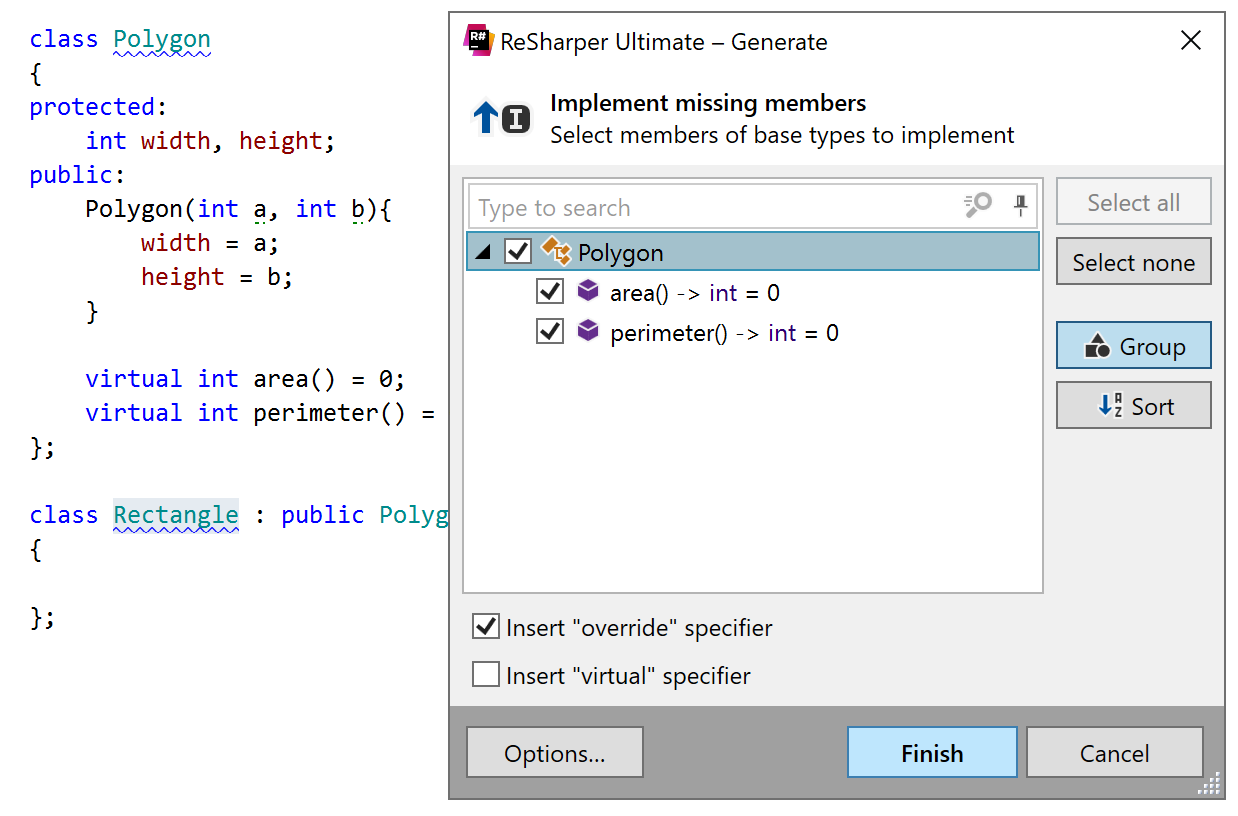
Generate missing members
This generation action creates overrides for pure virtual functions defined in the base abstract class.
Generate overriding members
This generation action creates overrides of virtual functions in a derived class:
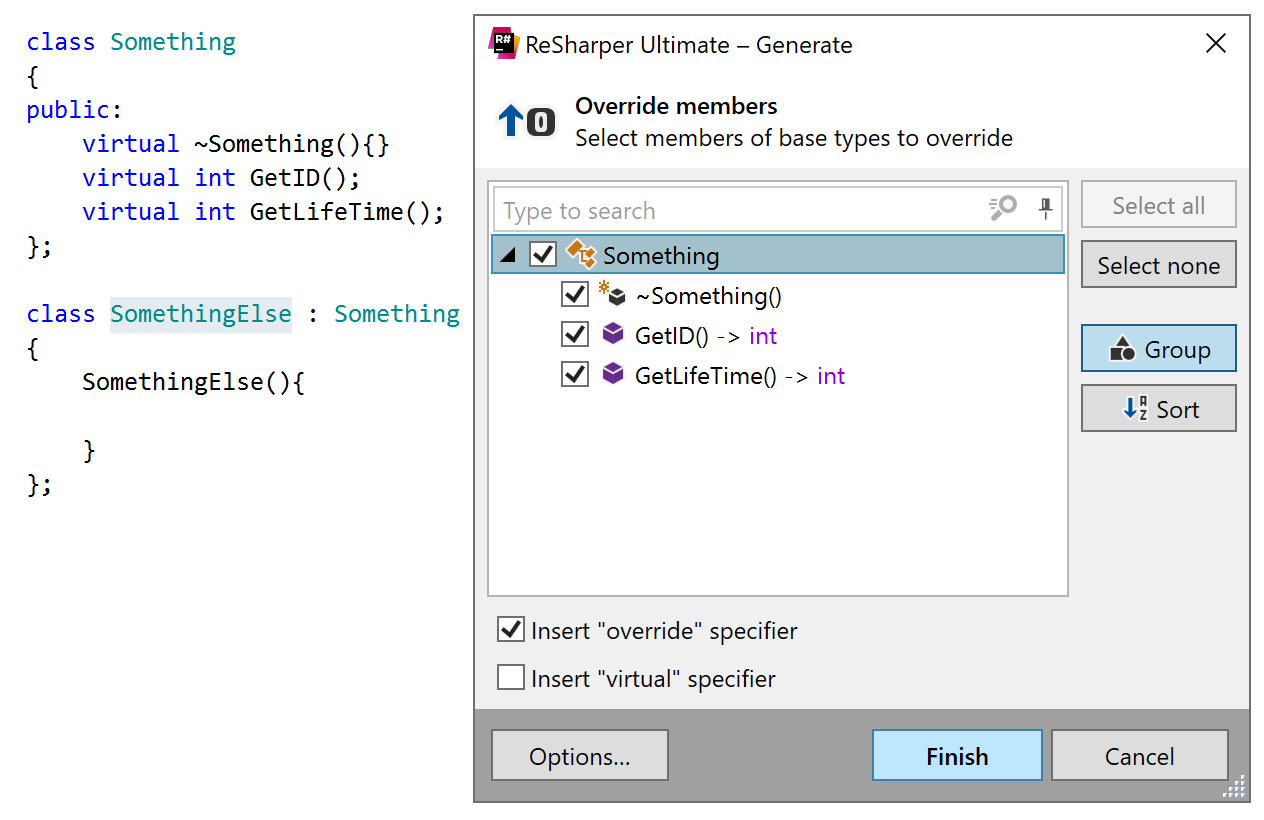
In the Override members dialog, you will be able to choose the desired functions and configure the following preferences for the generated overrides:
Insert 'override' specifier — you can clear this checkbox if you want to generate a function that hides the corresponding function in the base class.
Insert 'virtual' specifier allows you to make the generated methods virtual.
Generate definitions
This generation action lets you quickly create definition stubs for all member functions that are declared in the class but have no definitions.
Copy and move operations
This generation action creates copy constructors and operator= functions that define how objects of the current class are copied and moved.
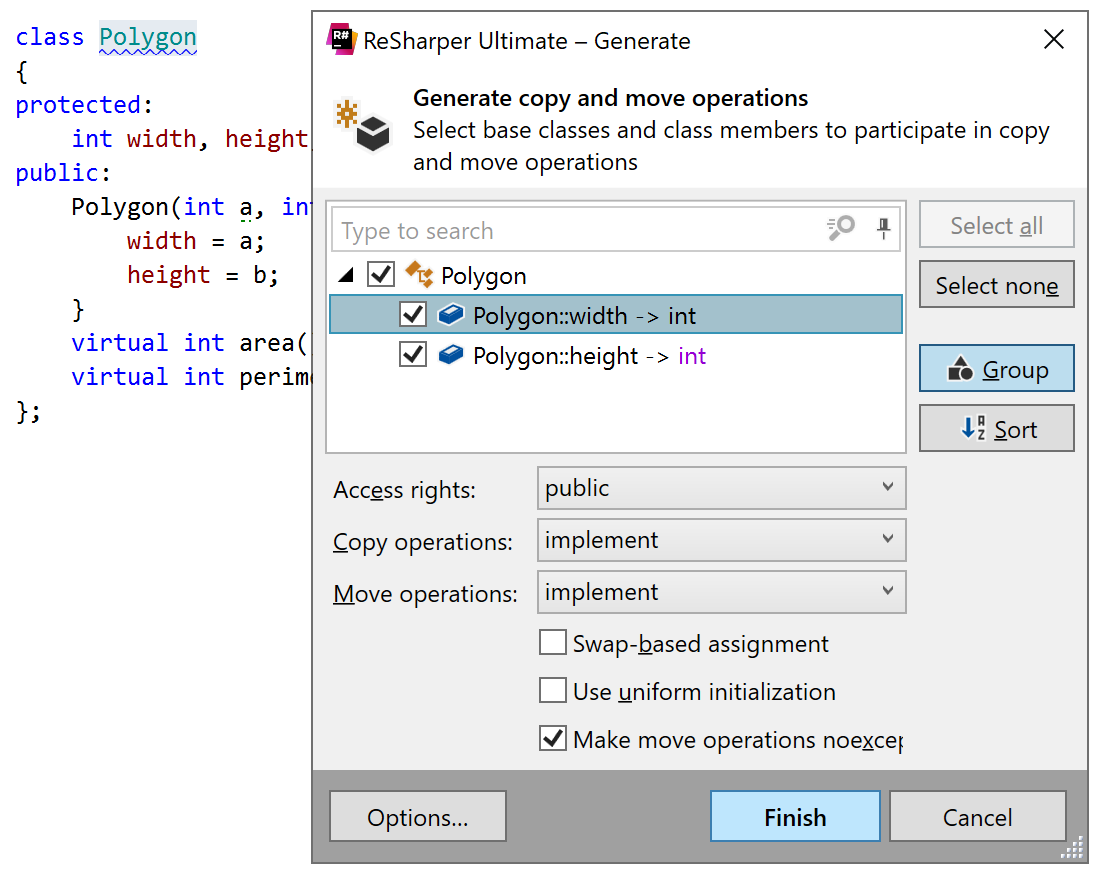
In the Generate copy and move operations dialog, you will be able to choose which base classes and class members should be taken into account when copying or moving the class objects and configure the following preferences for the generated functions:
Access rights to allows you choose
public,protectedorprivateaccess modifiers.Copy/Move operations — these selectors allows you to choose how the operations are created. By default, the implementations of the operations are generated. However, you can generate them as Explicitly defaulted and deleted functions, only generate declarations, or skip one or another operation.
Swap-based assignment — select this checkbox to use the
swapfunction in the implementation of theoperator=. For example,Rectangle& operator=(Rectangle other) { using std::swap; swap(*this, other); return *this; }
Generate getters and setters
With ReSharper, you can quickly generate getter and setter functions for a class based on the existing fields:
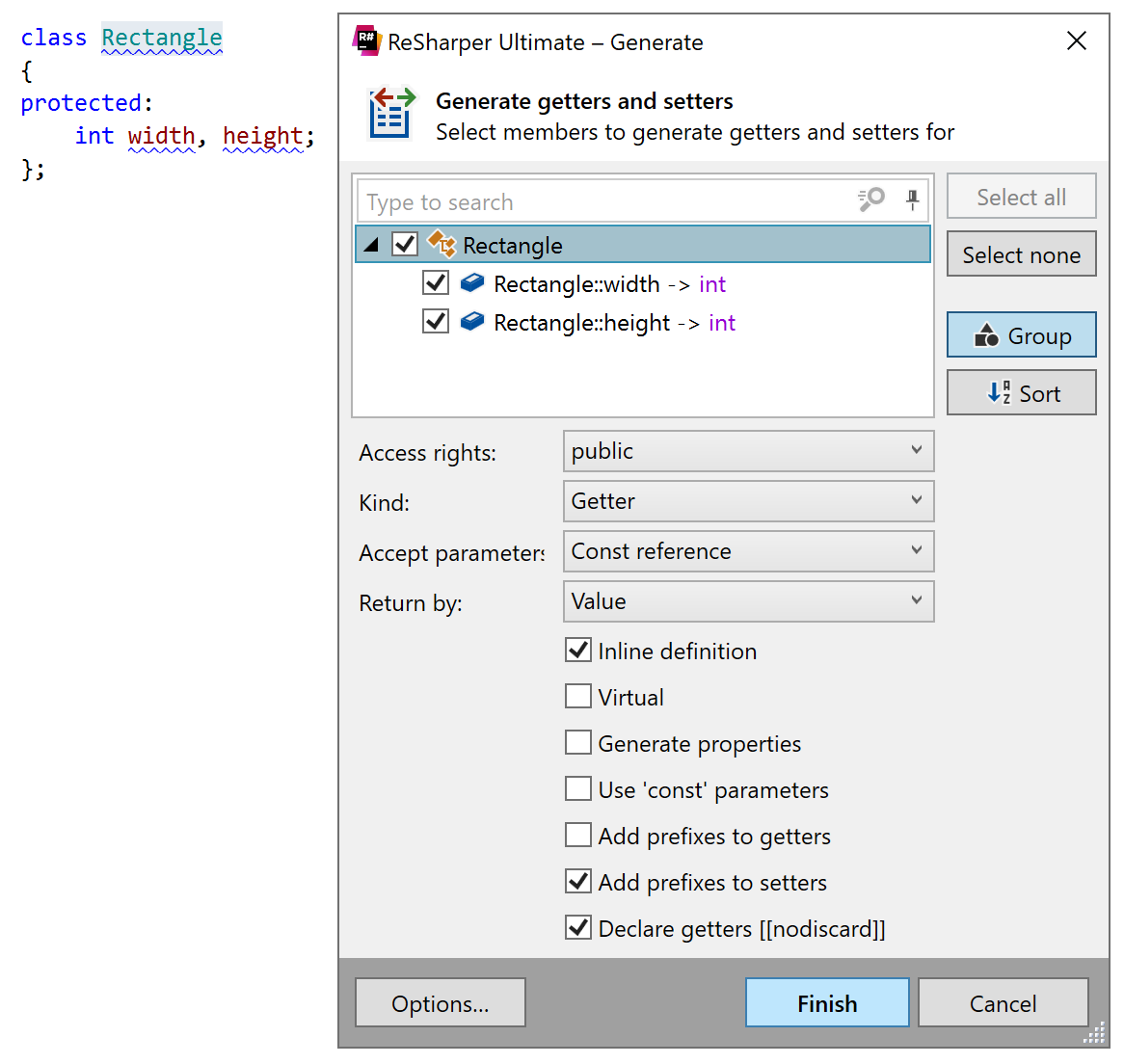
In the Generate getters and setters dialog, you will be able to choose the desired fields and configure the following preferences for the generated functions:
Access rights to allows you choose
public,protectedorprivateaccess modifiers.Kind allows you to choose whether getters, setters, or both should be generated.
Accept parameters by allows you to choose how parameters should be passed to the generated setters: by const reference or by value.
Return by allows you to choose how the generated getters should return fields: by value, reference, or const reference.
Generate equality operators
This code generation command lets you generate operator== and operator== functions that will use selected fields to compare objects of the current class.
Generate relational operators
This code generation command helps you generate operator<, operator>, operator<=, and operator>= functions that will use selected fields to compare objects of the current class.
Generate stream operations
This code generation command lets you generate the insertion operator operator<< that will use selected fields to define how to generate stream output for objects of the current class. For example:
If necessary, you can use wostream instead of ostream. To do so, select Use wide-character stream in the Generate stream operations dialog.
Another option for generating stream output is to generate stubs for Boost Serialization functions: save() and load() or serialize(). To do so, select the desired option in the Operation type selector in the Generate stream operations dialog.
Generate hash function
This code generation command lets you generate a hash function for your class. You can select one of the two hashing algorithms:
boost::hash_combine, for example:
#include <boost/functional/hash.hpp> ... friend std::size_t hash_value(const Rectangle& obj) { std::size_t seed = 0x315E4139; boost::hash_combine(seed, obj.width); boost::hash_combine(seed, obj.height); return seed; }shift and xor, for example:
friend std::size_t hash_value(const Rectangle& obj) { std::size_t seed = 0x315E4139; seed ^= (seed << 6) + (seed >> 2) + 0x3449770D + static_cast<std::size_t>(obj.width); seed ^= (seed << 6) + (seed >> 2) + 0x49751560 + static_cast<std::size_t>(obj.height); return seed; }
Generate swap function
This code generation command lets you generate the swap function that will use selected fields to swap objects of the current class. For example:
Generate Google Mock Methods
This code generation action automatically creates mocking methods MOCK_METHOD() when you are creating mock classes with Google Mock framework.
It becomes available for derived classes if the Google Mock header file is included.
In your mock class, you do not have to manually write methods that you are mocking. Instead, you can invoke the Generate GMock methods action (which is also available as a context action with Alt+Enter).
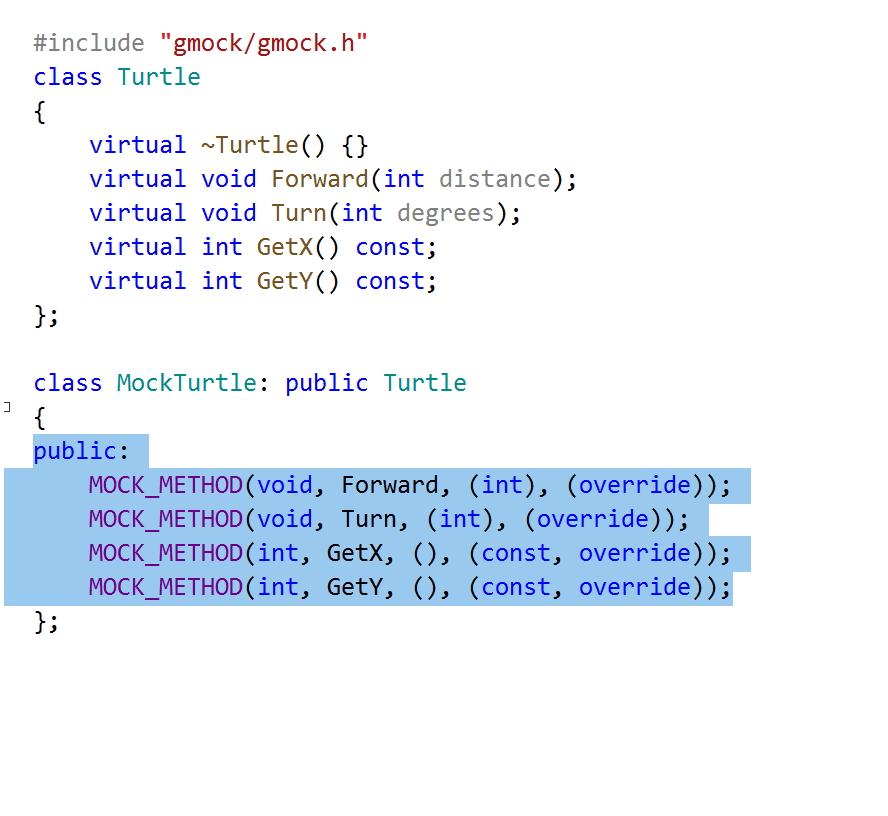
By default, all base class methods are selected, if you do not want to generate mock methods for some of them, you can clear the corresponding check-boxes.