Run/debug configurations
CLion uses run/debug configurations to run, debug, and test your code. Each configuration is a named set of startup properties that define what to execute and what parameters and environment should be used.
There are two types of run/debug configurations:
Temporary — created every time you run/debug a test, test suite, fixture, or a
main()entry use the gutter icons/
.
Permanent — created explicitly from a template or by saving a temporary configuration. Permanent configurations remain as part of your project until you remove them.
Whenever you run, debug, or test your code, CLion either uses an existing permanent run/debug configuration or creates a new temporary one.
Permanent configurations have opaque icons while the icons of temporary configurations are semi-transparent. The red cross over the configuration icon indicates an error in configuration settings.
The maximum number of temporary configurations is 5. The older ones are automatically deleted when new ones are added. If necessary, you can increase this limit in .
Create permanent run/debug configurations
CLion provides the following ways to create a permanent run/debug configuration:
Create from a template or copy an existing configuration.
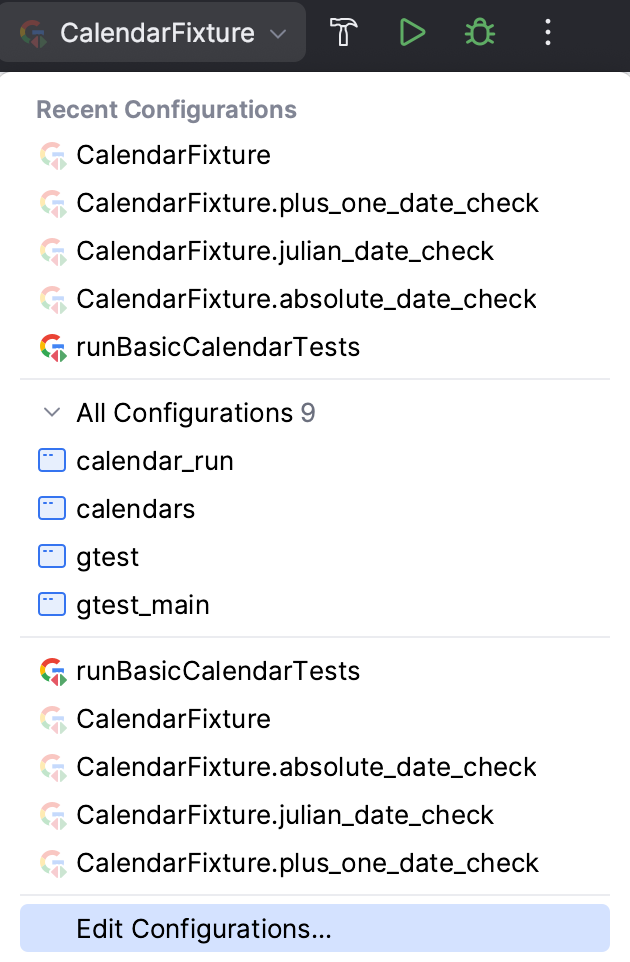
Save a temporary configuration as permanent
Select a temporary configuration in the run/debug configuration switcher, click
and select Save Configuration.
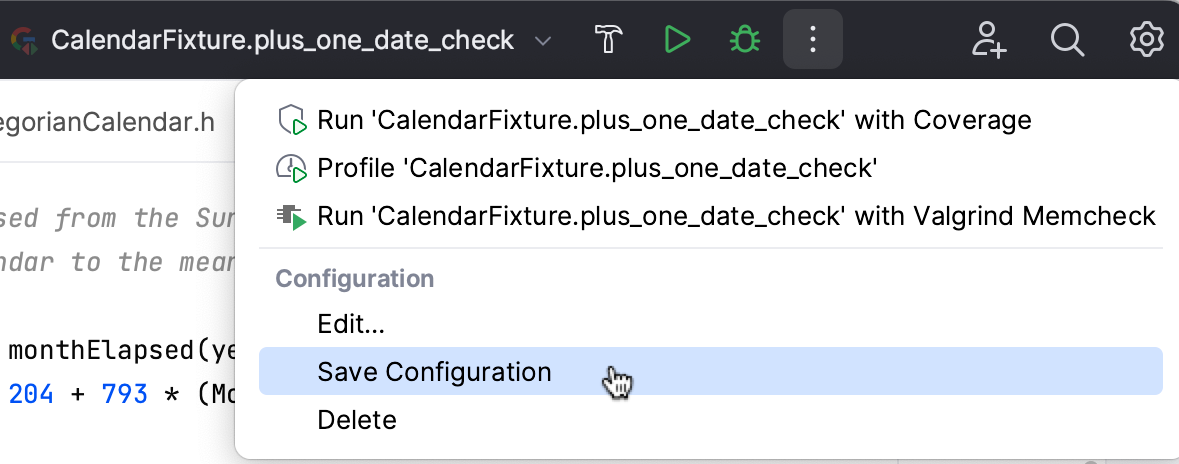
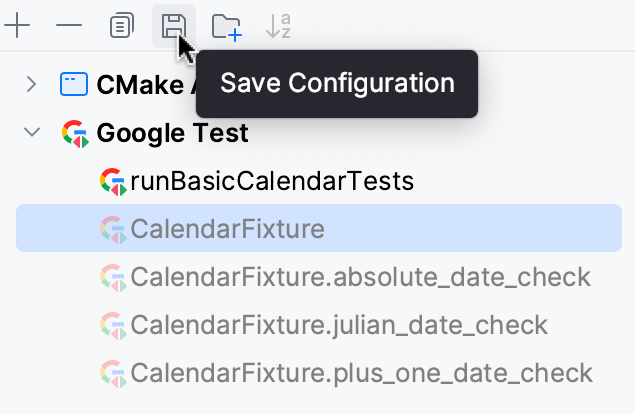
Alternatively, select a temporary configuration in the Run/debug configurations dialog and click
on the toolbar.
CLion provides run/debug configuration templates for different languages, tools, and frameworks. The list of available templates varies depending on the installed and enabled plugins.
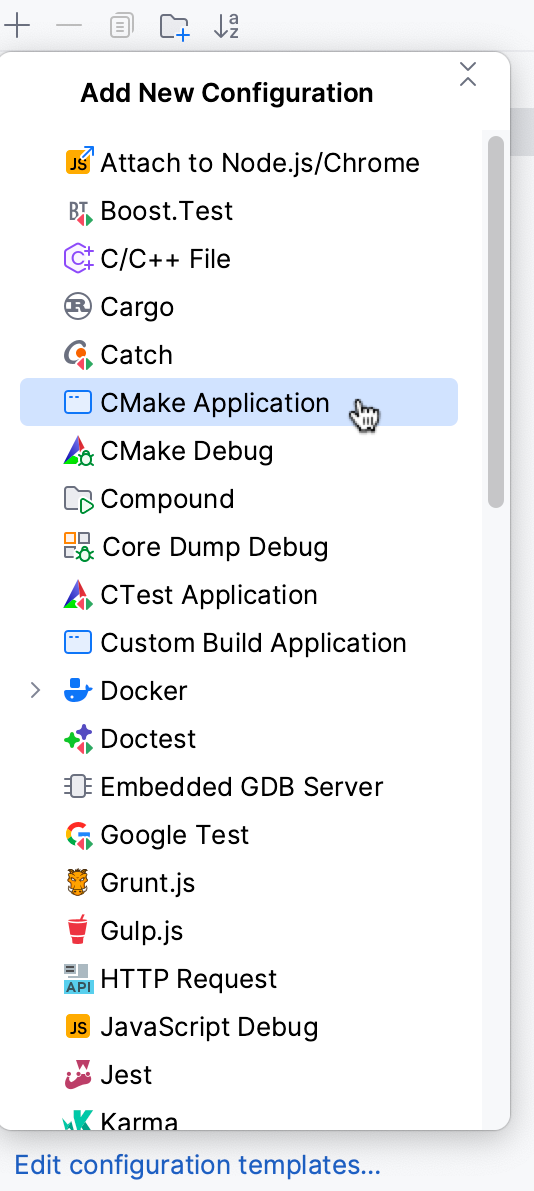
Create a run/debug configuration from a template
Go to . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click
on the toolbar or press Alt+Insert. The list shows the run/debug configuration templates.
Specify the run/debug configuration name in the Name field. This name will be used to identify the run/debug configuration in lists and menus.
Select Allow multiple instances if you want to allow multiple instances of the configuration to run at the same time. If this option is disabled, attempting to re-run the configuration will terminate the active session.
Depending on the chosen template, fill up the configuration settings. For example, CMake Application, Custom Build Application, Gradle / Gradle Native Application.
In the Before launch section, define whether you want to perform any specific actions before launching the application, for example, launch an external tool or another build configuration before run. To skip the build stage, remove Build from the Before launch list .
You can either run the configuration right away or save the configuration to run it later.
To save the run configuration for later, click OK.
To run the configuration right away, click Run.
Before launch
In this area, you can specify tasks to be performed before starting the selected run/debug configuration. The tasks are performed in the order they appear in the list.
Item | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
Alt+Insert | Click this icon to add one of the following available tasks:
| |
Alt+Delete | Click this icon to remove the selected task from the list. | |
Enter | Click this icon to edit the selected task. Make the necessary changes in the dialog that opens. | |
Alt+Up Alt+Down | Click these icons to move the selected task one line up or down in the list. The tasks are performed in the order that they appear in the list. | |
Show this page | Select this checkbox to show the run/debug configuration settings prior to actually starting the run/debug configuration. | |
Activate tool window | By default this checkbox is selected and the Run or the Debug tool window opens when you start the run/debug configuration. Otherwise, if the checkbox is cleared, the tool window is hidden. However, when the configuration is running, you can open the corresponding tool window for it yourself by pressing Alt+4 or Alt+5. |
Share run/debug configurations
You might want to share your run/debug configurations so that your teammates could run the application using the same configuration or enable them to remotely attach to the process you are running.
CLion provides a mechanism to store your run/debug configurations as project files and share them through VCS. The same mechanism can also be used when you want to send your configuration as a file to someone else, create a local backup of your run/debug configurations, or import them from a file.
Go to . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
Select the run/debug configuration you want to share, enable the Store as project file option, and specify the location where the configuration file will be stored.
You can configure any location unless compatibility with CLion 2019.3 and earlier is required. For compatibility with these versions, store the file in the suggested location.
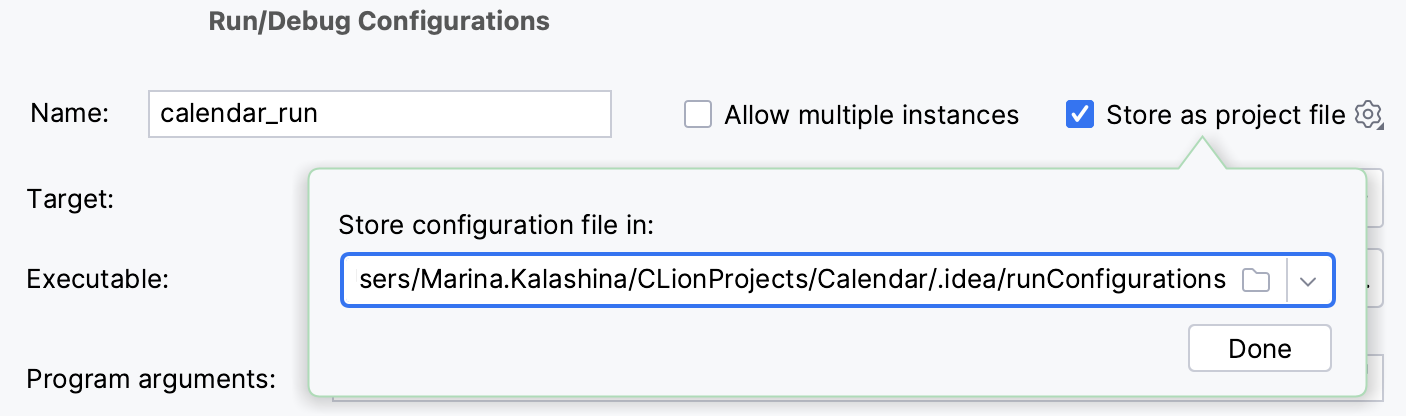
(Optional) If the .idea directory is added to VCS ignored files, the .idea/runConfigurations subfolder will be ignored, too. If the project uses Git, you can share .idea/runConfigurations and leave .idea ignored by modifying .gitignore as follows:
/.idea/* !/.idea/runConfigurations
Run/debug configuration templates
All run/debug configurations are based on templates, which implement the startup logic, define the list of parameters and their default values. The list of available templates is predefined in the installation and can only be extended via plugins. However, you can edit default parameter values in each template to facilitate the setup of new run/debug configurations.
Configure the default values for a template
Go to . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
In the left-hand pane of the run/debug configuration dialog, click Edit configuration templates.
In the Run/Debug Configuration Templates dialog that opens, select a configuration type.
Specify the desired default parameters and click OK to save the template.
Environment variables and program arguments
You can influence the runtime behavior of your app by adding program arguments and environment variables to suitable run/debug configurations.
Go to . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog that opens, select a configuration where you want to pass the arguments and add the environment variables.
Type the arguments in the Program arguments field. The arguments should be separated with spaces or new lines.
Click
to expand the text field, so you can view and edit the arguments as a list.
In the Environment variables field, type the variable name and value:
<name>=<value>. If you add several variables, they should be separated with semicolons.Alternatively, click
and add the variable name and value to the User environment variables list.
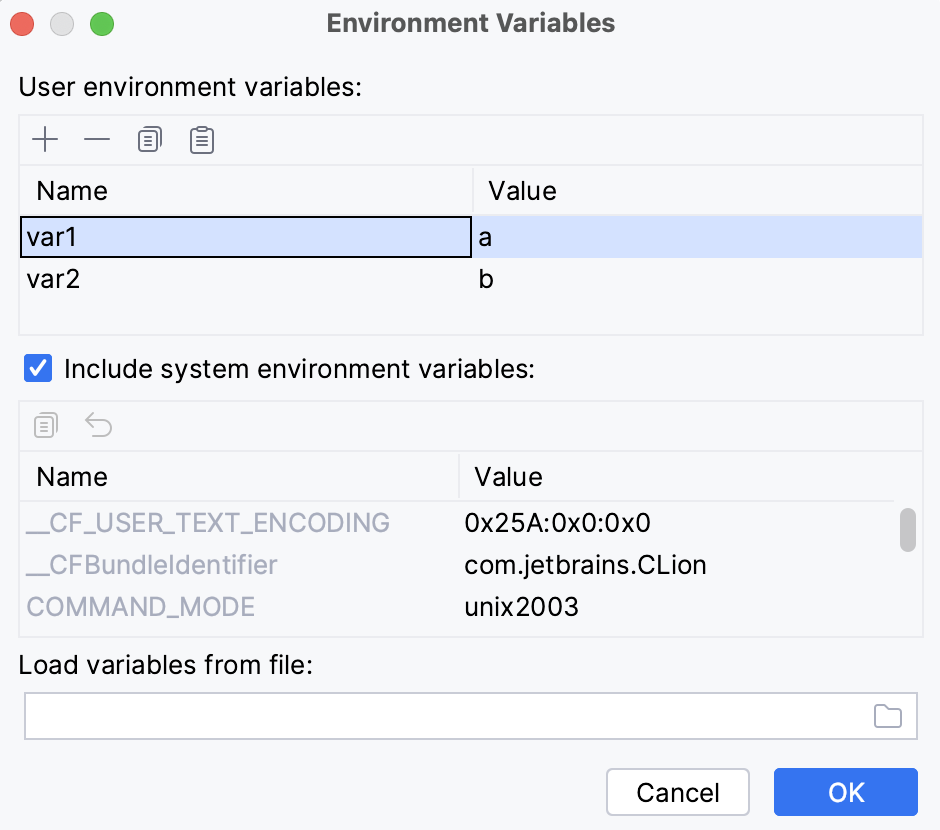
In the dialog that opens, you can also see the list of available system environment variables. Clear the System environment variables checkbox if you don't want to use the system environment variables for the selected configuration.
You can reference existing variables, including the parent environment variables, using the
$VAR$syntax. Note that such references are case-sensitive: for example,PATH=xxx:$PATH$for Linux/macOS andPath=xxx;$Path$for Windows. Referencing existing variables is currently not available for remote toolchains (CPP-15693).Use the Load variables from file field to point CLion to a script that configures the environment. This option is available for CMake, Makefile, Gradle Native, Custom Build, and test configurations (Boost.Test, Catch, Google Test, Doctest, CTest).
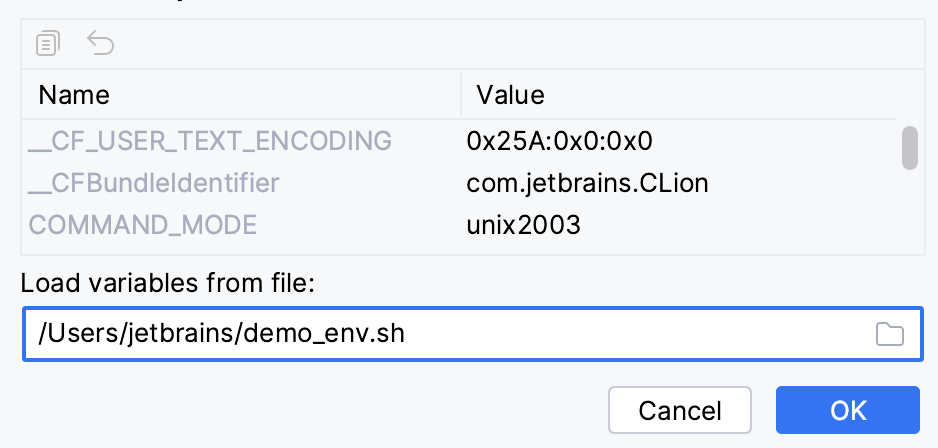
Use the following syntax for setting variables in your script:
set VAR=valueexport VAR=valueNote that the environment created by a script is applied only to a single launch of the corresponding configuration and takes precedence over custom values.
The specified script will be run after all the Before launch steps.
Run/debug configuration folders
When there are many run/debug configurations of the same type, you can group them in folders for easier access.
Create a folder for run/debug configurations
Go to . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, select a configuration type and click
on the toolbar. A new empty folder for the selected type is created.
Specify the folder name in the text field to the right or accept the default name.
Select the desired run/debug configurations and move them under the target folder.
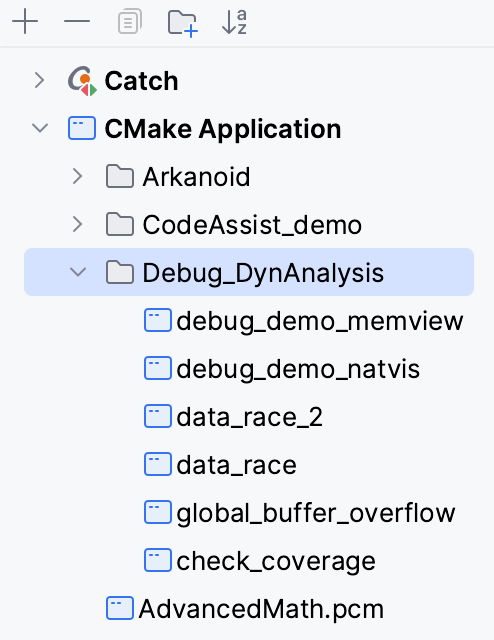
Apply the changes. If a folder is empty, it will not be saved.
When you no longer need a folder, you can delete it Delete. The run/debug configurations grouped under this folder will be moved under the root of the corresponding run/debug configuration type.