Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift is a petabyte-scale cloud data warehouse that allows users to analyze structured and semi-structured data using standard SQL and popular analytics tools.
With the native connector, Datalore allows you to access data in Amazon Redshift instances from your notebook environment. You can query datasets directly using SQL, Python, Scala, Kotlin, or R without the need for intermediate data exports.
- Before you begin
Make sure your database instance is configured to accept incoming connections from the following IP address:
63.33.83.29
Step 1. Create a connection
You can create an Amazon Redshift connection either in your notebook or workspace.
In the sidebar on the Home page, select the workspace where you want to create an Amazon Redshift connection.
In the expanded list of workspace resources, select
Data and switch to the Databases tab.
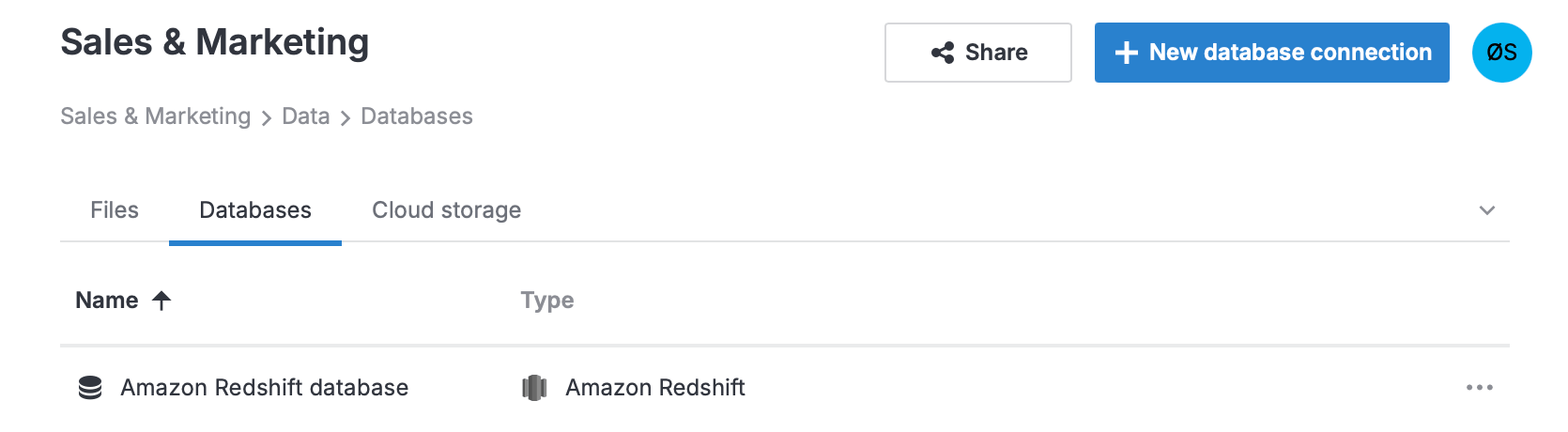
Click
New database connection at the top right.
In the dialog, select
Amazon Redshift.
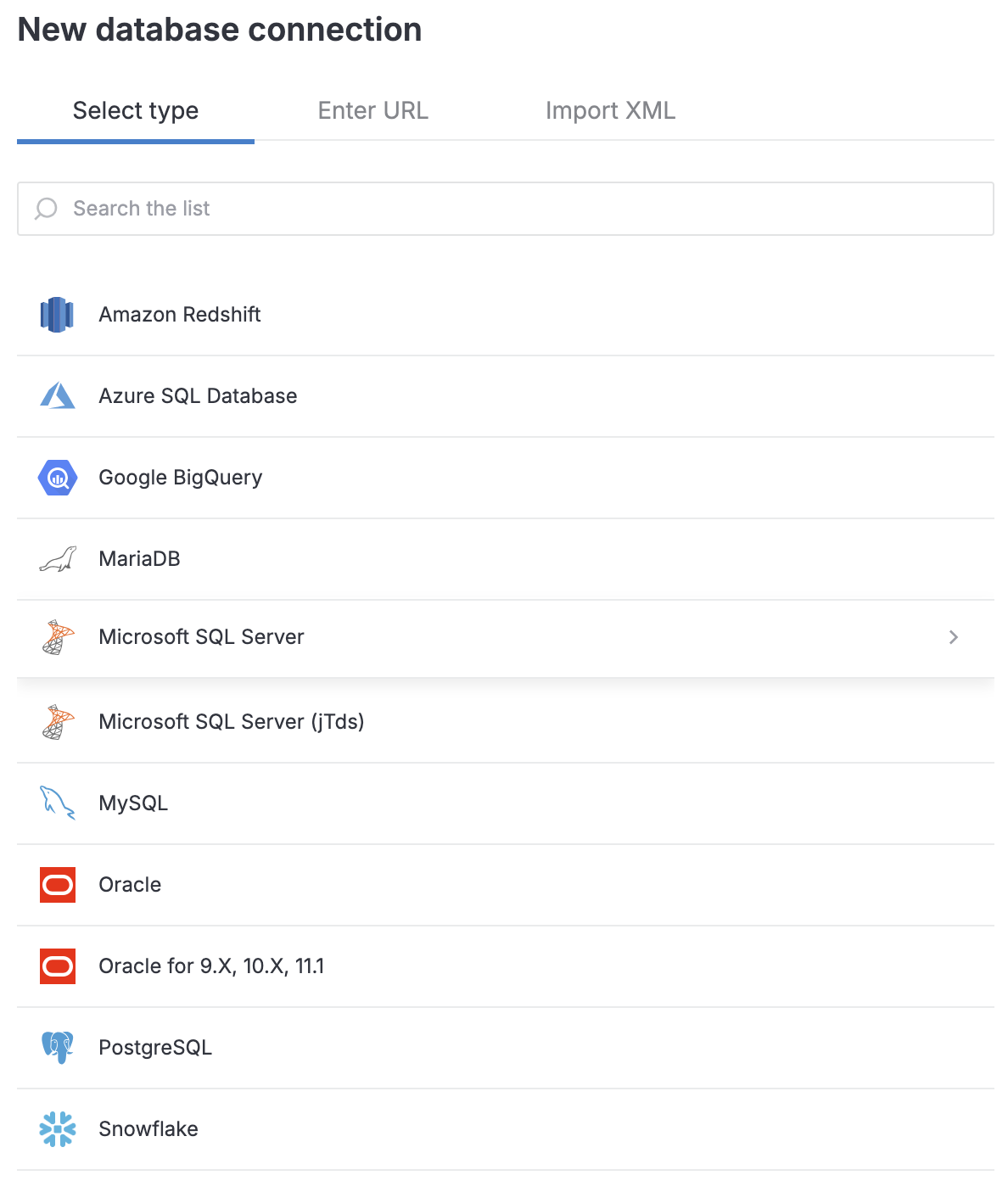
Open the Attached data tool from the left-hand sidebar.
Switch to the Databases tab. You will see the list of all database connections available from the respective workspace.
Click
New database.
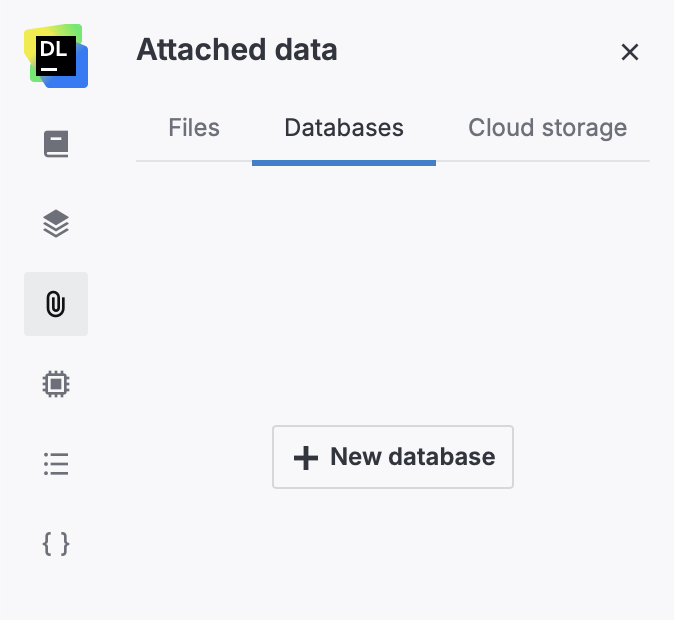
In the New database connection dialog, select Amazon Redshift.

Step 2. Configure the connection
On the General tab, select the connection type.
Default: to connect by specifying the Host, Port, and Database.
IAM cluster/region: to connect by using Database, Region, and Cluster.
URL only: to connect by providing the URL of a pre-built connection.
Proceed based on the selected connection type:
In the Host field, type your server address.
In the Port field, type the port of Amazon Redshift. The default port is 5439.
From the Authentication list, select the authentication method that you want to use to authenticate the connection. The following options are available:
User & Password: by using your login and password.
AWS Vault AppRole: by using AWS Vault for your AWS credentials. Visit this page for more details.
AWS profile: by using a named profile. A named profile is a collection of settings and credentials that you can use for authentication. Named profiles are stored in CREDENTIALS files. Default directories for these files are ~/.aws/credentials (Linux and macOS) and %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials (Windows).
No auth: without authentication.
In the User and Password, provide your credentials if required by the selected authentication type.
In the Database field, enter the name of the database to which you want to connect.
From the Authentication list, select the authentication method that you want to use to authenticate the connection. The following options are available:
User & Password: by using your login and password.
AWS Vault AppRole :by using AWS Vault for your AWS credentials. Visit this page for more details.
AWS profile: by using a named profile. A named profile is a collection of settings and credentials that you can use for authentication. Named profiles are stored in CREDENTIALS files. Default directories for these files are ~/.aws/credentials (Linux and macOS) and %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials (Windows).
No auth: without authentication.
In the User and Password, provide your credentials if required by the selected authentication type.
In the Database field, enter the name of the database to which you want to connect.
In the Region field, enter the AWS Region of the database that you are connecting to.
In the Cluster field, enter the name of Amazon Redshift cluster that contains your database.
From the Authentication list, select the authentication method that you want to use to authenticate the connection. The following options are available:
User & Password: by using your login and password.
AWS Vault AppRole :by using AWS Vault for your AWS credentials. Visit this page for more details.
AWS profile: by using a named profile. A named profile is a collection of settings and credentials that you can use for authentication. Named profiles are stored in CREDENTIALS files. Default directories for these files are ~/.aws/credentials (Linux and macOS) and %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials (Windows).
No auth: without authentication.
In the User and Password, provide your credentials if required by the selected authentication type.
In the URL field, provide the URL of the pre-built connection you want to establish.
(Optional) For other options (SSH tunneling, scope inspection, or additional connection parameters), switch to the respective tab of the dialog and follow one of these procedures.
Click the Test connection button at the bottom of the dialog.
Once the connection is successfully tested, click the Create and close button.
Step 3. Attach the connection to a notebook
Open the notebook you want to attach the connection to.
If the notebook is not running, start it by clicking .
In the sidebar, select Attached data and switch to the Databases tab.
Enable the toggle in your Amazon Redshift connection.
If the notebook is not running, start it by clicking .
In the sidebar, select Attached data and switch to the Databases tab.
Enable the toggle in your Amazon Redshift connection.
Next steps
To retrieve and process data from the connected database, use Query data with SQL cells.
Learn how to manage and delete database connections in a workspace and in a notebook.