Use third-party and local models
By default, AI Assistant provides access to a set of cloud-based models from various AI providers through the JetBrains AI service subscription. These models power AI Assistant features and can be selected in AI Chat to have a conversation about your codebase.
In addition, you can configure AI Assistant to use locally hosted models or models provided by third parties. Supported providers include:
Anthropic – provides the Claude family of models.
OpenAI – offers GPT, o-series, and other general-purpose models.
OpenAI-compatible endpoints – services that expose an API compatible with the OpenAI API (for example, llama.cpp or LiteLLM).
Ollama – runs open-source models locally on your machine.
LM Studio – runs local models and exposes them through an OpenAI-compatible API.
By configuring models from different sources, you can control which models AI Assistant uses and how those models are provided.
Access models from third-party AI providers
To access models from third-party providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, or other OpenAI-compatible endpoints, AI Assistant requires an API key and, in some cases, an endpoint URL. Entering the key allows AI Assistant to authenticate with the provider and access its models.
To provide the API key:
Navigate to .
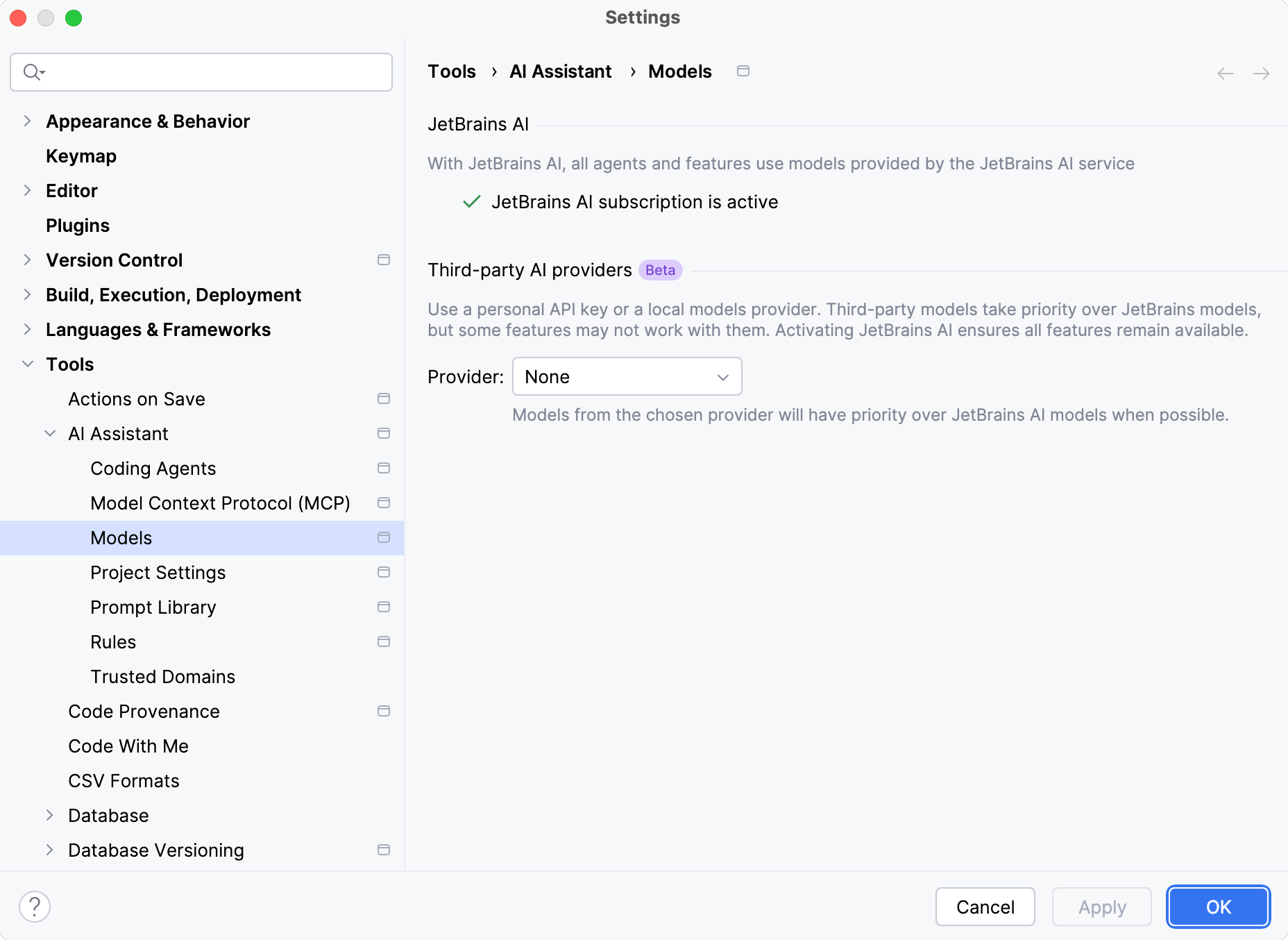
In the Third-party AI providers section, select the Provider.
Enter the API Key and click Test Connection to check whether the connection is established successfully.
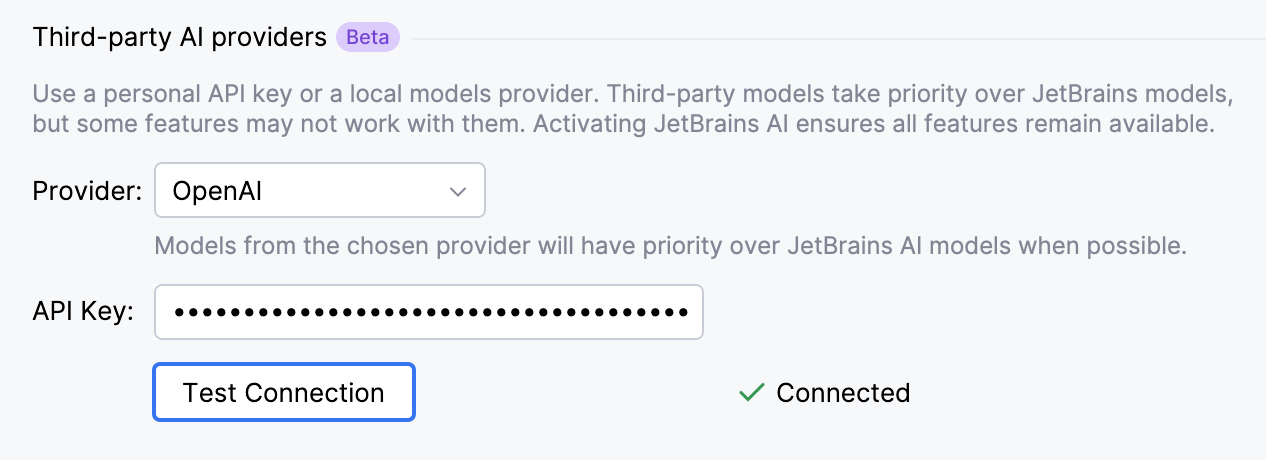
If you are configuring an OpenAI-compatible provider, specify the URL of the provider's API endpoint in addition to the API Key. Also, indicate whether the model supports calling tools configured through the Model Context Protocol (MCP) by enabling or disabling the Tool calling setting.
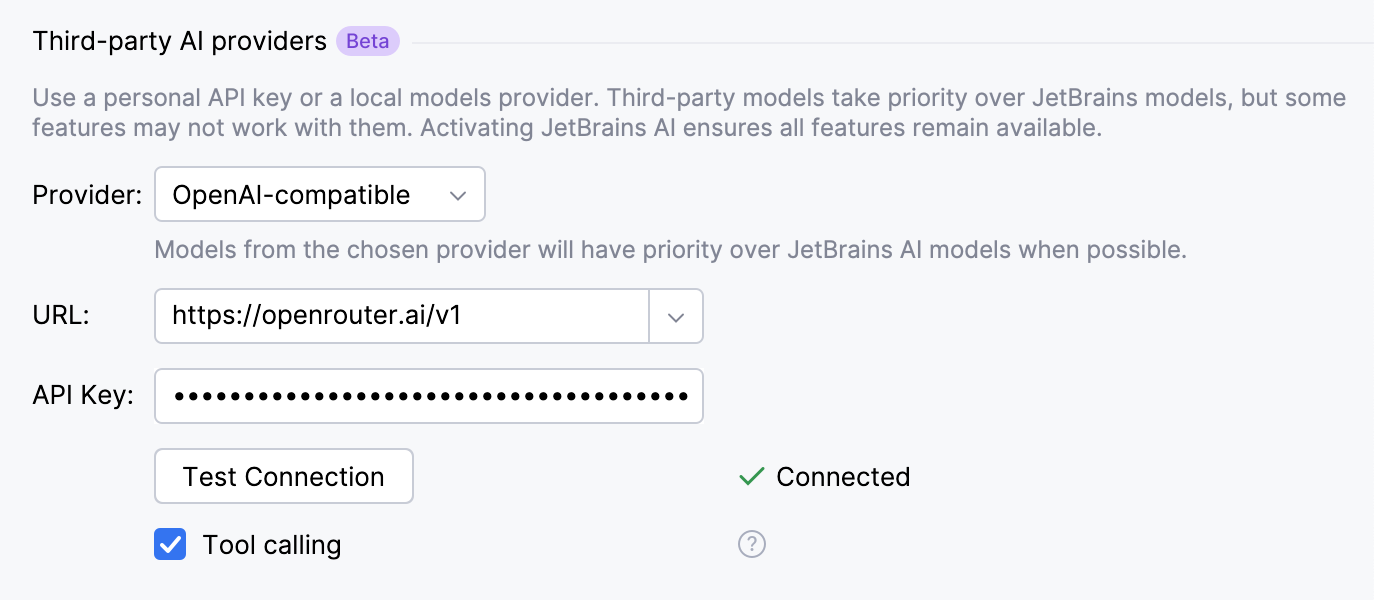
Click Apply to save changes.
To verify that the models from the configured provider became available for use, open AI Chat and click the model selector. Provider's models are available under a corresponding section.
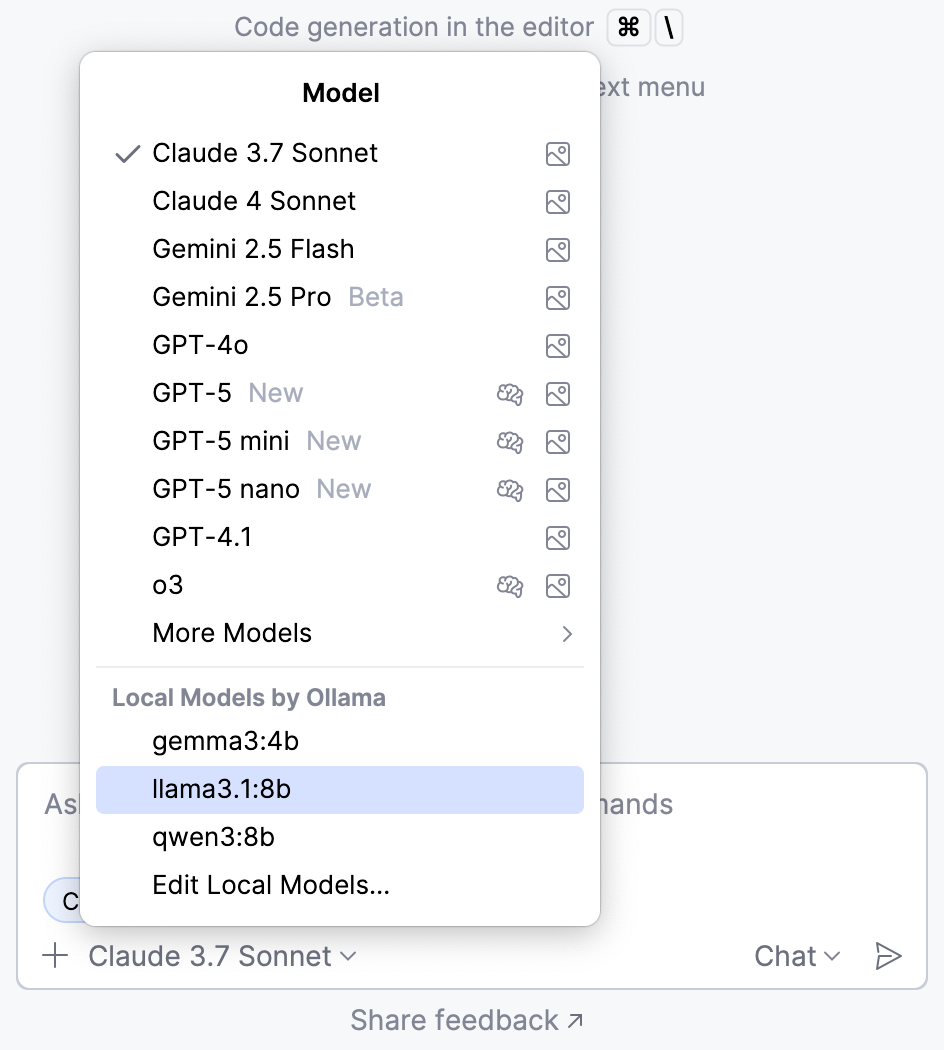
Models accessed from a third-party AI provider are assigned to AI Assistant features automatically. If these models do not support certain AI Assistant features, those features become unavailable.
For more information on what models are used for AI Assistant features, refer to List of assigned and fallback models.
Connect local models
Providers like Ollama and LM Studio run models on your machine. Connecting to them in AI Assistant allows you to use these models directly from your local setup.
Navigate to .
In the Third-party AI providers section, select the Provider.
Specify the URL where it can be accessed and click Test Connection to check whether the connection is established successfully.

Click Apply to save changes.
Once the connection is established, local models become available for use in AI Chat. Additionally, locally hosted models can also be assigned to specific AI Assistant features.
Assign models to AI Assistant features
Each AI Assistant feature has a predefined list of models assigned to it. These models are used when the feature is triggered. Some features also have a predefined list of fallback models, which are used if none of the assigned models are available.
When a feature is triggered, AI Assistant checks whether any of the models available to you match the models assigned to that feature. If no match is found and fallback models are defined for the feature, the system checks for a match among the fallback models. If no compatible model is available, the feature is unavailable.
The mechanism works as follows:
By default, AI Assistant features use models provided through the JetBrains AI service, ensuring that all features are available.
However, models obtained from third-party AI providers or local models can also be used for AI Assistant features. Depending on the model source, models are assigned differently:
Model source | Feature support |
|---|---|
Third-party AI providers | Models are assigned to features automatically. If the provider models do not support a specific feature, that feature is unavailable. |
Local models and models from OpenAI-compatible endpoints | Models can be assigned to groups of AI Assistant features manually. |
To assign local models and models accessed from the OpenAI-compatible endpoint to AI Assistant features:
Go to .
In the Models Assignment section, specify the models that you want to use for core, lightweight, and code completion features. Also, define the model context window size if needed.

Core features – this model will be used for in-editor code generation, commit message generation, as a default model in chat, and other core features.
Instant helpers – this model will be used for lightweight features, such as chat context collection, chat title generation, and name suggestions.
Completion model – this model will be used for the inline code completion feature in the editor. Works only with Fill-in-the-Middle (FIM) models.
Context window – allows you to configure the model context window for local models. A larger window lets the model handle more context in a request, while a smaller one reduces memory usage and may improve performance. This helps balance context length with system resources. The default value is 64 000 tokens.
Click Apply to save changes.
As a result, AI Assistant uses the assigned models when the corresponding feature is triggered.
List of assigned and fallback models
This section lists AI Assistant features and the models they require, helping you assess compatibility with models from third-party providers.
Core features
Feature | Application area | Used model(s) |
|---|---|---|
Editor |
| |
Editor |
| |
Editor |
| |
Fix with AI (only in RustRover) | Editor |
|
VCS |
| |
VCS |
|
Instant helpers
Feature | Application area | Used model(s) |
|---|---|---|
AI Chat |
| |
File name generation | AI Chat |
|
Chat context collection | AI Chat |
|
Chat title generation | AI Chat |
|
Editor |
|
Completion model
Feature | Where the feature is invoked | Used model(s) |
|---|---|---|
Editor, AI Chat, Commit message |
| |
Code completion (for AI Enterprise, if opted to use a different AI provider) | Editor, AI Chat, Commit message |
|
Fallback models
For features that support fallback, this list is compared with the models available to you. If no matching model is found, the feature is unavailable.
The following models are defined as fallback models:
Anthropic models: Claude 4.5 Sonnet, Claude 4 Sonnet, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Claude 4.5 Haiku, Claude 3.5 Haiku
Google models: Gemini 2.5 Pro, Gemini 2.5 Flash, Gemini 2.0 Flash
OpenAI models: GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini
Alibaba models (Mainland China only): Qwen Max
Activate JetBrains AI
If you are using AI Assistant without a JetBrains AI service subscription, some features may not work properly when using models from third-party AI providers.
To ensure that all features are available and work as expected, you can purchase and activate a JetBrains AI service subscription. An active subscription covers the features that might not work properly or are unavailable with models from third-party AI providers.
To enable your JetBrains AI subscription:
Navigate to .
In the JetBrains AI section, click Activate JetBrains AI. You will be redirected to AI Chat.
Click Log in to JetBrains Account, enter your credentials, and wait for the login process to complete.
After you sign in with a JetBrains Account that has an active JetBrains AI subscription, you can start using AI Assistant with full functionality.
Switch to offline mode
Not available in IDE versions starting from 2025.3.1
If you want to restrict calls to remote models and only use the local ones, you can enable the offline mode. In this mode, most cloud model calls will be blocked, and all AI-related features will rely on the local models instead.
To enable offline mode:
Go to .
Select your local third-party provider.
In the Local models section, specify the models that you want to use for AI features.
Enable the Offline mode setting.

Click Apply to save changes.
Once you have finished the setup, you can toggle offline mode on and off whenever applicable:
Click the
JetBrains AI widget located in the toolbar in the window header.
Hover over the Offline Mode option and click Enable or Disable.
