Code Syntax Style: Named/Positional Arguments
If you prefer to use named arguments for specific types of parameters, JetBrains Rider can help you enforce this practice.
Consider the following method call:
When you read this code, you have to stop and study the method signature to understand what happens here (you can do it either with the parameter information tooltip or by navigating to method declaration). With named arguments, the same call becomes much clearer:
If you prefer to have named arguments for specific types, you can enforce this preference with the help of JetBrains Rider.
JetBrains Rider helps you arrange arguments in the existing code and takes your preferences into account when it produces new code with code completion and code generation features, applies code templates and performs refactorings.
Apply style preferences for arguments
By default, JetBrains Rider suggests using positional arguments everywhere, and you have to explicitly specify which types of parameters require named arguments. According to your preferences, JetBrains Rider highlights positional arguments that require names or named arguments that should be positional, and then suggests the corresponding quick-fix or fix in scope:
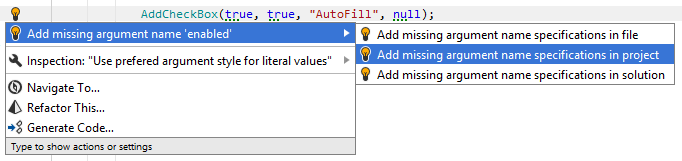
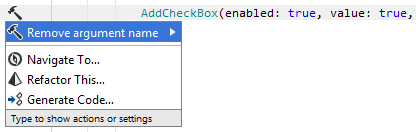
Even if you do not have any style preferences for arguments, you can always press Alt+Enter on any named or positional argument and choose to add or remove the argument name with the corresponding context action:
Another option to enforce preferences for named/positional arguments in a bulk mode is code cleanup. You can either run code cleanup with one of the built-in profiles Full Cleanup or Reformat & Apply Syntax Style, or create and run a custom profile solely targeted at your specific task as described below.
Apply argument style with custom Code Cleanup profile
Press Ctrl+Alt+S or choose (Windows and Linux) or (macOS) from the menu .
Go to the cleanup profiles settings page: .
Create a new profile as described in the Create a new custom cleanup profile section. In the profile preferences on the right, expand the node and select the Apply arguments style (named vs. positional) checkbox.
Click Save in the Settings dialog to apply the modifications and let JetBrains Rider choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer by choosing this layer from the Save selector. For more information, see layer-based settings.
Select the scope where you want to enforce your preferences:
Place the caret anywhere in the file to enforce your preferences to the file.
Select one or more items in the Solution Explorer to enforce your preferences in the files under these nodes and their child items.
Press Ctrl+R, C or choose from the main menu.
In the Reformat and Cleanup Code dialog that opens, select the newly created profile and choose another scope if needed. .
Click OK. JetBrains Rider will enforce your preferences in the selected scope.
If you want to arrange arguments without opening the Reformat and Cleanup Code dialog to choose a profile, you can bind the created profile to the silent cleanup and run it by pressing Ctrl+R, G. You can also create a custom cleanup profile that would combine arranging arguments with other code style tasks.
To apply preferences for named/positional arguments together with all other formatting and syntax style rules to the selected code block, Alt+Enter and choose .
You can arrange arguments in code that you have recently modified and are going to commit to Git. JetBrains Rider will run the selected cleanup profile before committing.
Clean up code before committing it to Git
Press Ctrl+K or select from the main menu.
In the Commit tool window, click
and in the Commit Checks area, select the Cleanup with... checkbox.
Click Choose profile and choose your custom Code Cleanup profile.
Click Commit or Commit and Push. JetBrains Rider will run code cleanup in files staged for the commit, and then commit the changes.
You can arrange arguments every time you save changes in a file to make sure that your edits always comply with your code style. Note that this will only happen when you save changes explicitly with Ctrl+S or Ctrl+S and will not be triggered by auto-saving. However, all auto-saved files are placed to the 'reformat and cleanup' queue and will be processed on the next explicit save.
Automatically arrange arguments on saving changes
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Select Reformat and Cleanup Code, choose your custom Code Cleanup profile and whether to apply it to the whole file or only to the changed lines.
The next time you finish editing and save the file or all files , JetBrains Rider will clean up the affected files using the selected profile.
Configure preferences for named/positional arguments
Your arguments style preferences are saved using the mechanism of layer-based settings. Among other things, this mechanism allows you to maintain different preferences for different solutions as well as to keep these preferences under a VCS and automatically share them with your team members.
Configure preferences of arguments style
Go to the page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S, and then select the Syntax Style tab .
In the Arguments category select whether to use named or positional arguments for specific parameter types. Note that Literal values refers to all literals (
bool,int,double, and so on) except strings. The preference for strings is defined in the String literal values selector.The category Other applies to all other expression types, like conditional, null-coalescing, binary, invocation or
typeofexpressions.The selectors in the right column allow you to set severity levels of code inspections detecting code that differs from your preferences.
Click Save in the Settings dialog to apply the modifications and let JetBrains Rider choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer by choosing this layer from the Save selector. For more information, see layer-based settings.
You can configure syntax style settings via EditorConfig. These settings can be stored in .editorconfig files on different levels of your solution hierarchy. The files are normally put under VCS so that settings defined there are shared among the project team.
JetBrains Rider lets you use EditorConfig to define any of its syntax style preferences that are available in the JetBrains Rider's Settings dialog. You can find names and descriptions of supported EditorConfig properties in the EditorConfig reference.
It is important to note that any syntax style property defined in an .editorconfig file will override the same property defined in JetBrains Rider settings in the scope where this .editorconfig file applies.
Configure preferences for arguments style using EditorConfig
Open the desired .editorconfig file.
Add the required arguments style properties to the file. For example:
arguments_literal = named